|
Sarrus Linkage
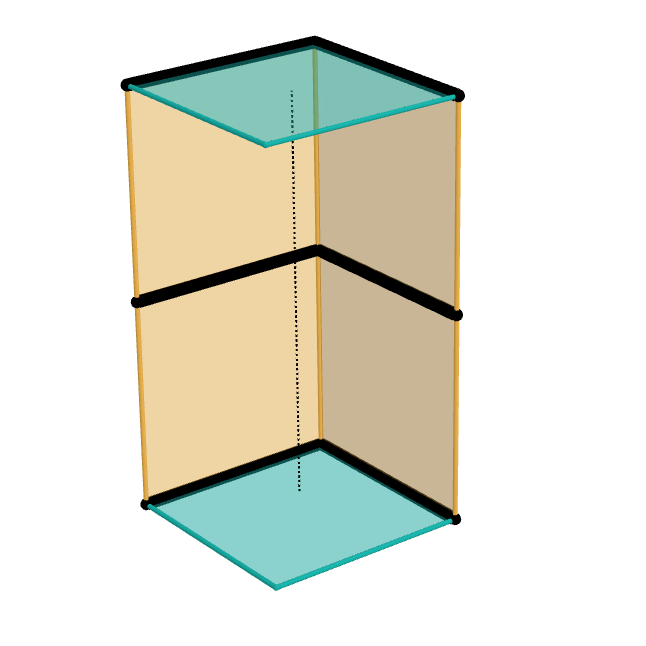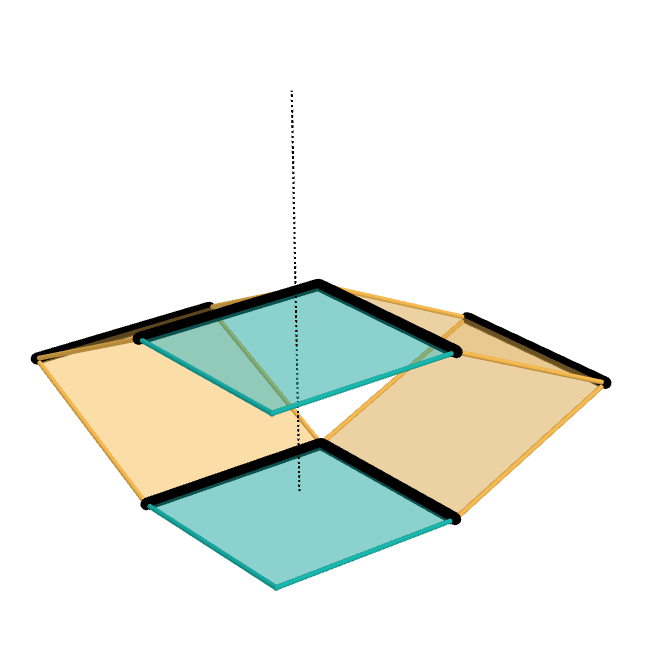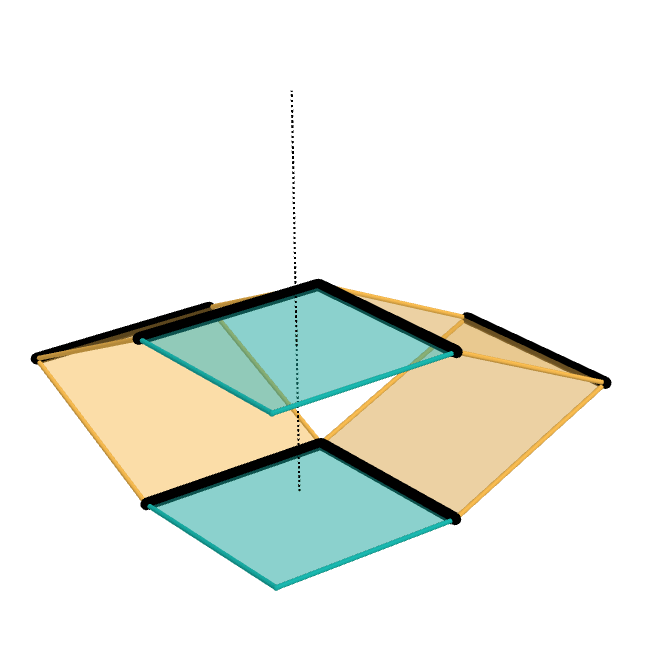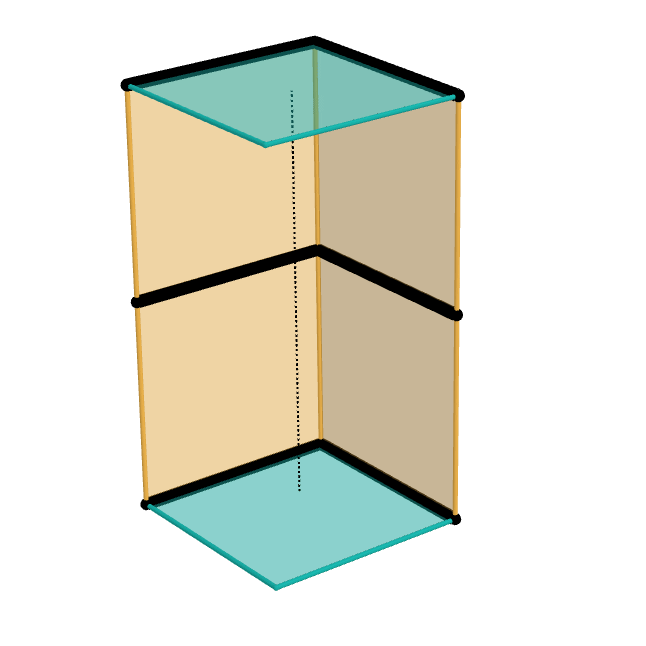
The Sarrus linkage, invented in 1853 by Pierre Frédéric Sarrus, is a mechanical linkage to convert a limited circular motion to a linear motion or vice versa without reference guideways. It is a spatial six-bar linkage (6R) with two groups of three parallel adjacent joint-axes. Although Charles-Nicolas Peaucellier was widely recognized for being the first to invent such a straight-line mechanism, the Sarrus linkage had been invented earlier; however, it was largely unnoticed for a time. – Sarrus' mechanism Description The Sarrus linkage consists of four links in two identical groups that are perpendicular to each other, with all links having equal lengths. In the examples shown, the linkage uses two horizontal plates (cyan) ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarrus Linkage - Links Ver , a mechanical linkage
{{surname ...
Sarrus is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Pierre-Auguste Sarrus (1813–1876), French musician and inventor ** Sarrusophone, a musical instrument * Pierre Frédéric Sarrus (1798–1861), French mathematician ** Sarrus linkage The Sarrus linkage, invented in 1853 by Pierre Frédéric Sarrus, is a mechanical linkage to convert a limited circular motion to a linear motion or vice versa without reference guideways. It is a spatial six-bar linkage (6R) with two groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarrus Linkage
The Sarrus linkage, invented in 1853 by Pierre Frédéric Sarrus, is a mechanical linkage to convert a limited circular motion to a linear motion or vice versa without reference guideways. It is a spatial six-bar linkage (6R) with two groups of three parallel adjacent joint-axes. Although Charles-Nicolas Peaucellier was widely recognized for being the first to invent such a straight-line mechanism, the Sarrus linkage had been invented earlier; however, it was largely unnoticed for a time. – Sarrus' mechanism Description The Sarrus linkage consists of four links in two identical groups that are perpendicular to each other, with all links having equal lengths. In the examples shown, the linkage uses two horizontal plates (cyan) ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Frédéric Sarrus
Pierre Frédéric Sarrus (; 10 March 1798, Saint-Affrique – 20 November 1861) was a French mathematician. Sarrus was a professor at the University of Strasbourg, France (1826–1856) and a member of the French Academy of Sciences in Paris (1842). He is the author of several treatises, including one on the solution of numeric equations with multiple unknowns (1842); one on multiple integrals and their integrability conditions; and one on the determination of the orbits of the comets. He also discovered a mnemonic rule for solving the determinant of a 3-by-3 matrix, named Sarrus' scheme. Sarrus also demonstrated the fundamental lemma of the calculus of variations. Sarrus numbers are pseudoprime A pseudoprime is a probable prime (an integer that shares a property common to all prime numbers) that is not actually prime. Pseudoprimes are classified according to which property of primes they satisfy. Some sources use the term pseudoprime to ...s to base 2. Sarrus also develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linkage (mechanical)
A mechanical linkage is an assembly of systems connected to manage forces and movement. The movement of a body, or link, is studied using geometry so the link is considered to be rigid. The connections between links are modeled as providing ideal movement, pure rotation or sliding for example, and are called joints. A linkage modeled as a network of rigid links and ideal joints is called a kinematic chain. Linkages may be constructed from open chains, closed chains, or a combination of open and closed chains. Each link in a chain is connected by a joint to one or more other links. Thus, a kinematic chain can be modeled as a graph in which the links are paths and the joints are vertices, which is called a linkage graph. The movement of an ideal joint is generally associated with a subgroup of the group of Euclidean displacements. The number of parameters in the subgroup is called the degrees of freedom (DOF) of the joint. Mechanical linkages are usually designed to tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Motion
In physics, circular motion is a movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or rotation along a circular path. It can be uniform, with constant angular rate of rotation and constant speed, or non-uniform with a changing rate of rotation. The rotation around a fixed axis of a three-dimensional body involves circular motion of its parts. The equations of motion describe the movement of the center of mass of a body. In circular motion, the distance between the body and a fixed point on the surface remains the same. Examples of circular motion include: an artificial satellite orbiting the Earth at a constant height, a ceiling fan's blades rotating around a hub, a stone which is tied to a rope and is being swung in circles, a car turning through a curve in a race track, an electron moving perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field, and a gear turning inside a mechanism. Since the object's velocity vector is constantly changing direction, the moving object is undergoing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Motion
In kinematics, the parallel motion linkage is a six-bar mechanical linkage invented by the Scottish engineer James Watt in 1784 for the double-acting Watt steam engine. It allows a rod moving practically straight up and down to transmit motion to a beam moving in an arc, without putting significant sideways strain on the rod. Description In previous engines built by Newcomen and Watt, the piston pulled one end of the walking beam downwards during the power stroke using a chain, and the weight of the pump pulled the other end of the beam downwards during the recovery stroke using a second chain, the alternating forces producing the rocking motion of the beam. In Watt's new double-acting engine, the piston produced power on both the upward and downward strokes, so a chain could not be used to transmit the force to the beam. Watt designed the parallel motion to transmit force in both directions whilst keeping the piston rod very close to vertical. He called it "parallel motion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Six-bar Linkage
In mechanics, a six-bar linkage is a mechanism with one degree of freedom that is constructed from six links and seven joints. An example is the Klann linkage used to drive the legs of a walking machine. In general, each joint of a linkage connects two links, and a binary link supports two joints. If we consider a hexagon constructed from six binary links with six of the seven joints forming its vertices, then the seventh joint can be added to connect two sides of the hexagon to form a six-bar linkage with two ternary links connected by one joint. This type of six-bar linkage is said to have the Watt topology.An animation oa six-bar linkage with the Watt topology./ref> A six-bar linkage can also be constructed by first assembling five binary links into a pentagon, which uses five of the seven joints, and then completing the linkage by adding a binary link that connects two sides of the pentagon. This again creates two ternary links that are now separated by one or more binar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles-Nicolas Peaucellier
Charles-Nicolas Peaucellier (16 June 1832 – 4 October 1919) was a French engineer who graduated from the ''École polytechnique''. He made a career in the French army and was promoted to ''général de division'' in 1888. He is best known for the ''Peaucellier–Lipkin linkage'' which was partly named after him. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Crank
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as spacetime. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. Debates concerning the nature, essence and the mode of existence of space date back to antiquity; namely, to treatises like the ''Timaeus'' of Plato, or Socrates in his reflections on what the Greeks called ''khôra'' (i.e. "space"), or in the ''Physics'' of Aristotle (Book IV, Delta) in the definition of ''topos'' (i.e. place), or in the later "geometrical conception of place" as "space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peaucellier–Lipkin Linkage
The Peaucellier–Lipkin linkage (or Peaucellier–Lipkin cell, or Peaucellier–Lipkin inversor), invented in 1864, was the first true planar straight line mechanism – the first planar linkage (mechanical), linkage capable of transforming rotary motion into perfect straight-line motion, and vice versa. It is named after Charles-Nicolas Peaucellier (1832–1913), a French army officer, and Yom Tov Lipman Lipkin (1846–1876), a Lithuanian Jew and son of the famed Rabbi Israel Salanter. Until this invention, no planar method existed of converting exact straight-line motion to circular motion, without reference guideways. In 1864, all power came from steam engines, which had a piston moving in a straight-line up and down a cylinder. This piston needed to keep a good seal with the cylinder in order to retain the driving medium, and not lose energy efficiency due to leaks. The piston does this by remaining perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder, retaining its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree Of Freedom
Degrees of freedom (often abbreviated df or DOF) refers to the number of independent variables or parameters of a thermodynamic system. In various scientific fields, the word "freedom" is used to describe the limits to which physical movement or other physical processes are possible. This relates to the philosophical concept to the extent that people may be considered to have as much freedom as they are physically able to exercise. Applications Statistics In statistics, degrees of freedom refers to the number of variables in a statistic calculation that can vary. It can be calculated by subtracting the number of estimated parameters from the total number of values in the sample. For example, a sample variance calculation based on n samples will have n-1 degrees of freedom, because sample variance is calculated using the sample mean as an estimate of the actual mean. Mathematics In mathematics, this notion is formalized as the dimension of a manifold or an algebraic variety. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight Line Mechanism
A straight-line mechanism is a Mechanism (engineering), mechanism that converts any type of rotary or angular motion to perfect or near-perfect straight-line motion, or ''vice-versa''. Straight-line motion is linear motion of definite length or "stroke", every forward stroke being followed by a return stroke, giving reciprocating motion. The first such mechanism, patented in 1784 by James Watt, produced approximate straight-line motion, referred to by Watt as Watt's linkage, parallel motion. Straight-line mechanisms are used in a variety of applications, such as engines, vehicle suspensions, walking robots, and rover wheels. History In the late eighteenth century, before the development of the Planer (metalworking), planer and the milling machine, it was extremely difficult to machine straight, flat surfaces. During that era, much thought was given to the problem of attaining a straight-line motion, as this would allow the flat surfaces to be machined. To find a solution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


