|
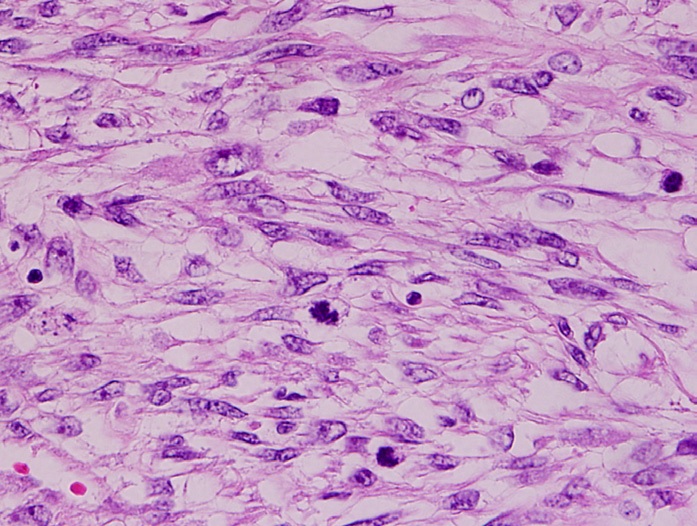
Sarcomas
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal (connective tissue) origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sarcomas can arise in any of these types of tissues. As a result, there are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates. Sarcomas are ''primary'' connective tissue tumors, meaning that they arise in connective tissues. This is in contrast to ''secondary'' (or "metastatic") connective tissue tumors, which occur when a cancer from elsewhere in the body (such as the lungs, breast tissue or prostate) spreads to the connective tissue. The word ''sarcoma'' is derived from the Greek σάρκωμα ''sarkōma'' "fleshy excrescence or substance", itself from σάρξ ''sarx'' meaning "flesh". Classification Sarcomas are typically divided into two major groups: bone sarcoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft-tissue Sarcoma
A soft-tissue sarcoma (STS) is a malignant tumour, a type of cancer, that develops in soft tissue. A soft tissue sarcoma is often a painless mass that grows slowly over months or years. They may be superficial or deep-seated. Any such unexplained mass must be diagnosed by biopsy. Treatment may include, surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapy. The other type of sarcoma is a bone sarcoma. There are many types. The World Health Organization lists more than fifty subtypes. Types ''An earlier version of this article was taken from the US National Cancer Center's Cancer Information Service.'' Signs and symptoms In their early stages, soft-tissue sarcomas usually do not cause symptoms. Because soft tissue is relatively elastic, tumors can grow rather large, pushing aside normal tissue, before they are felt or cause any problems. The first noticeable symptom is usually a painless lump or swelling. As the tumor grows, it may cause other symptoms, such as pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synovial Sarcoma
A synovial sarcoma (also known as malignant synovioma) is a rare form of cancer which occurs primarily in the extremities of the arms or legs, often in proximity to joint capsules and tendon sheaths. It is a type of soft-tissue sarcoma. The name "synovial sarcoma" was coined early in the 20th century, as some researchers thought that the microscopic similarity of some tumors to synovium, and its propensity to arise adjacent to joints, indicated a synovial origin; however, the actual cells from which the tumor develops are unknown and not necessarily synovial. Primary synovial sarcomas are most common in the soft tissue near the large joints of the arm and leg but have been documented in most human tissues and organs, including the brain, prostate, and heart. Synovial sarcoma occurs in about 1–2 per 1,000,000 people a year. They occur most commonly in the third decade of life, with males being affected more often than females (ratio around 1.2:1). Signs and symptoms Synovial s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordoma
Chordoma is a rare slow-growing neoplasm thought to arise from cellular remnants of the notochord. The evidence for this is the location of the tumors (along the neuraxis), the similar immunohistochemical staining patterns, and the demonstration that notochordal cells are preferentially left behind in the clivus and sacrococcygeal regions when the remainder of the notochord regresses during fetal life. In layman's terms, chordoma is a type of spinal cancer. Presentation Chordomas can arise from bone in the skull base and anywhere along the spine. The two most common locations are cranially at the clivus and in the sacrum at the bottom of the spine. Sacral chordoma is presented with chronic low back pain. Genetics A small number of families have been reported in which multiple relatives have been affected by chordoma. In four of these families, duplication of the brachyury gene was found to be responsible for causing chordoma. A possible association with tuberous sclerosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an imaging technique that uses low-coherence light to capture micrometer-resolution, two- and three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media (e.g., biological tissue). It is used for medical imaging and industrial nondestructive testing (NDT). Optical coherence tomography is based on low-coherence interferometry, typically employing near-infrared light. The use of relatively long wavelength light allows it to penetrate into the scattering medium. Confocal microscopy, another optical technique, typically penetrates less deeply into the sample but with higher resolution. Depending on the properties of the light source ( superluminescent diodes, ultrashort pulsed lasers, and supercontinuum lasers have been employed), optical coherence tomography has achieved sub-micrometer resolution (with very wide-spectrum sources emitting over a ~100 nm wavelength range). Optical coherence tomography is one of a class of optical tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ewing Sarcoma
Ewing sarcoma is a type of cancer that forms in bone or soft tissue. Symptoms may include swelling and pain at the site of the tumor, fever, and a bone fracture. The most common areas where it begins are the legs, pelvis, and chest wall. In about 25% of cases, the cancer has already spread to other parts of the body at the time of diagnosis. Complications may include a pleural effusion or paraplegia. It is a type of small round cell sarcoma. The cause of Ewing sarcoma is unknown. Most cases appear to occur randomly. Sometimes there has been a germline mutation. The underlying mechanism often involves a genetic change known as a reciprocal translocation. Diagnosis is based on biopsy of the tumor. Treatment often includes chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, and stem cell transplant. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are being studied. Five-year survival is about 70%. A number of factors, however, affect this estimate. James Ewing in 1920 established that the tumor is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Cell Fibroblastoma
Giant cell fibroblastoma (GCF) is a rare type of soft-tissue tumor marked by painless nodules in the dermis (the inner layer of the two main layers of tissue that make up the skin) and subcutaneous (beneath the skin) tissue. These tumors may come back after surgery, but they do not spread to other parts of the body. They occur mostly in boys. GCF tumor tissues consist of bland spindle-shaped or stellate-shaped cells interspersed among multinucleated giant cells. GCF tumors are closely related to dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, fibrosarcomatous (DFSP-FS) (also termed fibrosarcomatous dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans) tumors. The World Health Organization (2020) classified these three tumors as different tumors in the category of fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors with GCF and DFSP sub-classified as benign but aggressive tumors and DFSP-FS subclassified as a rarely metastasizing tumor. However, The three tumor types may contain ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans, Fibrosarcomatous
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, fibrosarcomatous (DFSP-FS), also termed fibrosarcomatous dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, is a rare type of tumor located in the dermis (i.e. layer of the skin below the epidermis). DFSP-FS tumors have been viewed as: 1) a more aggressive form of the dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) tumors because they have areas that resemble and tend to behave like malignant fibrosarcomas or 2) as a distinctly different tumor than DFSP. DFSP-FS tumors are related to DFSP. For example, surgically removed DFSP tumors often recur with newly developed fibrobosarcoma-like areas. Nonetheless, the World Health Organization (WHO), 2020, classified DFSP and DFSP-FS as different tumors with DFSP being in the category of benign and DFSP-FS in the category of rarely metastasizing fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors. This article follows the WHO classification: the 5-15% of DFSP tumors that have any areas of fibrosarcomatous microscopic histopathology are here con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare locally aggressive malignant cutaneous soft-tissue sarcoma. DFSP develops in the connective tissue cells in the middle layer of the skin (dermis). Estimates of the overall occurrence of DFSP in the United States are 0.8 to 4.5 cases per million persons per year. In the United States, DFSP accounts for between 1 and 6 percent of all soft tissue sarcomas and 18 percent of all cutaneous soft tissue sarcomas. In the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) tumor registry from 1992 through 2004, DFSP was second only to Kaposi sarcoma. Presentation Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans begins as a minor firm area of skin most commonly about to 1 to 5 cm in diameter. It can resemble a bruise, birthmark, or pimple. It is a slow-growing tumor and is usually found on the torso but can occur anywhere on the body. About 90% of DFSPs are low-grade sarcomas. About 10% are mixed, containing a high-grade sarcomatous component (DFSP-FS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a highly aggressive form of cancer that develops from mesenchymal cells that have failed to fully differentiate into myocytes of skeletal muscle. Cells of the tumor are identified as rhabdomyoblasts. There are four subtypes – embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma, and spindle cell/sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma. Embryonal, and alveolar are the main groups, and these types are the most common soft tissue sarcomas of childhood and adolescence. The pleomorphic type is usually found in adults. It is generally considered to be a disease of childhood, as the vast majority of cases occur in those below the age of 18. It is commonly described as one of the small-blue-round-cell tumors of childhood due to its appearance on an H&E stain. Despite being relatively rare, it accounts for approximately 40% of all recorded soft tissue sarcomas. RMS can occur in any soft tissue site in the body, but is primarily found in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
A malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is a form of cancer of the connective tissue surrounding nerves. Given its origin and behavior it is classified as a sarcoma. About half the cases are diagnosed in people with neurofibromatosis; the lifetime risk for an MPNST in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 is 8–13%. MPNST with rhabdomyoblastomatous component are called malignant triton tumors. The first-line treatment is surgical resection with wide margins. Chemotherapy (e.g. high-dose doxorubicin) and often radiotherapy are done as adjuvant and/or neoadjuvant treatment. Signs and symptoms Symptoms may include: * Swelling in the extremities (arms or legs), also called peripheral edema; the swelling often is painless. * Difficulty in moving the extremity that has the tumor, including a limp. * Soreness localized to the area of the tumor or in the extremity. * Neurological symptoms. * Pain or discomfort: numbness, burning, or "pins and needles." * Dizziness and/or lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiomyosarcoma
Leiomyosarcoma is a malignant (cancerous) smooth muscle tumor. A benign tumor originating from the same tissue is termed leiomyoma. While leiomyosarcomas are not thought to arise from leiomyomas, some leiomyoma variants' classification is evolving. About one in 100,000 people are diagnosed with leiomyosarcoma (LMS) each year. LMS is one of the more common types of soft-tissue sarcoma, representing 10 to 20% of new cases. (Leiomyosarcoma of the bone is more rare.) Sarcoma is rare, consisting of only 1% of cancer cases in adults. Leiomyosarcomas can be very unpredictable; they can remain dormant for long periods of time and recur after years. It is a resistant cancer, meaning generally not very responsive to chemotherapy or radiation. The best outcomes occur when it can be removed surgically with wide margins early, while small and still ''in situ''. Mechanism Smooth muscle cells make up the involuntary muscles, which are found in most parts of the body, including the uterus, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liposarcoma
Liposarcomas are the most common subtype of soft tissue sarcomas, accounting for at least 20% of all sarcomas in adults. Soft tissue sarcomas are rare neoplasms with over 150 different histological subtypes or forms. Liposarcomas arise from the precursor lipoblasts of the adipocytes (i.e. fat cells) in adipose (i.e. fat) tissues. Adipose tissues are distributed throughout the body, including such sites as the deep and more superficial layers of subcutaneous tissues as well as in less surgically accessible sites like the retroperitoneum (i.e. space behind the abdominal cavity) and visceral fat inside the abdominal cavity. All liposarcomas consist of at least some cells that bear a resemblance to fat cells when examined for their histopathologic appearances under a microscope. However, the liposarcomas do have several forms based on differences in their clinical presentations (e.g. ages, gender preferences, sites of tumors, signs, and symptoms), severities (i.e. potential to inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |