|
Santos-Dumont 21 Demoiselle
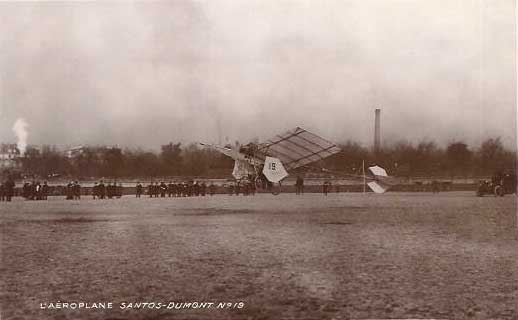
The Santos-Dumont ''Demoiselle'' was a series of aircraft built in France by world aviation pioneer Alberto Santos-Dumont. They were light-weight monoplanes with a wire-braced wing mounted above an open-framework fuselage built from bamboo. The pilot's seat was below the wing and between the main wheels of the undercarriage. The rear end of the boom carried a tailwheel and a cruciform tail. The name is a synonym for "jeune fille"—young girl or woman—but also the common name in French for a Damselfly. No. 19 The first aircraft of the type was the Santos-Dumont No. 19, which was built to attempt to win the ''Grand Prix d'Aviation offered for a one kilometre closed-circuit flight. Powered by a 15 kW (20 hp) air-cooled Dutheil & Chalmers flat-twin engine mounted on the leading edge of the wing, it had a wingspan of 5.1 m. (16 ft 9 in), was 8 m (26 ft 3 in) long and weighed only 56 kg (123 lb) including fuel. It had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longeron
In engineering, a longeron and stringer is the load-bearing component of a framework. The term is commonly used in connection with aircraft fuselages and automobile chassis. Longerons are used in conjunction with stringers to form structural frameworks. Aircraft In aircraft fuselage, stringers are attached to formers (also called frames) and run in the longitudinal direction of the aircraft. They are primarily responsible for transferring the aerodynamic loads acting on the skin onto the frames and formers. In the wings or horizontal stabilizer, longerons run spanwise (from wing root to wing tip) and attach between the ribs. The primary function here also is to transfer the bending loads acting on the wings onto the ribs and spar. Sometimes the terms "longeron" and "stringer" are used interchangeably. Historically, though, there is a subtle difference between the two terms. If the longitudinal members in a fuselage are few in number (usually 4 to 8) and run all along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolphe Clément
''Adolphe'' is a classic French novel by Benjamin Constant, first published in 1816. It tells the story of an alienated young man, Adolphe, who falls in love with an older woman, Ellénore, the Polish mistress of the Comte de P***. Their illicit relationship serves to isolate them from their friends and from society at large. The book eschews all conventional descriptions of exteriors for the sake of detailed accounts of feelings and states of mind. Constant began the novel on 30 October 1806, and completed it some time before 1810. While still working on it he read drafts to individual acquaintances and to small audiences, and after its first publication in London and Paris in June 1816 it went through three further editions: in July 1816 (new preface), July 1824 in Paris (restorations to Ch. 8, third preface), and in 1828. Many variants appear, mostly alterations to Constant's somewhat archaic spelling and punctuation. Plot summary Adolphe, the narrator, is the son of a go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buc, Yvelines
Buc () is a commune in the Yvelines department and Île-de-France region of north central France. Geography Buc is located some 20 km south-west of central Paris and 3 km south of Versailles. The old town lies in the valley of the River Bièvre at an elevation of around 100 m above sea level. Most of Buc's residential districts have been built on the plateau de Saclay, some 50 m higher. The surrounding communes are: *Versailles to the north *Jouy-en-Josas to the north-east *Les Loges-en-Josas to the south-east *Toussus-le-Noble to the south * Châteaufort to the extreme south-west *Guyancourt to the west. Demography History The name Buc derives from the Latin ''buscum'' which means boxwood. The inhabitants of Buc are known in French as ''Bucois'' (m.) and ''Bucoises'' (f.). * Territory attached to the domain of Versailles in 1660 and used to be frequented by Louis XIV of France mostly for hunting. * 1684-1686 : Construction of the Buc aqueduct. * 1880 : Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Cyr-l'École
Saint-Cyr-l'École () is a commune in the western suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the centre of Paris. It used to host the training school for officers of the French army, the École spéciale militaire de Saint-Cyr (ESM), which was relocated to Coëtquidan in 1945. The old buildings of the ESM are now used by the lycée militaire de Saint-Cyr (military high school of Saint-Cyr). Inhabitants are called ''Saint-Cyriens'' (uppercase, with students or graduates from the school called ''saint-cyriens'' with lowercase). Geography Saint-Cyr lies in the ''arrondissement'' of Versailles, west of the Park of Versailles. It is named after St. Cyricus. Saint-Cyr-l'École is served by Saint-Cyr station, which is an interchange station on Paris RER line C, on the Transilien Line U suburban rail line, and on the Transilien Line N suburban rail line. Saint-Cyr-l'Ecole airfield is long established and lies on the edge of the commune. It is used by light aircraft flown by priva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the lift vector. Movement around this axis is called 'rolling' or 'banking'. Considerable controversy exists over credit for the invention of the aileron. The Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss fought a years-long legal battle over the Wright patent of 1906, which described a method of wing-warping to achieve lateral control. The brothers prevailed in several court decisions which found that Curtiss's use of ailerons violated the Wright patent. Ultimately, the First World War compelled the U.S. Government to legislate a legal resolution. A much earlier aileron concept was patented in 1868 by British scientist Matthew Piers Watt Bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
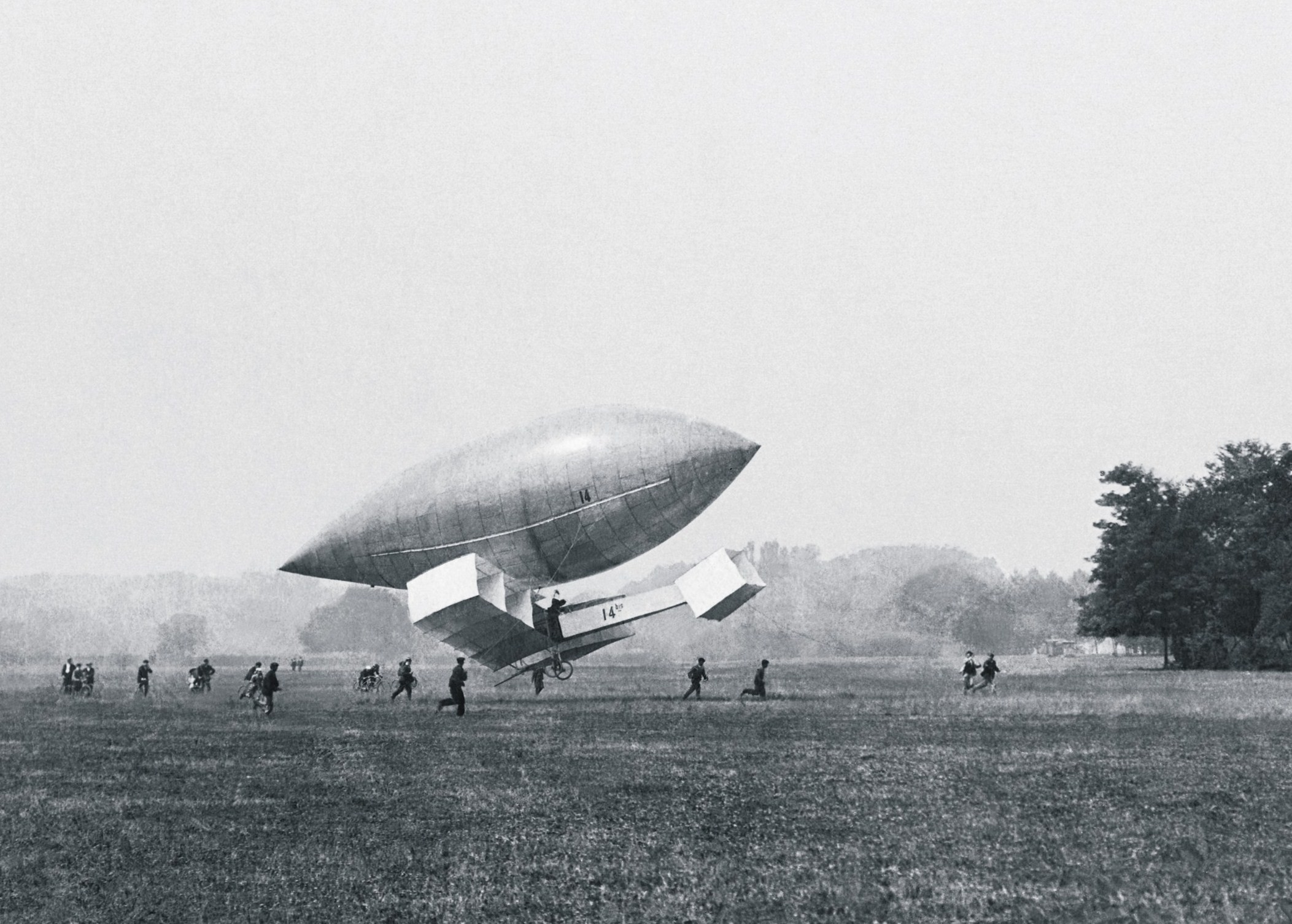
Santos-Dumont 14-bis
The ''14-bis'' (french: Quatorze-bis), (), also known as ("bird of prey" in French), was a pioneer era, canard-style biplane designed and built by Brazilian aviation pioneer Alberto Santos-Dumont. In 1906, near Paris, the ''14-bis'' made a manned powered flight that was the first to be publicly witnessed by a crowd. Background In June 1905, French aviator Gabriel Voisin had flown a glider towed by a fast boat on the river Seine, making a flight of over . The glider's wing and tail were made up of Hargrave cells, a box kite-like structure that provided a degree of inherent stability. This established the Hargrave cell as a configuration useful not only for kites but also for heavier-than-air aircraft. Santos-Dumont was living in Paris at the time, and was one of the most active "aeronauts" in Europe, having developed a series of non-rigid airships that displayed unparalleled agility, speed, endurance, and ease of control. Santos-Dumont met Voisin at the end of 1905, and commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AEA June Bug
The ''June Bug'' (or ''Aerodrome #3'') was an American "pioneer era" aircraft designed and flown by Glenn H. Curtiss and built by the Aerial Experiment Association (A.E.A) in 1908. The ''June Bug'' is famous for winning the first aeronautical prize ever awarded in the United States, the Scientific American Cup. Design and development The competition offered a solid silver sculpted trophy, and $25,000 in cash, to be awarded to whoever made the first public flight of over 1 kilometer (3,280 ft). Glenn Curtiss had a passion of collecting trophies so he and the Aerial Experiment Association built the ''June Bug'' with hopes of winning the Scientific American Cup. ''Aerodrome #3'' included the previously used aileron steering system, but a shoulder yoke made it possible for the pilot to steer by leaning from side to side. The varnish that sealed the wing fabric cracked in the heat, and so a mixture of turpentine, paraffin, and gasoline was used. The ''June Bug'' had yellow wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenn Curtiss
Glenn Hammond Curtiss (May 21, 1878 – July 23, 1930) was an American aviation and motorcycling pioneer, and a founder of the U.S. aircraft industry. He began his career as a bicycle racer and builder before moving on to motorcycles. As early as 1904, he began to manufacture engines for airships. In 1908, Curtiss joined the Aerial Experiment Association, a pioneering research group, founded by Alexander Graham Bell at Beinn Bhreagh, Nova Scotia, to build flying machines. Curtiss won a race at the world's first international air meet in France and made the first long-distance flight in the U.S. His contributions in designing and building aircraft led to the formation of the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company, which later merged into the Curtiss-Wright Corporation. His company built aircraft for the U.S. Army and Navy, and, during the years leading up to World War I, his experiments with seaplanes led to advances in naval aviation. Curtiss civil and military aircraft were some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing Warping
Wing warping was an early system for lateral (roll) control of a fixed-wing aircraft. The technique, used and patented by the Wright brothers, consisted of a system of pulleys and cables to twist the trailing edges of the wings in opposite directions. In many respects, this approach is similar to that used to trim the performance of a paper airplane by curling the paper at the back of its wings. Description In 1900, Wilbur Wright wrote, "...my observations of the flight of birds convince me that birds use more positive and energetic methods of regaining equilibrium than that of shifting the center of gravity...they regain their lateral balance...by a torsion of the tips of the wings. If the rear edge of the right wing tip is twisted upward and the left downward the bird becomes an animated windmill and instantly begins to turn, a line from its head to its tail being the axis." After Wilbur demonstrated the method, Orville noted, "From this it was apparent that the wings of a mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (aircraft)
In aeronautics, the chord is an imaginary straight line joining the leading edge and trailing edge of an aerofoil. The chord length is the distance between the trailing edge and the point where the chord intersects the leading edge.L. J. Clancy (1975), ''Aerodynamics'', Section 5.2, Pitman Publishing Limited, London. The point on the leading edge used to define the chord may be the surface point of minimum radius. p.18 For a turbine aerofoil the chord may be defined by the line between points where the front and rear of a 2-dimensional blade section would touch a flat surface when laid convex-side up. The wing, horizontal stabilizer, vertical stabilizer and propeller/rotor blades of an aircraft are all based on aerofoil sections, and the term ''chord'' or ''chord length'' is also used to describe their width. The chord of a wing, stabilizer and propeller is determined by measuring the distance between leading and trailing edges in the direction of the airflow. (If a wing has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight International
''Flight International'' is a monthly magazine focused on aerospace. Published in the United Kingdom and founded in 1909 as "A Journal devoted to the Interests, Practice, and Progress of Aerial Locomotion and Transport", it is the world's oldest continuously published aviation news magazine. ''Flight International'' is published by DVV Media Group. Competitors include Jane's Information Group and ''Aviation Week''. Former editors of, and contributors include H. F. King, Bill Gunston, John W. R. Taylor and David Learmount. History The founder and first editor of ''Flight'' was Stanley Spooner. He was also the creator and editor of ''The Automotor Journal'', originally titled ''The Automotor Journal and Horseless Vehicle''.Guide To British Industrial History: Biographies: ''Stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)



