|
Santa Rosa First Peoples Community
The Santa Rosa First Peoples Community is the major organisation of indigenous people in Trinidad and Tobago. The Caribs of Arima are descended from the original Amerindian inhabitants of Trinidad; Amerindians from the former ''encomiendas'' of Tacarigua and Arauca ( Arouca) were resettled to Arima between 1784 and 1786. The SRCC was incorporated in 1973 to preserve the culture of the Caribs of Arima and maintain their role in the annual Santa Rosa Festival (dedicated to Santa Rosa de Lima, the first Catholic saint canonised in the New World). The SRCC is headed by its President Ricardo Bharath Hernandez and maintains a leadership role among indigenous organisations in Trinidad. The community is also the base for the Carib Queen. The Amerindians were relocated to open their lands for settlement by the influx of French settlers brought in by the ''Cedula of Population'' and to separate the indigenous people from the newcomers (''see: History of Trinidad and Tobago''). The Mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad And Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of Grenada and off the coast of northeastern Venezuela. It shares maritime boundaries with Barbados to the northeast, Grenada to the northwest and Venezuela to the south and west. Trinidad and Tobago is generally considered to be part of the West Indies. The island country's capital is Port of Spain, while its largest and most populous city is San Fernando. The island of Trinidad was inhabited for centuries by Indigenous peoples before becoming a colony in the Spanish Empire, following the arrival of Christopher Columbus, in 1498. Spanish governor José María Chacón surrendered the island to a British fleet under the command of Sir Ralph Abercromby in 1797. Trinidad and Tobago were ceded to Britain in 1802 under the Treaty of Amiens as se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 33: "[16c: from the feminine of ''Americus'', the Latinized first name of the explorer Amerigo Vespucci (1454–1512). The name ''America'' first appeared on a map in 1507 by the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, referring to the area now called Brazil]. Since the 16c, a name of the western hemisphere, often in the plural ''Americas'' and more or less synonymous with ''the New World''. Since the 18c, a name of the United States of America. The second sense is now primary in English: ... However, the term is open to uncertainties: ..." The term gained prominence in the early 16th century, during Europe's Age of Discovery, shortly after the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci concluded that America (now often called ''the Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Groups In Trinidad And Tobago
This article is about the demographics, demography of the population of Trinidad and Tobago including population density, Ethnic group, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population. Population The total population of Trinidad and Tobago was 1,328,018 according to the 2011 census, an increase of 5.2% since the 2000 census. According to the total population was estimated at in , compared to only 646,000 in 1950. The proportion of children below the age of 15 in 2010 was 20.7%, 71% was between 15 and 65 years of age, while 8.3% was 65 years or older.Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carib People
“Carib” may refer to: People and languages *Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of South America **Carib language, also known as Kalina, the language of the South American Caribs *Kalinago people, or Island Caribs, an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean **Island Carib language, or simply Carib, the language of the Island Caribs *Cariban languages, the wider family of languages that includes Carib (but not Island Carib) *Black Carib, indigenous people from the island of Saint Vincent, descended from Island Caribs and black slaves *Garifuna people, Central American people descended from Saint Vincent's Black Caribs Birds *''Eulampis'', a genus of hummingbird with the following species: **Green-throated carib **Purple-throated carib *Carib grackle, a New World tropical blackbird Other uses *Carib Aviation, a former airline based in Antigua and Barbuda *Carib Brewery, a brewery headquartered in Trinidad and Tobago *Carib Territory, a district in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Rosa First Peoples Community
The Santa Rosa First Peoples Community is the major organisation of indigenous people in Trinidad and Tobago. The Caribs of Arima are descended from the original Amerindian inhabitants of Trinidad; Amerindians from the former ''encomiendas'' of Tacarigua and Arauca ( Arouca) were resettled to Arima between 1784 and 1786. The SRCC was incorporated in 1973 to preserve the culture of the Caribs of Arima and maintain their role in the annual Santa Rosa Festival (dedicated to Santa Rosa de Lima, the first Catholic saint canonised in the New World). The SRCC is headed by its President Ricardo Bharath Hernandez and maintains a leadership role among indigenous organisations in Trinidad. The community is also the base for the Carib Queen. The Amerindians were relocated to open their lands for settlement by the influx of French settlers brought in by the ''Cedula of Population'' and to separate the indigenous people from the newcomers (''see: History of Trinidad and Tobago''). The Mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Woodford
Sir Ralph James Woodford, 2nd Baronet (1784–17 May 1828), was a British colonial administrator who was the longest-serving governor of Trinidad. Young and energetic, from 1813 he sought to bring order to Trinidad society and greatly improved the public infrastructure, especially in Port of Spain. At the same time, he institutionalised class and racial divisions and was not in favour of emancipation. His governorship was cut short by his death at sea. Early life Ralph James Woodford, born in 1784, was the son of the 1st Baronet of Carleby, the diplomat Sir Ralph Woodford, and Gertrude Reessen, of Dutch extraction. Between 1809 and 1811 Woodford was in Madeira, caring for his invalid sister, Elizabeth. Their parents both died in 1810 and on his return he sought an appointment. Governor of Trinidad After declining the offer of the new post of Registrar of Slaves in Trinidad, Woodford secured the governorship of Trinidad under the patronage of Lord Bathurst, then Secre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José María Chacón
Don José María Chacón (1 January 1749 – 1 January 1833) was the last Spanish Governor of Trinidad, serving from 1783 to 1797. He was responsible for signing the Cedula of Population in 1783, leading to extensive French immigration to Trinidad. Chacón founded the city of San Fernando in 1784. In 1797 Chacón surrendered Trinidad to a British fleet under the command of Sir Ralph Abercromby. The King of Spain set up a "Council of War" to look into the surrender. By royal decree, Chacón and Rear Admiral Sebastián Ruiz de Apodaca (who had scuttled his small fleet) were banished for life from the "Royal Domain." Apodaca's case was reconsidered and he was reinstated in 1809, but Chacón died in exile. Trinidad and Tobago's national flower, the chaconia, is named after Chacón. References See also *''History of Trinidad and Tobago The history of Trinidad and Tobago begins with the settlements of the islands by Indigenous peoples, Indigenous First Peoples. Trinidad was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Trinidad And Tobago
The history of Trinidad and Tobago begins with the settlements of the islands by Indigenous peoples, Indigenous First Peoples. Trinidad was visited by Christopher Columbus on his Voyages of Christopher Columbus, third voyage in 1498, (he never landed in Tobago), and claimed in the name of Spain. Trinidad was administered by Spaniards, Spanish hands until 1797, but it was largely settled by French colonists. Tobago changed hands between the British colonization of the Americas, British, French colonization of the Americas, French, Dutch colonization of the Americas, Dutch, and Courland colonization of the Americas, Courlanders, but eventually ended up in British hands following the second Treaty of Paris (1814). In 1889, the two islands were incorporated into a single political entity. Trinidad and Tobago obtained its independence from the British Empire in 1962 and became a republic in 1976. Pre-Columbian period Human settlement in Trinidad dates back at least 7,000 years. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carib Queen
The Carib Queen is the leader of the indigenous community in Trinidad and Tobago. The Queen, whose title was established in 1875, is based at the Santa Rosa First Peoples Community in Arima, Trinidad and Tobago. The position is a lifetime appointment. The use of "Carib" in the title "Carib Queen" is meant to represent all people of indigenous Amerindian descent in Trinidad, rather than referring specifically to ethnic Caribs. History The Spanish were the first Europeans to colonise the island of Trinidad, which was already home to the Carib and other indigenous groups. Catholic Catalan Capuchin friars were tasked with converting the Amerindian population to Catholicism. The Caribs and other groups resisted the Spanish, but the population shrunk due to disease and other factors. The Spanish eventually settled all of Trinidad's remaining indigenous population on a reservation at the Spanish mission at Santa Rosa de Arima, now the present-day the Santa Rosa First Peoples Commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of Q-D-Š, holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denomination. In Catholic Church, Catholic, Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican Communion, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheranism, Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but some are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and consequently a public cult of veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. While the English word ''saint'' originated in Christianity, History of religion, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special holiness t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Caribs
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language known as Island Carib. They also spoke a pidgin language associated with the Mainland Caribs. At the time of Spanish contact, the Kalinago were one of the dominant groups in the Caribbean, which owes its name to them. They lived throughout northeastern South America, Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, the Windward Islands, Dominica, and possibly the southern Leeward Islands. Historically, it was thought their ancestors were mainland peoples who had conquered the islands from their previous inhabitants, the Igneri. However, linguistic and archaeological evidence contradicts the notion of a mass emigration and conquest; the Kalinago language appears not to have been Cariban, but like that of their neighbors, the Taíno. Irving Rouse and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



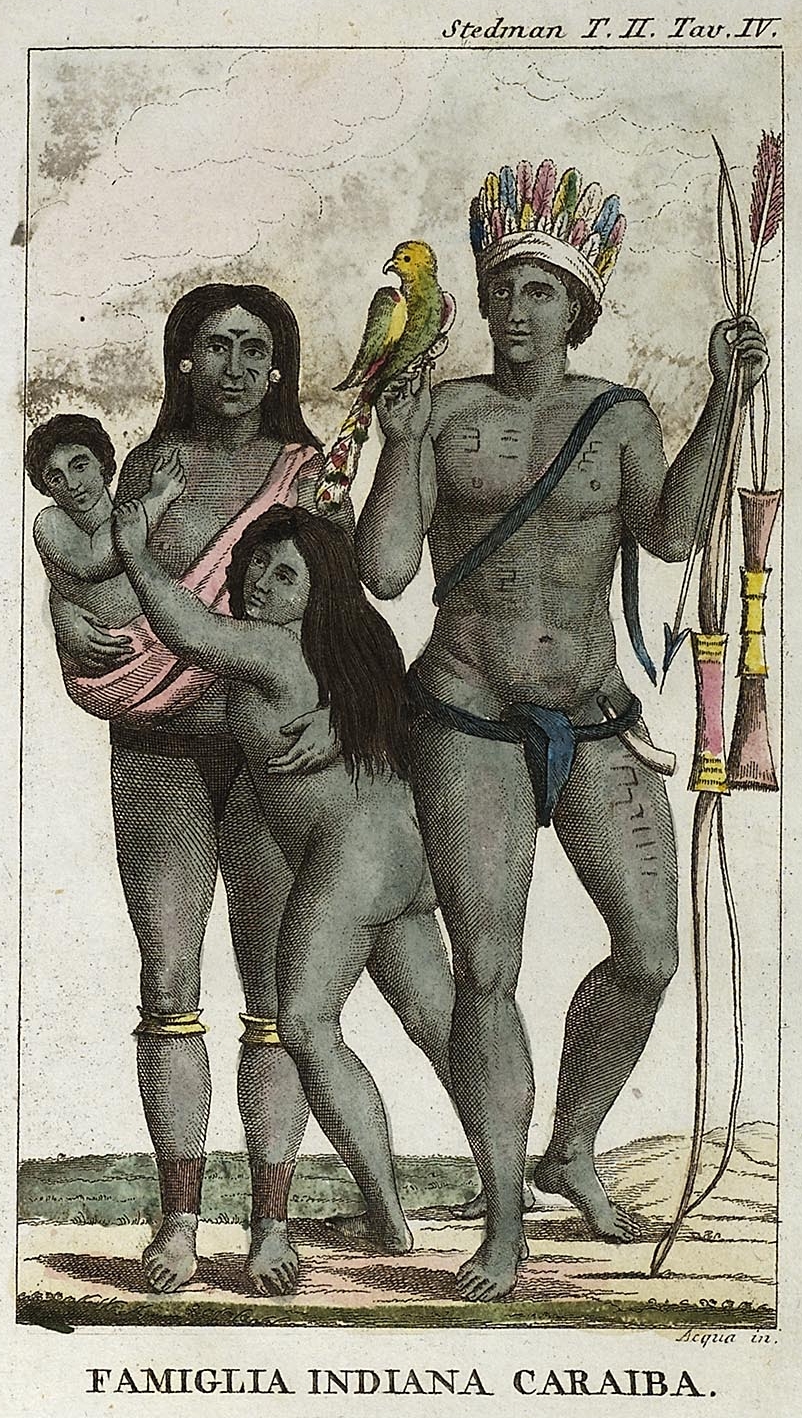
.jpg)