|
San Healing Practices
In the culture of the San (also known as Ju/'oansi, !Kung, or Bushmen), an indigenous people of Botswana, Namibia, South Africa, and Angola, healers administer a wide range of practices, from oral remedies containing plant and animal material, making cuts on the body and rubbing in 'potent' substances, inhaling smoke of smouldering organic matter like certain twigs or animal dung, wearing parts of animals or 'jewellery' that 'makes them strong.' Anecdotal records reveal that the Khoikhoi and San people have used ''Sceletium tortuosum'' since ancient times as an essential part of the indigenous culture and materia mediac. The trance dance is one of the most distinctive features of San culture. Trance dance The San heal whilst in an altered state of consciousness in what is known as a 'trance dance' or 'healing dance'. Trance dance rituals take place over an entire night. Participants will sometimes tie offerings to animal spirits to the trees, and will use drums in order to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San People
The San peoples (also Saan), or Bushmen, are members of various Khoe, Tuu, or Kxʼa-speaking indigenous hunter-gatherer cultures that are the first cultures of Southern Africa, and whose territories span Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Lesotho and South Africa. In 2017, Botswana was home to approximately 63,500 San people (roughly 2.8% of the population) making it the country with the highest number of San people. Definition The term "San" has a long vowel and is spelled Sān (in Khoekhoegowab orthography). It is a Khoekhoe exonym with the meaning of "foragers" and was often used in a derogatory manner to describe nomadic, foraging people. Based on observation of lifestyle, this term has been applied to speakers of three distinct language families living between the Okavango River in Botswana and Etosha National Park in northwestern Namibia, extending up into southern Angola; central peoples of most of Namibia and Botswana, extending into Zambia and Zimbabwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namibian Culture
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and east. Although it does not border Zimbabwe, less than 200 metres (660 feet) of the Botswanan right bank of the Zambezi River separates the two countries. Namibia gained independence from South Africa on 21 March 1990, following the Namibian War of Independence. Its capital and largest city is Windhoek. Namibia is a member state of the United Nations (UN), the Southern African Development Community (SADC), the African Union (AU) and the Commonwealth of Nations. The driest country in sub-Saharan Africa, Namibia has been inhabited since pre-historic times by the San, Damara and Nama people. Around the 14th century, immigrating Bantu peoples arrived as part of the Bantu expansion. Since then, the Bantu groups, the largest being the Ovambo, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botswana Culture
Besides referring to the language of the dominant people groups in Botswana, ''Setswana'' is the adjective used to describe the rich cultural traditions of the Batswana - whether construed as members of the Setswana ethnic groups or of all citizens of Botswana. the Batswana believe in the rich culture of Botho-Ubuntu, ‘‘People are not individuals, living in a state of independence, but part of a community, living in relationships and interdependence.’ Batswana believe in working together and in being united. The name Batswana is used as a nationality for the people of Botswana and as an ethnicity for people who practice the same culture and speak the same language in neighbouring South Africa.There are different ethnic groups in the country Botswana among them are the Tswana(Barolong, Bakwena, Bangwato,Batlokwa,Bakgatla, Baphuthing, Bataung, Bangwaketse, Batawana, Bahurutshe,Balete);BaKalanga(BaLilima,Baperi,BaWumbe ,BaNambya);Ovaherero(Baherero,Ovambanderu);Wayei, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Medicine
Energy medicine is a branch of alternative medicine based on a pseudo-scientific belief that healers can channel "healing energy" into a patient and effect positive results. Practitioners use a number of names including various synonyms for medicine (e.g., energy healing) and sometimes use the word vibrational instead of or in concert with energy. In most cases there is no empirically measurable energy involved: the term refers instead to so-called subtle energy. Practitioners may classify practice as hands-on, hands-off, and distant (or absent) where the patient and healer are in different locations. Many schools of energy healing exist using many names: for example, biofield energy healing, spiritual healing, contact healing, distant healing, therapeutic touch, Reiki or ''Qigong''. Reviews of the scientific literature on energy healing have concluded that there is no evidence supporting clinical efficacy. The theoretical basis of healing has been criticised as implausible; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional African Medicine
Traditional African medicine is a range of traditional medicine disciplines involving Indigenous peoples of Africa, indigenous herbalism and Traditional African religions, African spirituality, typically including divination, diviners, midwives, and herbalism, herbalists. Practitioners of traditional African medicine claim to be able to cure a variety of diverse conditions including cancer, psychiatric disorders, high blood pressure, cholera, most venereal diseases, epilepsy, asthma, eczema, fever, anxiety, depression, benign prostatic hyperplasia, urinary tract infections, gout, and healing of wounds and burns and even Ebola. Diagnosis is reached through spiritual means and a treatment is prescribed, usually consisting of a herbal remedy that is considered to have not only healing abilities but also symbolic and spiritual significance. Traditional African medicine, with its belief that illness is not derived from chance occurrences, but through spiritual or social imbalance, dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
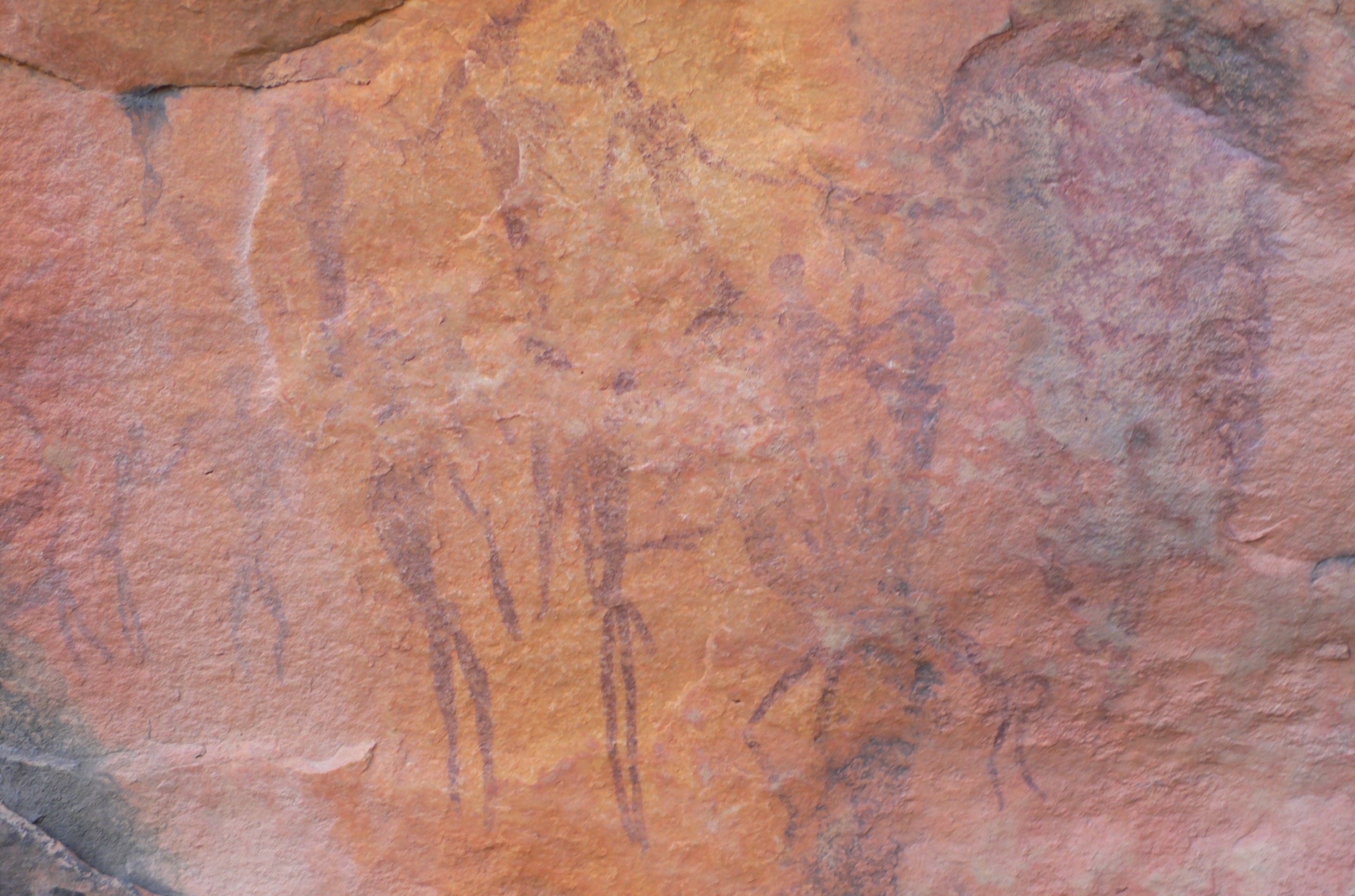
San Rock Art
The San, or Bushmen, are indigenous people in Southern Africa particularly in what is now South Africa and Botswana. Their ancient rock paintings and carvings (collectively called rock art) are found in caves and on rock shelters. The artwork depicts non-human beings, hunters, and half-human half-animal hybrids. The half-human hybrids are believed to be medicine men or healers involved in a healing dance.”Gall, Sandy. "The Bushmen of the Kalahari." Ecologist 33.7 (2003): 28-31. A painting discovered at Blombos Cave is thought to be the oldest known instance of human art, dating to around 73,000 years ago. Gall writes, “The Laurens van der Post panel at Tsodilo is one of the most famous rock paintings.” High on this rock face in Botswana is the image of a “magnificent red eland bull” painted, according to Van der Post, “only as a Bushman who had a deep identification with the eland could have painted him.” Also on this rock face is a female giraffe that is motionl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Religion
The San religion is the traditional religion and mythology of the San people. It is poorly attested due to their interactions with Christianity. Gods and mythical figures ;ǀXam The ǀXam prayed to the Sun and Moon. Many myths are ascribed to various stars. * ǀKágge̥n (sometimes corrupted to "Cagn") is Mantis, a demiurge and hero in ǀXam folklore. He is a trickster god who can shape-shift. He and his wife ǀHúnntuǃattǃatte̥n. * ǀHúnntuǃattǃatte̥n (also known as or corrupted to "Coti"), the Dassie, adopted !Xo, Porcupine, as their daughter. * !Xo, Porcupine, as their parents ǀKágge̥n and ǀHúnntuǃattǃatte̥n, married Ichneumon, son was the Ichneumon. * /Kwammang-a, a dangerous stranger carnivore, married !Xo, son was the Ichneumon. * Ichneumon, a small, furry carnivore, mongoose. * ǂKá̦gára and ǃHãunu are brothers-in-law who fought with lightning, causing massive storms in the east. ;Other ǃXu is the Khoikhoi word ''ǃKhub'' 'rich man, maste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
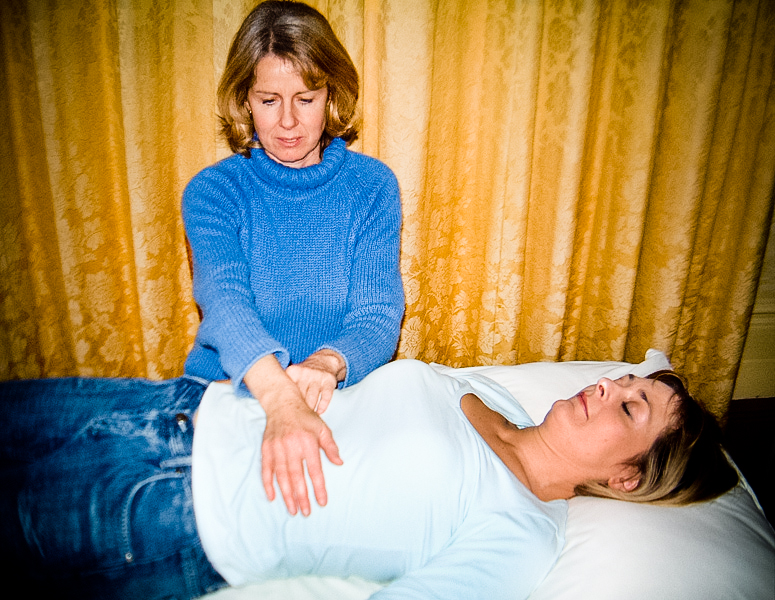
Laying On Of Hands
The laying on of hands is a religious practice. In Judaism ''semikhah'' ( he, סמיכה, "leaning f the hands) accompanies the conferring of a blessing or authority. In Christian churches, this practice is used as both a symbolic and formal method of invoking the Holy Spirit primarily during baptisms and confirmations, healing services, blessings, and ordination of priests, ministers, elders, deacons, and other church officers, along with a variety of other church sacraments and holy ceremonies. A similar practice of laying on of hands is also used in Navajo religious ceremonies. Jewish tradition The laying on of hands was an action referred to on numerous occasions in the Hebrew Bible to accompany the conferring of a blessing or authority. Moses ordained Joshua through ''semikhah''—i.e. by the laying on of hands: , . The Bible adds that Joshua was thereby "filled with the spirit of wisdom". Moses also ordained the 70 elders (). The elders later ordained their successors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalahari
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for , covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa. It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal desert, whose name is of Khoekhoegowab origin and means "vast place". Etymology ''Kalahari'' is derived from the Tswana word ''Kgala'', meaning "the great thirst", or ''Kgalagadi'', meaning "a waterless place"; the Kalahari has vast areas covered by red sand without any permanent surface water. History The Kalahari Desert was not always a dry desert. The fossil flora and fauna from Gcwihaba Cave in Botswana indicates that the region was much wetter and cooler at least from 30 to 11 thousand BP (before present) especially after 17,500 BP. Geography Drainage of the desert is by dry black valleys, seasonally inundated pans and the large salt pans of the Makgadikgadi Pan in Botswana and Etosha Pan in Namibia. The only permanent river, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorna Marshall
Lorna Marshall (born Lorna Jean McLean; September 14, 1898 – July 8, 2002) was an anthropologist who in the 1950s, 60s and 70s lived among and wrote about the previously unstudied !Kung people of the Kalahari Desert.Douglas Martin, "Lorna Marshall, 103, Early Scholar on Africa's Bushmen"obituaryin the New York Times, July 30, 2002.Expeditionary notebooks and journals of Lorna and Laurence Marshall, 1928, 1951–1968 : A Finding Aid . Peabody Museum Archives. Harvard University. October 2004 Background Marshall was born in Morenci, Arizona territory. She married Laurence Kennedy Marshall in 1926; they had a daughter |
Elizabeth Marshall Thomas
Elizabeth Marshall Thomas (born September 13, 1931) is an American author. She has published fiction and non-fiction books and articles on animal behavior, Paleolithic life, and the !Kung Bushmen of the Kalahari Desert. Early life and education Thomas was born to anthropologist Lorna Marshall and Laurence K. Marshall, co-founder of the Raytheon Corporation. She is the sister of ethnographic filmmaker John Marshall. She was raised in Cambridge, Massachusetts and attended Abbot Academy in Andover, Massachusetts. After beginning undergraduate studies at Smith College, Thomas took a break to travel in Africa with her family and later completed a degree in English from Radcliffe College. Career Between 1950 and 1956, she took part in three expeditions to live with and study the Ju/'hoansi ( !Kung Bushmen) of the Kalahari Desert in Namibia and Botswana. During these trips, Thomas kept a journal which she later drew on when writing her first book, ''The Harmless People''. She later d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |