|
Samuel Marolois
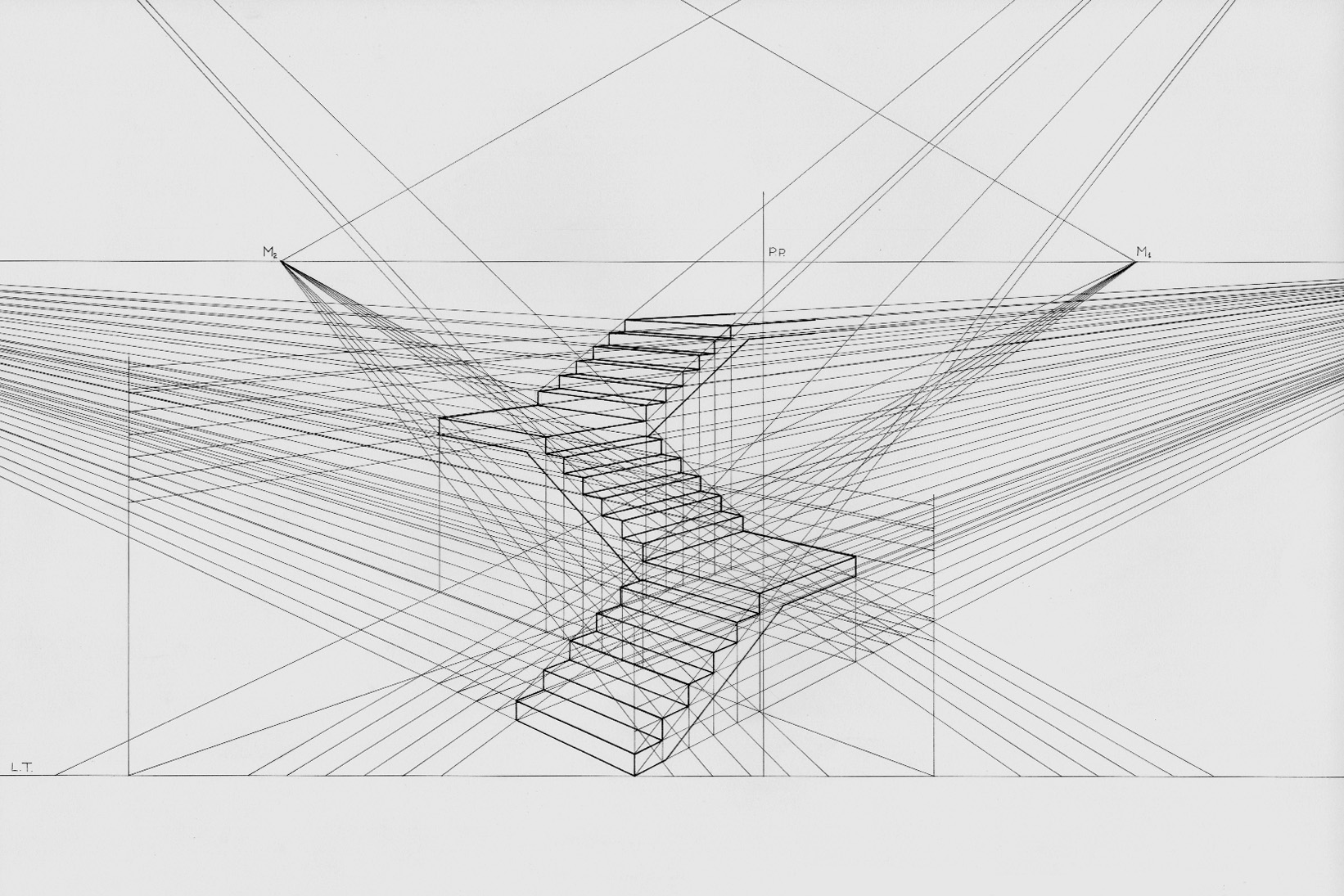
Samuel Marolois ( – before 1627) was a Dutch mathematician and military engineer who is best known for his work on perspective. Life and work Marolois (or Marlois) was born in the Dutch Republic (possibly in The Hague) as son of Nicolas Marolois, a Protestant native of Valenciennes who had been exiled from France and served the Prince of Orange. Marolois became a mathematician and earthworks engineer in the employ of Maurice, Prince of Orange He was married to Hester le Maire, which made him a brother-in-law of the Amsterdam merchants Thomas le Maire and Pieter le Fevre. In March 1611, he bought a house in The Hague. After the death of Ludolph van Ceulen, Marolois attempted unsuccessfully to succeed him as Chair of Mathematics in Leiden. Marolois wrote a book on perspective, , which was published in 1614 and printed many times in other languages including Dutch, German and Latin. The book had both theoretical and practical elements. The theoretical parts were mostly taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspective (graphical)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of 3D projection, graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a federal republic that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795 (the Batavian Revolution). It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. The republic was established after seven Dutch provinces in the Spanish Netherlands revolted against rule by Spain. The provinces formed a mutual alliance against Spain in 1579 (the Union of Utrecht) and declared their independence in 1581 (the Act of Abjuration). It comprised Groningen, Frisia, Overijssel, Guelders, Utrecht, Holland and Zeeland. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. Through its tradin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of the Netherlands is Amsterdam, The Hague has been described as the country's de facto capital. The Hague is also the capital of the province of South Holland, and the city hosts both the International Court of Justice and the International Criminal Court. With a population of over half a million, it is the third-largest city in the Netherlands, after Amsterdam and Rotterdam. The Hague is the core municipality of the Greater The Hague urban area, which comprises the city itself and its suburban municipalities, containing over 800,000 people, making it the third-largest urban area in the Netherlands, again after the urban areas of Amsterdam and Rotterdam. The Rotterdam–The Hague metropolitan area, with a population of approximately 2.6&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valenciennes
Valenciennes (, also , , ; nl, label=also Dutch, Valencijn; pcd, Valincyinnes or ; la, Valentianae) is a commune in the Nord department, Hauts-de-France, France. It lies on the Scheldt () river. Although the city and region experienced a steady population decline between 1975 and 1990, it has since rebounded. The 1999 census recorded that the population of the commune of Valenciennes was 41,278, and that of the metropolitan area was 399,677. History Before 1500 Valenciennes is first mentioned in 693 in a legal document written by Clovis II (''Valentiana''). In the 843 Treaty of Verdun, it was made a neutral city between Neustria and the Austrasia. Later in the 9th century the region was overrun by the Normans, and in 881 the town passed to them. In 923 it passed to the Duchy of Lower Lotharingia dependent on the Holy Roman Empire. Once the Empire of the Franks was established, the city began to develop, though the archaeological record has still not revealed all it has to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Of Orange
Prince of Orange (or Princess of Orange if the holder is female) is a title originally associated with the sovereign Principality of Orange, in what is now southern France and subsequently held by sovereigns in the Netherlands. The title "Prince of Orange" was created in 1163 by the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, by elevating the county of Orange to a principality, in order to bolster his support in that area in his conflict with the Papacy. The title and land passed to the French noble houses of Baux, in 1173, and of Chalons, in 1393, before arriving with Rene of Nassau in 1530. The principality then passed to a Dutch nobleman, Rene's cousin William (known as "the Silent"), in 1544. In 1702, after William the Silent's great-grandson William III of England died without children, a dispute arose between his cousins, Johan Willem Friso and Frederick I of Prussia. In 1713, under the Treaty of Utrecht Frederick William I of Prussia ceded the Principality of Orange to King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice, Prince Of Orange
Maurice of Orange ( nl, Maurits van Oranje; 14 November 1567 – 23 April 1625) was ''stadtholder'' of all the provinces of the Dutch Republic except for Friesland from 1585 at the earliest until his death in 1625. Before he became Prince of Orange upon the death of his eldest half-brother Philip William in 1618, he was known as Maurice of Nassau. Maurice spent his youth in Dillenburg in Nassau, and studied in Heidelberg and Leiden. He succeeded his father William the Silent as stadtholder of Holland and Zeeland in 1585, and became stadtholder of Utrecht, Guelders and Overijssel in 1590, and of Groningen in 1620. As Captain-General and Admiral of the Union, Maurice organized the Dutch rebellion against Spain into a coherent, successful revolt and won fame as a military strategist. Under his leadership and in cooperation with the Land's Advocate of Holland Johan van Oldenbarnevelt, the Dutch States Army achieved many victories and drove the Spaniards out of the north and ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludolph Van Ceulen
Ludolph van Ceulen (, ; 28 January 1540 – 31 December 1610) was a German-Dutch mathematician from Hildesheim. He emigrated to the Netherlands. Biography Van Ceulen moved to Delft most likely in 1576 to teach fencing and mathematics and in 1594 opened a fencing school in Leiden. In 1600 he was appointed the first professor of mathematics at the Engineering School, Duytsche Mathematique, established by Maurice, Prince of Orange, at the relatively new Leiden University. He shared this professorial level at the school with the surveyor and cartographer, , which shows that the intention was to promote practical, rather than theoretical instruction. The curriculum for the new Engineering School was devised by Simon Stevin who continued to act as the personal advisor to the Prince. At first the professors at Leiden refused to accept the status of Van Ceulen and Van Merwen, especially as they taught in Dutch rather than Latin. Theological professors generally believed that practica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guidobaldo Del Monte
Guidobaldo del Monte (11 January 1545 – 6 January 1607, var. Guidobaldi or Guido Baldi), Marquis del Monte, was an Italian mathematician, philosopher and astronomer of the 16th century. Biography Del Monte was born in Pesaro. His father, Ranieri, was from a leading wealthy family in Urbino. Ranieri was noted for his role as a soldier and also as the author of two books on military architecture. The Duke of Urbino, Duke Guidobaldo II, honoured him with the title Marchese del Monte so the family had only become a noble one in the generation before Guidobaldo. On the death of his father Guidobaldo inherited the title of Marchese. Guidobaldo studied mathematics at the University of Padua in 1564. While there he became a friend of the great Italian poet Torquato Tasso. In fact Guidobaldo may have known Tasso before they studied at Padua together, for Tasso was almost exactly the same age as Guidobaldo and had been educated at the court of the Duke of Urbino, with the duke's so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua Kirby
Joshua Kirby (1716, Parham, Suffolk – 1774, Kew), often mistakenly called John Joshua Kirby, was an English 18th-century landscape painter, engraver, writer, draughtsman and architect famed for his publications and teaching on linear perspective based on Brook Taylor's mathematics. Biography Joshua was the second of five sons of topographer John Kirby. In early life he assisted his father in the preparation of his important Survey of Suffolk, which took the form of a volume (1735) entitled ''The Suffolk Traveller'', an extensive gazetteer in which the parishes and towns, and the principal landowners, seats, advowsons, antiquities and industries of the two counties of West and East Suffolk were described, the text counterpart of John Kirby's County Map published in 1736. In 1739 Joshua married Sarah Bull, and his children Sarah (afterwards Mrs. Sarah Trimmer) and William soon followed. From an early age he was very studious, but, showing special aptitude as an artist, he set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coevorden
Coevorden (; nds-nl, Koevern) is a city and municipality in the province of Drenthe, Netherlands. During the 1998 municipal reorganisation in the province, Coevorden merged with Dalen, Sleen, Oosterhesselen and Zweeloo, retaining its name. In August 2017, it had a population of 35,267. Etymology The name ''Coevorden'' means "cow ford(s)" or "cow crossing", similar to ''Bosporus'' or ''Oxford''. History Coevorden received city rights in 1408. It is the oldest city in the province of Drenthe. The city was captured from the Spanish in 1592 by a Dutch and English force under the command of Maurice, Prince of Orange. The following year it was besieged by a Spanish force but the city held out until its relief in May 1594. Coevorden was then reconstructed in the early seventeenth century to an ''ideal city'' design, similar to Palmanova. The streets were laid out in a radial pattern within polygonal fortifications and extensive outer earthworks. The city of Coevorden indir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Girard
Albert Girard () (11 October 1595 in Saint-Mihiel, France − 8 December 1632 in Leiden, The Netherlands) was a French-born mathematician. He studied at the University of Leiden. He "had early thoughts on the fundamental theorem of algebra" and gave the inductive definition for the Fibonacci numbers. He was the first to use the abbreviations 'sin', 'cos' and 'tan' for the trigonometric functions in a treatise. Girard was the first to state, in 1625, that each prime of the form 1 mod 4 is the sum of two squares. (See Fermat's theorem on sums of two squares.) It was said that he was quiet-natured and, unlike most mathematicians, did not keep a journal for his personal life. In the opinion of Charles Hutton, Girard was ...the first person who understood the general doctrine of the formation of the coefficients of the powers from the sum of the roots and their products. He was the first who discovered the rules for summing the powers of the roots of any equation. This had previously b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)