|
Samogitian Nobility
Samogitian nobility was nobility originating in the Lithuanian region of Samogitia. The Samogitian nobility was an integral part of Lithuanian nobility. Historically, the local gentry was formed of people of various ethnic backgrounds, including Lithuanian, Polish, Tartar, German and Ruthenian., also published in English as: As the Duchy of Samogitia maintained a certain level of autonomy within the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, its nobility was considered a separate subject of the laws, on par with the nobility of other Commonwealth lands. In the Grand Duchy of Lithuania the Samogitian nobles were electing Elders of Samogitia who had voivode rights and were the third highest ranked statesmen in the Lithuanian Council of Lords (after voivodes of Vilnius and Trakai). The self-elected Elders of Samogitia were only confirmed by the Grand Duke of Lithuania. Samogitian nobility, especially its lower class, preserved knowledge of the Lithuanian language and the Samogitian dialec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narutowicz Pilsudski
Narutowicz is a Polish surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Gabriel Narutowicz (1865-1922), president of Poland * Joanna Narutowicz (1868-1948), wife of Stanislaw * Stanisław Narutowicz (1862-1932), brother of Gabriel, Polish-Lithuanian activist * Kazimierz Narutowicz Kazimierz Narutowicz (1904, Brewiki, Kovno Governorate - 1987) was a Polish Lithuanian political activist. Son of Stanisław Narutowicz, in interwar Lithuania in 1934-1938 he tried to mediate between the ministries of diplomacy of Poland and Lithu ... (1904-1987), son of Stanisław and Joanna, Polish-Lithuanian activist {{surname, Narutowicz Polish-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samogitian Dialect
Samogitian ( sgs, žemaitiu kalba, link=no or sometimes ', ''žemaitiu šnekta'' or '; lt, žemaičių tarmė, žemaičių kalba) is an Eastern Baltic language spoken mostly in Samogitia (in the western part of Lithuania). In Lithuania, it is mostly treated as a dialect of Lithuanian, but it is also considered as a separate language by some linguists inside and outside of Lithuania. Its recognition as a distinct language is increasing in recent years, and attempts have been made to standardize it. The Samogitian language should not be confused with the interdialect of the Lithuanian language as spoken in the Duchy of Samogitia before Lithuanian became a written language, which later developed into one of the two variants of written Lithuanian used in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania based on the so-called middle dialect of the Kėdainiai region. This was called the Samogitian (Žemaitian) language; the term "Lithuanian language" then referred to the other variant, which had been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World War. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of the Second World War. In 1938, the Second Republic was the sixth largest country in Europe. According to the 1921 census, the number of inhabitants was 27.2 million. By 1939, just before the outbreak of World War II, this had grown to an estimated 35.1 million. Almost a third of the population came from minority groups: 13.9% Ruthenians; 10% Ashkenazi Jews; 3.1% Belarusians; 2.3% Germans and 3.4% Czechs and Lithuanians. At the same time, a significant number of ethnic Poles lived outside the country's borders. When, after several regional conflicts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshal Of Poland
Marshal of Poland ( pl, Marszałek Polski) is the highest rank in the Polish Army. It has been granted to only six officers. At present, Marshal is equivalent to a Field Marshal or General of the Army (OF-10) in other NATO armies. History Today there are no living Marshals of Poland, since this rank is bestowed only on military commanders who have achieved victory in war. Recently, however, the rank of four-star with modernized name Generał has been introduced, and on August 15, 2002, was granted to Czesław Piątas, at present civilian, former Chief of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of Poland. List of Marshals In all, the following people have served as Marshals of Poland Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Marshal Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naczelnik Państwa
The Chief of State ( pl, Naczelnik Państwa; ) was the title of the head of state of Poland in the early years of the Second Polish Republic. This office was held only by Józef Piłsudski, from 1918 to 1922. Until 1919, the title was called the Provisional Chief of State ( pl, Tymczasowy Naczelnik Państwa). After 1922, the Polish head of state became the President of Poland. The office of Chief of State was created by a Regency Council decree of 22 November 1918, which established a system of governance for Poland pending its revision by a democratically elected ''Sejm'' (parliament). The ''Naczelnik'' exercised the highest civil and military power in the country. He was Commander-in-Chief of the Polish armed forces, with powerful prerogatives in the field of foreign relations. He appointed government ministers, who answered to him, including the Prime Minister. Provisional decrees could be promulgated by the Chief of State with the countersignatures of the Prime Minister an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Naczelnik państwa, Chief of State (1918–1922) and Marshal of Poland, First Marshal of Second Polish Republic, Poland (from 1920). He was considered the ''de facto'' leader (1926–35) of the Second Polish Republic as the Ministry of National Defence (Poland), Minister of Military Affairs. After World War I, he held increasing dominance in Politics of Poland, Polish politics and was an active player in international diplomacy. He is viewed as a father of the Second Polish Republic re-established in 1918, 123 years after the final Partitions of Poland, Partition of Poland in 1795. Seeing himself as a descendant of the culture and traditions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Piłsudski believed in a multi-ethnic Poland—"a home of nations" including indigenous ethnic and religious minorities. Early in his political career, Piłsudski became a leader of the Polish Socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
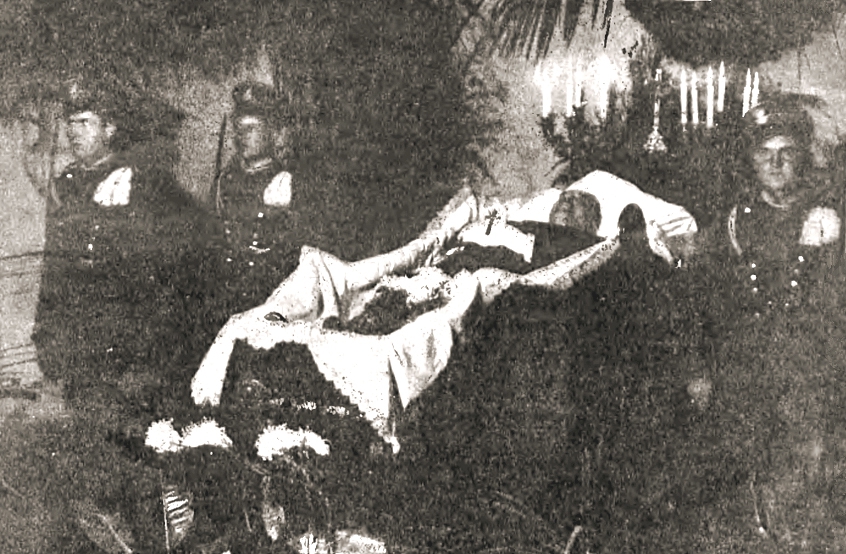
Assassination Of Gabriel Narutowicz
Gabriel Narutowicz, the first president of Poland after regaining independence, was assassinated on 16 December 1922, five days after taking office, aged 57. He was fatally shot by Eligiusz Niewiadomski, an artist and art critic, while visiting an exhibition at Warsaw's Zachęta gallery. Background Poland regained independence in 1918 in the aftermath of World War I. Soon afterwards, Gabriel Narutowicz, professor of engineering, became one of the left-wing leaders in the Sejm (Polish parliament). Following the 1921 March Constitution of Poland and the November 1922 Polish legislative election, Narutowicz was elected the first president of Poland in the Polish presidential election, 9 December 1922. His election was not accepted by the right-wing nationalist '' endecja'' faction, which staged a number of protests. Narutowicz's forthcoming murder would be the culmination of an aggressive, right wing and anti-semitic propaganda campaign vilifying him; in the background of stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Poland
The president of Poland ( pl, Prezydent RP), officially the president of the Republic of Poland ( pl, Prezydent Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej), is the head of state of Poland. Their rights and obligations are determined in the Constitution of Poland. The president heads the executive branch. In addition, the president has a right to dissolve parliament in certain cases, can veto legislation and represents Poland in the international arena. History The first president of Poland, Gabriel Narutowicz, was sworn in as president of the Second Polish Republic on 11 December 1922. He was elected by the National Assembly (the Sejm and the Senate) under the terms of the 1921 March Constitution. Narutowicz was assassinated on 16 December 1922. Previously Józef Piłsudski had been "Chief of State" ('' Naczelnik Państwa'') under the provisional Small Constitution of 1919. In 1926 Piłsudski staged the " May Coup", overthrew President Stanisław Wojciechowski and had the National Assem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel Narutowicz
Gabriel Józef Narutowicz (; 29 March 1865 – 16 December 1922) was a Polish professor of hydroelectric engineering and politician who served as the first President of Poland from 11 December 1922 until his assassination on 16 December, five days after assuming office. He previously served as the Minister of Public Works from 1920 to 1922 and briefly as Minister of Foreign Affairs in 1922. A renowned engineer and politically independent, Narutowicz was the first elected head of state following Poland's regained sovereignty from partitioning powers. Born into a noble family with the strong patriotic sentiment, Narutowicz studied at the University of St. Petersburg before relocating to Zurich Polytechnic and completing his studies in Switzerland. An engineer by profession, he was a pioneer of electrification and his works were presented at exhibitions across Western Europe. Narutowicz also directed the construction of the first European hydroelectric power plants in Monthey, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Lithuania
The Council of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Taryba, german: Litauischer Staatsrat, pl, Rada Litewska), after July 11, 1918 the State Council of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Valstybės Taryba) was convened at the Vilnius Conference that took place between 18 and 23 September 1917. The twenty men who composed the council at first were of different ages, social status, professions, and political affiliations. The council was granted the executive authority of the Lithuanian people and was entrusted to establish an independent Lithuanian state. On 16 February 1918, the members of the council signed the Act of Independence of Lithuania and declared Lithuania an independent state based on democratic principles. 16 February is celebrated as Lithuania's State Restoration Day. The council managed to establish the proclamation of independence despite the presence of German troops in the country until the autumn of 1918. By the spring of 1919, the council had almost doubled in size. The council ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław Narutowicz
Stanisław Narutowicz ( lt, Stanislovas Narutavičius ) (2 September 1862, Brewiki, Kovno Governorate – 31 December 1932, Kaunas, Lithuania) was a lawyer and politician, one of the twenty signatories of the Act of Independence of Lithuania and brother to the first president of Poland Gabriel Narutowicz. He was also the only Polish–Lithuanian member of the Taryba, the provisional Lithuanian parliament formed in the later stages of World War I. Biography The Narutowicz family, which had its roots in Lithuanian nobility, received a coat of arms in 1413, changing its name from Noručiai (singular Norutis) to Narutowicz in the process. He was a self-declared Samogitian, Lithuanian and a Pole. His parents, Jan Narutowicz and Wiktoria née Szczepkowska were landowners and ran a manor. His father took part in the January Uprising of 1863, which was a revolt that took place in the former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth against Tsarist oppression. While studying at the Lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elder Of Samogitia
The Duchy of Samogitia ( lt, Žemaičių seniūnija, sgs, Žemaitėjės seniūnėjė, pl, Księstwo żmudzkie)Grzegorz Błaszczyk, ''Żmudź w XVII i XVIII wieku: zaludnienie i struktura społeczna'', Uniwersytet im. Adama Mickiewicza w Poznaniu, 1985, , p.1-2 was an administrative unit of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1422 (and from 1569, a member country of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth). Between 1422 and 1441 it was known as the Eldership of Samogitia. The Grand Duke of Lithuania also held the title of Duke of Samogitia, although the actual ruler of the province, responsible to the Duke, was known as the General Elder (Seniūnas) of Samogitia. The Duchy was located in the western part of the present Republic of Lithuania. Historically, in the west it had access to the Baltic Sea; in the north, it bordered the Duchy of Courland and Ducal Prussia in the south. During the Middle Ages and until the last partition in 1795, Samogitia had clearly defined borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |