|
Salcatonin
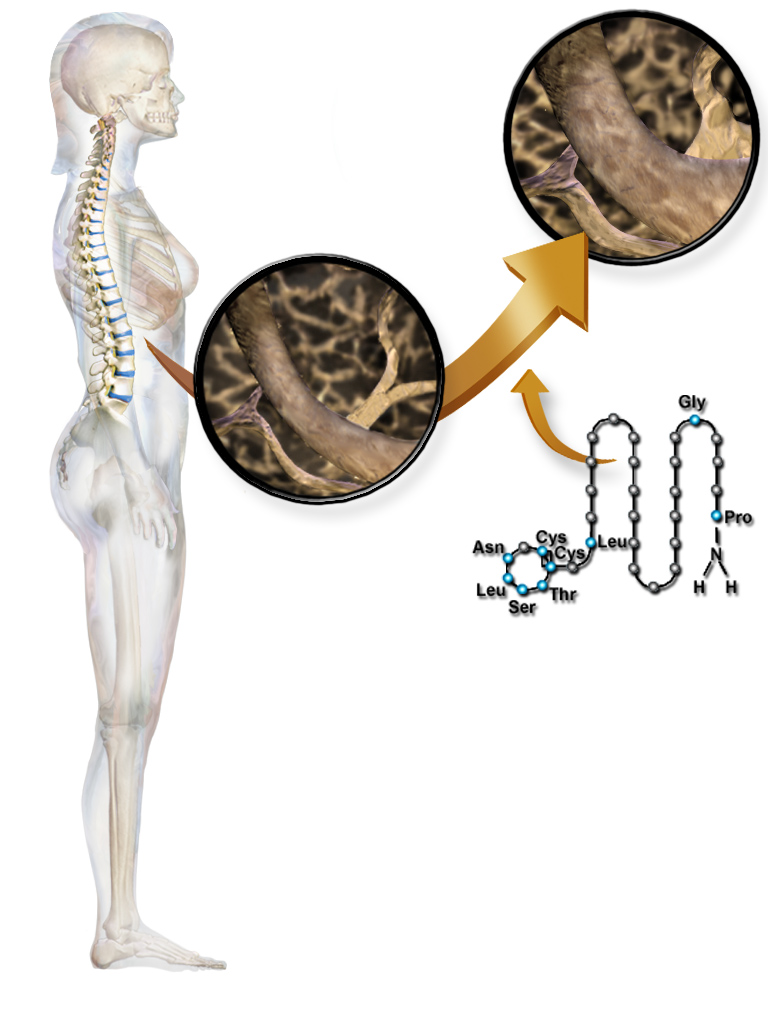
Salmon calcitonin () is the type of calcitonin hormone found in salmon. Similar to humans, salmon calcitonin is a peptide hormone produced in the ultimobranchial region by parafollicular cells in response to hypercalcemia and lowers blood calcium and phosphate by promoting renal excretion. Composition Salcatonin is composed of 32 amino acids, of which 13 differ from human calcitonin. The structure of human calcitonin and salcatonin is as follows: ''Human calcitonin:'' H-Cys1-Gly-Asn-Leu-Ser-Thr-Cys7-Met-Leu-Gly-Thr-Tyr-Thr-Gln-Asp-Phe-Asn-Lys-Phe-His-Thr-Phe-Pro-Gln-Thr-Ala-lle-Gly-Val-Gly-Ala-Pro-NH2 ''Salcatonin:'' H-Cys1-Ser-Asn-Leu-Ser-Thr-Cys7-Val-Leu-Gly-Lys-Leu-Ser-Gln-Glu-Leu-His-Lys-Leu-Gln-Thr-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Thr-Asn-Thr-Gly-Ser-Gly-Thr-Pro-NH2 The cysteine in the first and seventh positions form a disulfide bond. Therapeutic usage Synthetic salmon calcitonin may be used therapeutically in humans, as it is twenty times more active than human calcitonin and has a longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates. in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Its importance in humans has not been as well established as its importance in other animals, as its function is usually not significant in the regulation of normal calcium homeostasis. It belongs to the calcitonin-like protein family. Historically calcitonin has also been called thyrocalcitonin. Biosynthesis and regulation Calcitonin is formed by the proteolytic cleavage of a larger prepropeptide, which is the product of the CALC1 gene (). It is functionally an antagonist with PTH and Vitamin D3. The CALC1 gene belongs to a superfamily of related protein hormone precursors including islet amyloid precursor protein, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and the precursor of adrenomedullin. Secretion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paget's Disease Of Bone
Paget's disease of bone (commonly known as Paget's disease or, historically, osteitis deformans) is a condition involving cellular remodeling and deformity of one or more bones. The affected bones show signs of dysregulated bone remodeling at the microscopic level, specifically excessive bone breakdown and subsequent disorganized new bone formation. These structural changes cause the bone to weaken, which may result in deformity, pain, bone fractures, fracture or arthritis of associated joints. The exact cause is unknown, although leading theories indicate both genetic and acquired factors (see Paget's disease of bone#Causes, Causes). Paget's disease may affect any one or several bones of the body (most commonly pelvis, tibia, femur, lumbar vertebrae, and skull), but never the entire skeleton, and does not spread from bone to bone. Rarely, a bone affected by Paget's disease can transform into a Osteosarcoma, malignant bone cancer. As the disease often affects people differently, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus ''Oncorhynchus'') basin. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, grayling, Freshwater whitefish, whitefish, lenok and Hucho, taimen. Salmon are typically fish migration, anadromous: they hatch in the gravel stream bed, beds of shallow fresh water streams, migrate to the ocean as adults and live like sea fish, then return to fresh water to reproduce. However, populations of several species are restricted to fresh water throughout their lives. Folklore has it that the fish return to the exact spot where they hatched to spawn (biology), spawn, and tracking studies have shown this to be mostly true. A portion of a returning salmon run ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the correct development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organs and tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating a variety of physiological processes and behavioral activities such as diges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcemia. Those with a mild increase that has developed slowly typically have no symptoms. In those with greater levels or rapid onset, symptoms may include abdominal pain, bone pain, confusion, depression, weakness, kidney stones or an abnormal heart rhythm including cardiac arrest. Most outpatient cases are due to primary hyperparathyroidism and inpatient cases due to cancer. Other causes of hypercalcemia include sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, Paget disease, multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN), vitamin D toxicity, familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia and certain medications such as lithium and hydrochlorothiazide. Diagnosis should generally include either a corrected calcium or ionized calcium level and be confirmed after a week. Specific chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia (also spelled gynaecomastia) is the abnormal non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in males due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Updated by Brent Wisse (10 November 2018) Gynecomastia can cause significant psychological distress or unease. Gynecomastia can be normal in newborn babies due to exposure to estrogen from the mother, in adolescents going through puberty, in older men over age 50, and/or in obese men. Most occurrences of gynecomastia do not require diagnostic tests. Gynecomastia may be caused by abnormal hormone changes, any condition that leads to an increase in the ratio of estrogens/androgens such as liver disease, kidney failure, thyroid disease and some non-breast tumors. Alcohol and some drugs can also cause breast enlargement. Other causes may include Klinefelter syndrome, metabolic dysfunction, or a natural decline in testosterone production. This may occur even if the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the spine, the bones of the forearm, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, the person may have chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities. Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases after the menopause due to lower levels of estrogen, and after ' andropause' due to lower levels of testosterone. Osteoporosis may also occur due to a number of diseases or treatments, including alcoholism, anorexia, hyperthyroidism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resorption
Resorption is the absorption of cells or tissue into the circulatory system, usually by osteoclasts. Types of resorption include: * Bone resorption * Herniated Disc Resorption * Tooth resorption * Fetal resorption * Blood resorption See also * Nutrient resorption In plants Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plant ..., in plants References Set index articles {{biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Hormones
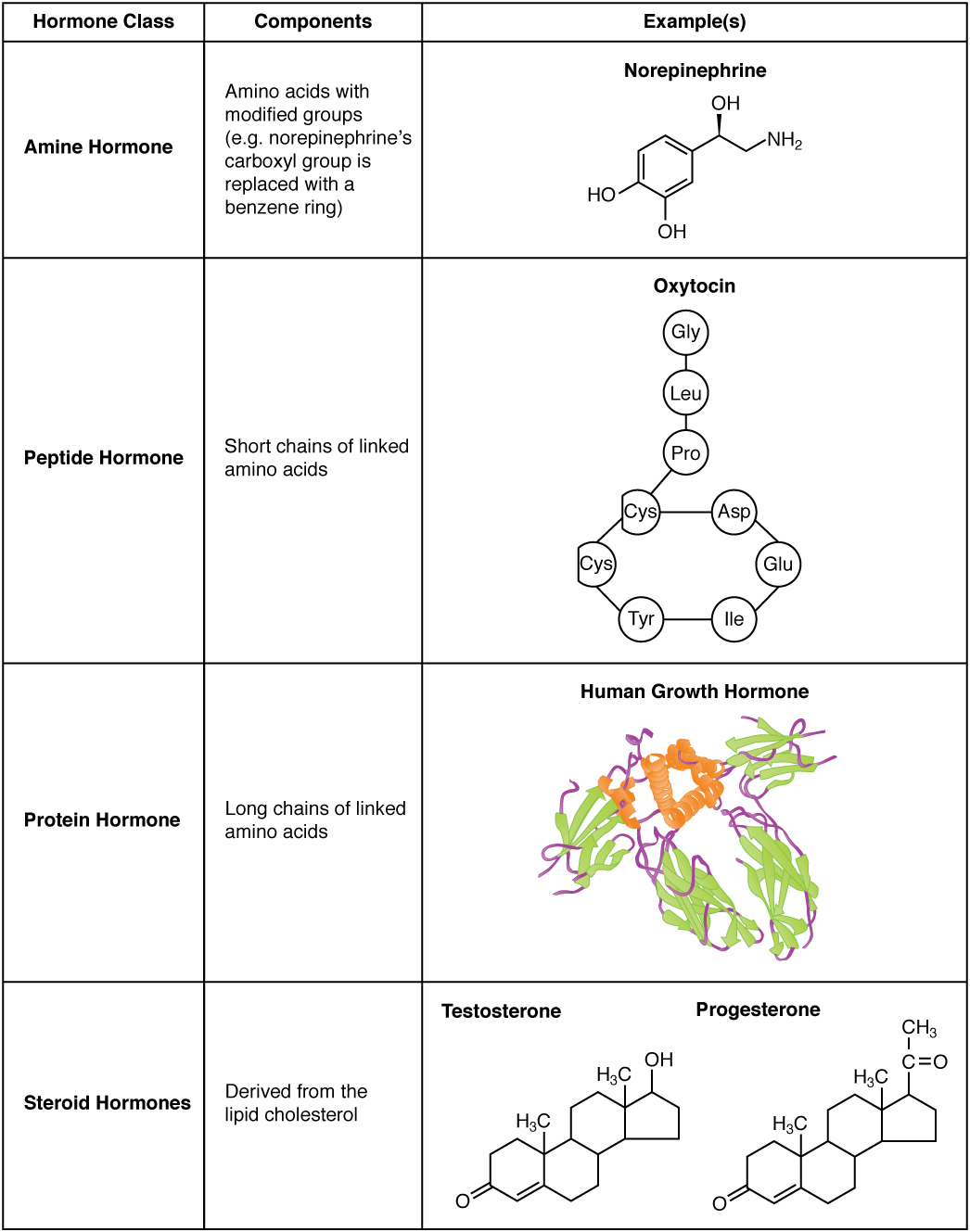
Peptide hormones or protein hormones are hormones whose molecules are peptide, or proteins, respectively. The latter have longer amino acid chain lengths than the former. These hormones have an effect on the endocrine system of animals, including humans. Most hormones can be classified as either amino acid–based hormones (amine, peptide, or protein) or steroid hormones. The former are water-soluble and act on the surface of target cells via second messengers; the latter, being lipid-soluble, move through the plasma membranes of target cells (both cytoplasmic and nuclear) to act within their nuclei. Like all peptides and proteins, peptide hormones and protein hormones are synthesized in cells from amino acids according to mRNA transcripts, which are synthesized from DNA templates inside the cell nucleus. Preprohormones, peptide hormone precursors, are then processed in several stages, typically in the endoplasmic reticulum, including removal of the N-terminal signal sequence an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Hormones
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a vertebrate, true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed placodermi, external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormones Of Calcium Metabolism
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the correct development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organs and tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating a variety of physiological processes and behavioral activities such as digestio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |