|
Sakai Tadakiyo
, also known as Uta-no-kami, Bodart-Bailey, Beatrice. (1999) ''Kaempfer's Japan: Tokugawa Culture Observed,'' p. 442./ref> was a ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) in Kōzuke Province, and a high-ranking government advisor and official in the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan. Sansom, George Bailey. (1963) ''A History of Japan: 1615-1867,'' pp. 54 The Sakai were identified as one of the '' fudai'' or insider ''daimyō'' clans which were hereditary vassals or allies of the Tokugawa clan,Alpert, Georges. (1888) ''Ancien Japon,'' pp. 76-77 in contrast with the '' tozama'' or outsider clans. Sakai clan genealogy Tadakiyo was part of the senior branch of the Sakai. The ''fudai'' Sakai clan originated in 14th century Mikawa Province.Appert p. 76 The Sakai claim descent from Minamoto Arichika. Arichika had two sons: one of them, Yasuchika, took the name Matsudaira; and the other son, Chikauji, took the name Sakai — and this samurai ancestor is the progenitor of this clan's name. Papinot, Edmond. ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beatrice Bodart-Bailey
Beatrice Bodart-Bailey (born 1942WorldCat (date unknown). Beatrice M. Bodart-Bailey. Retrieved from http://experiment.worldcat.org/entity/person/data/2632104239.) is a German people, German Australian people, Australian academic, author, and Japanologist. She was named professor of economics at Kobe University, becoming "the first female and first non-Japanese person actually appointed by the Ministry of Education".Kenrick, Vivienne (2006-06-24). "Personality Profile: Beatrice M. Bodart-Bailey". ''Japan Times'' (Tokyo), 24 June 2006. Retrieved on 2011-05-14 from http://search.japantimes.co.jp/cgi-bin/fl20060624vk.html. Biography Her early education was in German and British schools. She earned a BA at the Australian National University (ANU). Her master's and doctorate degrees were awarded at the Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies (RSPAS) at ANU in Canberra. Bodart-Bailey's MA thesis investigated "The Political Significance of the Tea Master Sen no Rikyū (1522–1591)" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Nobutada ''
{{disambiguation ...
Tokugawa may refer to: *Tokugawa era, an alternative term for the Edo period, 1603 to 1868 *Tokugawa shogunate, a feudal regime of Japan during the Edo period **Tokugawa clan, a powerful family of Japan ***Tokugawa Ieyasu (1543–1616), most notable member of the Tokugawa clan and founder of its shogunate *Tokugawa (surname), (Shinjitai spelling: 徳川; Kyūjitai spelling: 德川) a Japanese surname *Tokchon, South P'yŏngan province, North Korea, a city known as Tokugawa during Japanese rule *, a character in ''The Idolmaster Million Live! is a Japan, Japanese multimedia spin-off (media), spin-off series of ''The Idolmaster'', starting with the game of the same name. The series follows a new group of idols working alongside the idols of 765 Productions with a producer at the 76 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Ietsuna
was the fourth ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa dynasty of Japan who was in office from 1651 to 1680. He is considered the eldest son of Tokugawa Iemitsu, which makes him the grandson of Tokugawa Hidetada and the great-grandson of Tokugawa Ieyasu. Early life (1641–1651) Tokugawa Ietsuna was born in 1641, allegedly the eldest son of Tokugawa Iemitsu with his concubine, Oraku no Kata later Houjuin. Later Ietsuna was raised with his sister, Chiyohime (born by Ofuri) by Iemitsu's concubine, Oman no kata (later Eikoin) and Iemitsu's wife, Takatsukasa Takako later Honriin. After Eikoin retired, Senhime (also called Tenjuin) raised him with Honriin.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Tokugawa, Ietsuna''" in ; n.b., Louis-Frédéric is a pseudonym of Louis-Frédéric Nussbaum, ''see'Deutsche Nationalbibliothek Authority File. At that time his father was shogun in his own right and had enacted several anti-Christian measures after the bloody Shimabara Rebellion of 1637. Though the suppr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakura period, shoguns were themselves figureheads, with real power in hands of the Shikken of the Hōjō clan. The office of shogun was in practice hereditary, though over the course of the history of Japan several different clans held the position. The title was originally held by military commanders during Heian period in the eighth and ninth centuries. When Minamoto no Yoritomo gained political ascendency over Japan in 1185, the title was revived to regularize his position, making him the first shogun in the usually understood sense. The shogun's officials were collectively referred to as the ; they were the ones who carried out the actual duties of administration, while the Imperial court retained only nominal authority.Beasley, William G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Period
The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization by Western powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialized nation state and emergent great power, influenced by Western scientific, technological, philosophical, political, legal, and aesthetic ideas. As a result of such wholesale adoption of radically different ideas, the changes to Japan were profound, and affected its social structure, internal politics, economy, military, and foreign relations. The period corresponded to the reign of Emperor Meiji. It was preceded by the Keiō era and was succeeded by the Taishō era, upon the accession of Emperor Taishō. The rapid modernization during the Meiji era was not without its opponents, as the rapid changes to society caused many disaffected traditionalists from the former samurai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ruling emperors before the Meiji Restoration, the events restored practical abilities and consolidated the political system under the Emperor of Japan. The goals of the restored government were expressed by the new emperor in the Charter Oath. The Restoration led to enormous changes in Japan's political and social structure and spanned both the late Edo period (often called the Bakumatsu) and the beginning of the Meiji era, during which time Japan rapidly Industrialisation, industrialized and adopted Western culture, Western ideas and production methods. Foreign influence The Japanese knew they were behind the Western powers when US Commodore (United States), Commodore Matthew C. Perry came to Japan in 1853 in Black Ships, large warshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harima Province
or Banshū (播州) was a province of Japan in the part of Honshū that is the southwestern part of present-day Hyōgo Prefecture. Harima bordered on Tajima, Tanba, Settsu, Bizen, and Mimasaka Provinces. Its capital was Himeji. During the Edo period of Japanese history, the Akō Domain (fief) was part of Harima. The Forty-seven ''rōnin'' were samurai of Akō han. IHI Corporation, a shipbuilder and major Boeing engine subcontractor gets its name from the province. History Harima Province was established in 7th century. During the Meiji Restoration, Himeji Prefecture was established with the whole area of Harima Province as the territory. Himeji Prefecture was renamed to Shikama prefecture, and Shikama Prefecture was transferred to Hyōgo Prefecture finally. Temples and shrines ''Iwa jinja'' was the chief Shinto shrine (''ichinomiya'') of Harima. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himeji Domain
was a feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo period Japan, located in Harima Province in what is now the southern portion of modern-day Hyōgo Prefecture. It was centered around Himeji Castle, which is located in what is now the city of Himeji, Hyōgo. History During the Muromachi period, the area around Himeji was part of the vast holdings of the Akamatsu clan, the ''shugo'' of Harima Province; however, by the Sengoku period, the greatly weakened Akamatsu were defeated by the forces of Oda Nobunaga under his general Hashiba Hideyoshi and the early Himeji Castle was surrendered by Kuroda Yoshitaka. After Hideyoshi succeeded Oda Nobunaga, he assigned the castle to his son Kinoshita Iesada with an estate of 25,000 '' koku''. After the Battle of Sekigahara, Tokugawa Ieyasu relocated Kinoshita to Bitchu Province in 1600 and assigned Himeji to his general and son-in-law Ikeda Terumasa. Ikeda Terumasa was formerly lord of Yoshida Domain in Mikawa Province with a '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musashi Province
was a province of Japan, which today comprises Tokyo Metropolis, most of Saitama Prefecture and part of Kanagawa Prefecture. It was sometimes called . The province encompassed Kawasaki and Yokohama. Musashi bordered on Kai, Kōzuke, Sagami, Shimōsa, and Shimotsuke Provinces. Musashi was the largest province in the Kantō region. History Musashi had its ancient capital in modern Fuchū, Tokyo, and its provincial temple in what is now Kokubunji, Tokyo. By the Sengoku period, the main city was Edo, which became the dominant city of eastern Japan. Edo Castle was the headquarters of Tokugawa Ieyasu before the Battle of Sekigahara and became the dominant city of Japan during the Edo period, being renamed Tokyo during the Meiji Restoration. ''Hikawa-jinja'' was designated as the chief Shinto shrine (''ichinomiya'') of the province; and there are many branch shrines. The former province gave its name to the battleship of the Second World War. Timeline of important events * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawagoe Domain
Kawagoe Castle daimyō residence, administrative headquarters of Kawagoe Domain was a feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo period Japan. It is located in Musashi Province, Honshū. The domain was centered at Kawagoe Castle, located in what is the city of Kawagoe in Saitama Prefecture. History The domain had its beginning in 1590, when Toyotomi Hideyoshi defeated the later Hōjō clan in the Siege of Odawara. Hideyoshi awarded vast Hōjō holdings to Tokugawa Ieyasu, who enfeoffed Sakai Shigetada as ''daimyō'' of Kawagoe with a assessed '' kokudaka'' of 10,000 '' koku''. Shigetada was transferred in 1601, and the next daimyō was appointed in 1609. Afterwards, the domain was reassigned every couple of generations to a large number of fudai daimyō clans, spending the longest time under the control of a branch of the Echizen Matsudaira clan (1767–1867) with a rating of 170,000 ''koku''. The final ''daimyō'' of Kawagoe, Matsudaira Yasutoshi, served as domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakai Sigetada
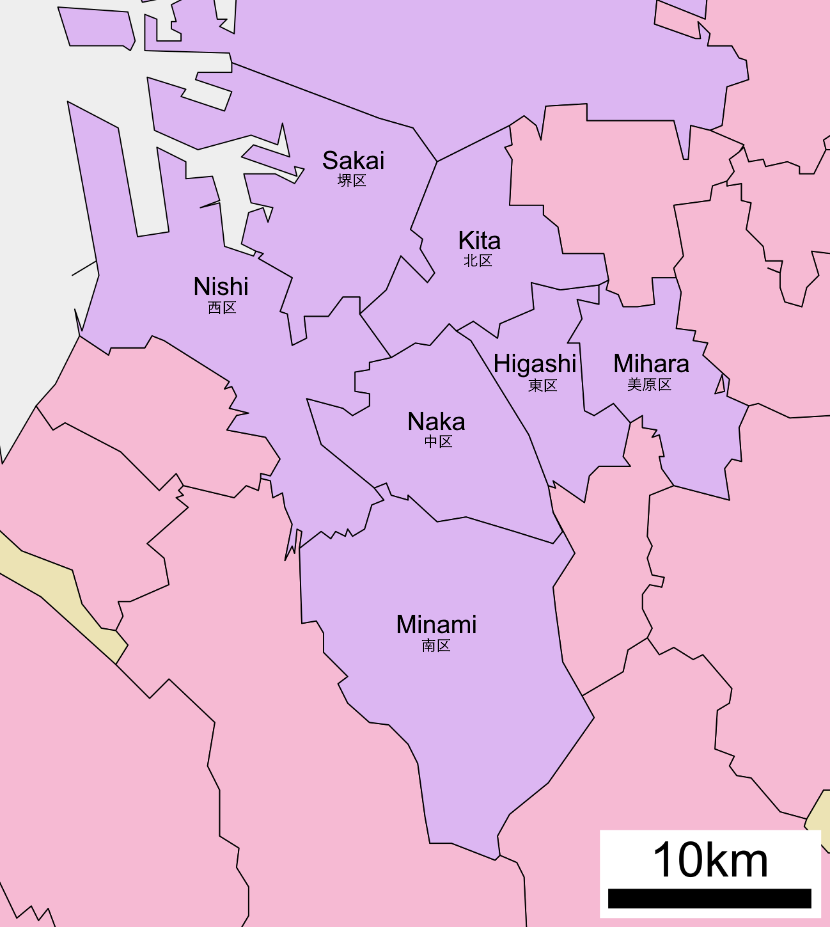
is a city located in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. It has been one of the largest and most important seaports of Japan since the medieval era. Sakai is known for its keyhole-shaped burial mounds, or kofun, which date from the fifth century and include Daisen Kofun, the largest grave in the world by area. Once known for swords, Sakai is now famous for the quality of its cutlery. , the city had an estimated population of 819,965, making it the fourteenth most populous city in Japan (excluding Tokyo). Geography Sakai is located in southern Osaka Prefecture, on the edge of Osaka Bay and directly south of the city of Osaka. Neighboring municipalities Osaka Prefecture *Osaka *Matsubara *Habikino *Ōsakasayama *Kawachinagano * Izumi * Takaishi Climate Sakai has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Sakai is . The average annual rainfall is with June as the wettest month. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |