|
Saint Sigrada
Sigrada of Alsace ( French: Sigrade d'Alsace; died c. 679 AD) was a Franco-Burgundian countess and mother of Ss. Warin, and Leodegar, and grandmother of St. Leudwinus. Life Hagiographies tend not to mention where she was born, but given that she is popularly known as Sigrada of Alsace, she was probably Alsatian.Cilleruelo, Álvaro Cancela. "An emendation to the Renotatio Isidori (CPL 1206°, BHL 4483)." Wiener Studien (2018): 217-227. She was from the Syagrii family of Gallo-Roman Patricians. Her brother was Bishop Dido (also called Desiderius) of Poitiers. She married Count Bodilon of Poitiers and gave birth to Warin and Leodegar in Autun, Saône-et-Loire, Burgundy. Through Warin, who inherited the County of Poitiers, she became the ancestor of the Franco-Lombard dynasty of the Widonids (also called the Lambertiners). She sent Warin to be educated at the court of Chlothar II, while she arranged for Leodegar to be educated under her brother Dido's tutelage. Leodegar quickly rose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
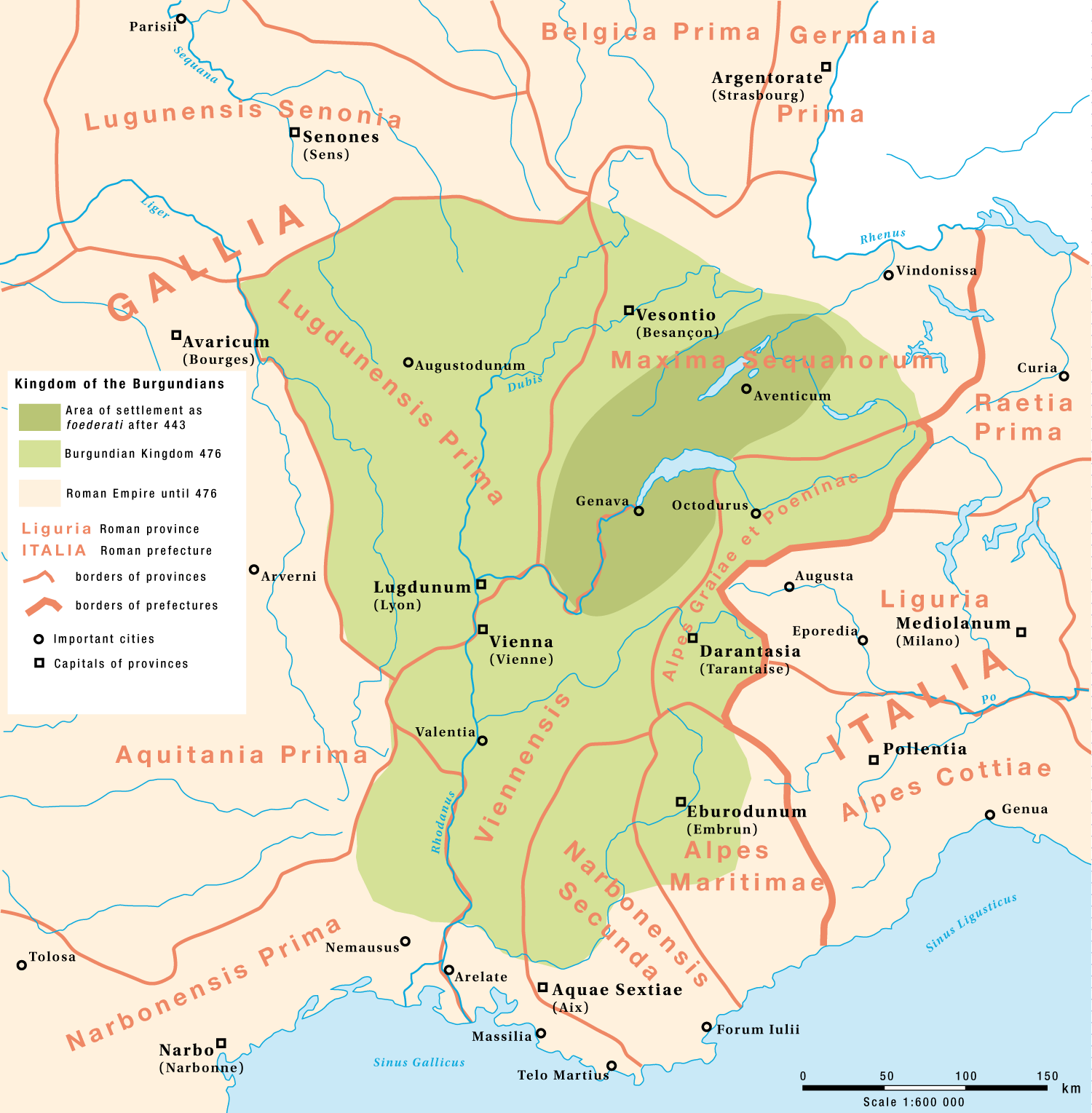
Kingdom Of Burgundy
Kingdom of Burgundy was a name given to various states located in Western Europe during the Middle Ages. The historical Burgundy correlates with the border area of France, Italy and Switzerland and includes the major modern cities of Geneva and Lyon. As a political entity, Burgundy existed in a number of forms with different boundaries, notably, when it was divided into Upper and Lower Burgundy and Provence. Two of the entities, the first around the 6th century and the second around the 11th century, were called the Kingdom of Burgundy. At other times were the Kingdom of Provence, the Duchy of Burgundy and the County of Burgundy. Kingdom of the Burgundians (411–534) Burgundy is named after a Germanic tribe of Burgundians who originated in mainland Scandinavia, then settled on the island of Bornholm, whose name in Old Norse was ''Burgundarholmr'' ("Island of the Burgundians"). From there they migrated south through Germanic lands into Roman Gaul and settled in the wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrician (ancient Rome)
The patricians (from la, patricius, Greek: πατρίκιος) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom, and the early Republic, but its relevance waned after the Conflict of the Orders (494 BC to 287 BC). By the time of the late Republic and Empire, membership in the patriciate was of only nominal significance. The social structure of Ancient Rome revolved around the distinction between the patricians and the plebeians. The status of patricians gave them more political power than the plebeians. The relationship between the patricians and the plebeians eventually caused the Conflict of the Orders. This time period resulted in changing the social structure of Ancient Rome. After the Western Empire fell, the term "patrician" continued as a high honorary title in the Eastern Empire. In the Holy Roman Empire and in many medieval Italian republics, medieval patrician classes were once again formal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
679 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 679 ( DCLXXIX) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 679 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Emperor Constantine IV signs a peace treaty, of a nominal 30-year duration, with Caliph Muawiyah I of the Umayyad Caliphate. Constantine pays an annual tribute of 3,000 (''nomismata'') pounds of gold, 50 horses and 50 slaves. The Arab garrisons are withdrawn from their bases on the Byzantine coastlands, including Crete & Cyzicus. Europe * December 23 – King Dagobert II is murdered in a hunting accident, near Stenay-sur-Meuse ( Ardennes), probably on orders from Pepin of Herstal, the mayor of the palace of Austrasia.E. Vagandard (1902), "Revue des Questions Historiques", pp. 63–67 He is succeeded by Theuderic III, who becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century Christian Saints
The 7th century is the period from 601 ( DCI) through 700 ( DCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Common Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate, a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor which assured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century of councils) ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notre-Dame De Soissons
Notre-Dame de Soissons was a nunnery dedicated to the Virgin Mary (Our Lady) in Soissons. It was founded during the Merovingian era, between 658 and 666, but the community was dissolved and the building partially demolished during the French Revolution (1789–99). The convent was founded by Ebroin, the mayor of the palace under the Merovingian kings, who appointed Aetheria, a nun from Jouarre, as its first abbess. Jouarre had been founded by Ado, a disciple of the Irish missionary Columban, and Notre-Dame therefore stood in the Columbanian tradition of monasticism. In the 660s the nunnery received a monastic rule from the bishop of Soissons, Drauscius. It was a ''mixta regula'', a mixed rule, combining elements of the Benedictine rule and the rule of Columban. The text of this unique rule has not been preserved. During the 660s, the nuns also adopted the practice of the ''laus perennis'' (perennial praise), whereby the Psalms were sung constantly, day and night, by alternating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Clergy
Regular clergy, or just regulars, are clerics in the Catholic Church who follow a rule () of life, and are therefore also members of religious institutes. Secular clergy are clerics who are not bound by a rule of life. Terminology and history The observance of the Rule of St. Benedict procured for Benedictine monks at an early period the name of "regulars". The Council of Verneuil (755) so refers to them in its third canon, and in its eleventh canon speaks of the "ordo regularis" as opposed to the "ordo canonicus", formed by the canons who lived under the bishop according to the canonical regulations. There was question also of a "regula canonicorum", or "regula canonica", especially after the extension of the rule which Chrodegang, Bishop of Metz, had drawn up from the sacred canons (766). And when the canons were divided into two classes in the eleventh century, it was natural to call those who added mendicant, religious poverty to their common life regulars, and those who ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leodegar
Leodegar of Poitiers ( la, Leodegarius; french: Léger; 615 – October 2, 679 AD) was a martyred Burgundian Bishop of Autun. He was the son of Saint Sigrada and the brother of Saint Warinus. Leodegar was an opponent of Ebroin, the Frankish Mayor of the Palace of Neustria, and the leader of the faction of Burgundian nobles. His torture and death made him a martyr and saint. Early life Leodegar was the son of a high-ranking Burgundian nobleman, Bodilon, Count of Poitiers and Paris Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ... and Saint Sigrada, St. Sigrada of Alsace, who later became a nun in the convent of Sainte-Marie at Soissons. His brother was Warinus. He spent his childhood in Paris at the court of Clotaire II, King of the Franks and was educated at the palace school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlothar II
Chlothar II, sometime called "the Young" (French language, French: le Jeune), (May/June 584 – 18 October 629), was king of Neustria and king of the Franks, and the son of Chilperic I and his third wife, Fredegund. He started his reign as an infant under the regency of his mother, who was in an uneasy alliance with Chlothar's uncle King Guntram of Burgundy, who died in 592. Chlothar took power upon the death of his mother in 597; though rich, Neustria was one of the smallest portions of Francia. He continued his mother's feud with Queen Brunhilda of Austrasia, Brunhilda with equal viciousness and bloodshed, finally achieving her execution in an especially brutal manner in 613, after winning the battle that enabled Chlothar to unite Francia under his rule. Like his father, he built up his territories by seizing lands after the deaths of other kings. His reign was long by contemporary standards, but saw the continuing erosion of royal power to the French nobility and the church ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Widonids
The Widonids, also called Guidonids,; german: Guidonen or ; it, Guideschi or or Lambertiner, after their leading names, were an Italian family of Frankish origin prominent in the ninth century. They were descended from Guy of Nantes, whose origins were Austrasian. They were an aggressive dynasty, expanding their base of power into the Papal States, ever loyal to the Empire and never the Papacy. They were related to the Carolingians in the female line and one even made a claim to the throne of France on that basis. The Widonids and the Rorgonids competed for control of the Breton March through much of the ninth century. The first member of the family to attain prominence was Lambert's son Guy I, who was made duke of Spoleto by the Emperor Lothair I in 842. He was active in Lotharingia and Italy, even marrying a local Lombard woman, Itta (or Itana), the daughter of Sico of Benevento. His descendants continued to rule Spoleto until 897. The most famous Guidoni were Guy III and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgundy (French Region)
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The capital of Dijon was one of the great European centres of art and science, a place of tremendous wealth and power, and Western Monasticism. In early Modern Europe, Burgundy was a focal point of courtly culture that set the fashion for European royal houses and their court. The Duchy of Burgundy was a key in the transformation of the Middle Ages toward early modern Europe. Upon the 9th-century partitions of the Kingdom of Burgundy, the lands and remnants partitioned to the Kingdom of France were reduced to a ducal rank by King Robert II of France in 1004. The House of Burgundy, a cadet branch of the House of Capet, ruled over a territory that roughly conformed to the borders and territories of the modern administrative region of Burgundy. Up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saône-et-Loire
Saône-et-Loire (; Arpitan: ''Sona-et-Lêre'') is a department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in France. It is named after the rivers Saône and Loire, between which it lies, in the country's central-eastern part. Saône-et-Loire is Bourgogne-Franche-Comté's most populous department with a population of 551,493 as of 2019.Populations légales 2019: 71 Saône-et-Loire INSEE It is also its southernmost department, as it is situated on the regional border with . Saône-et-Loire's |
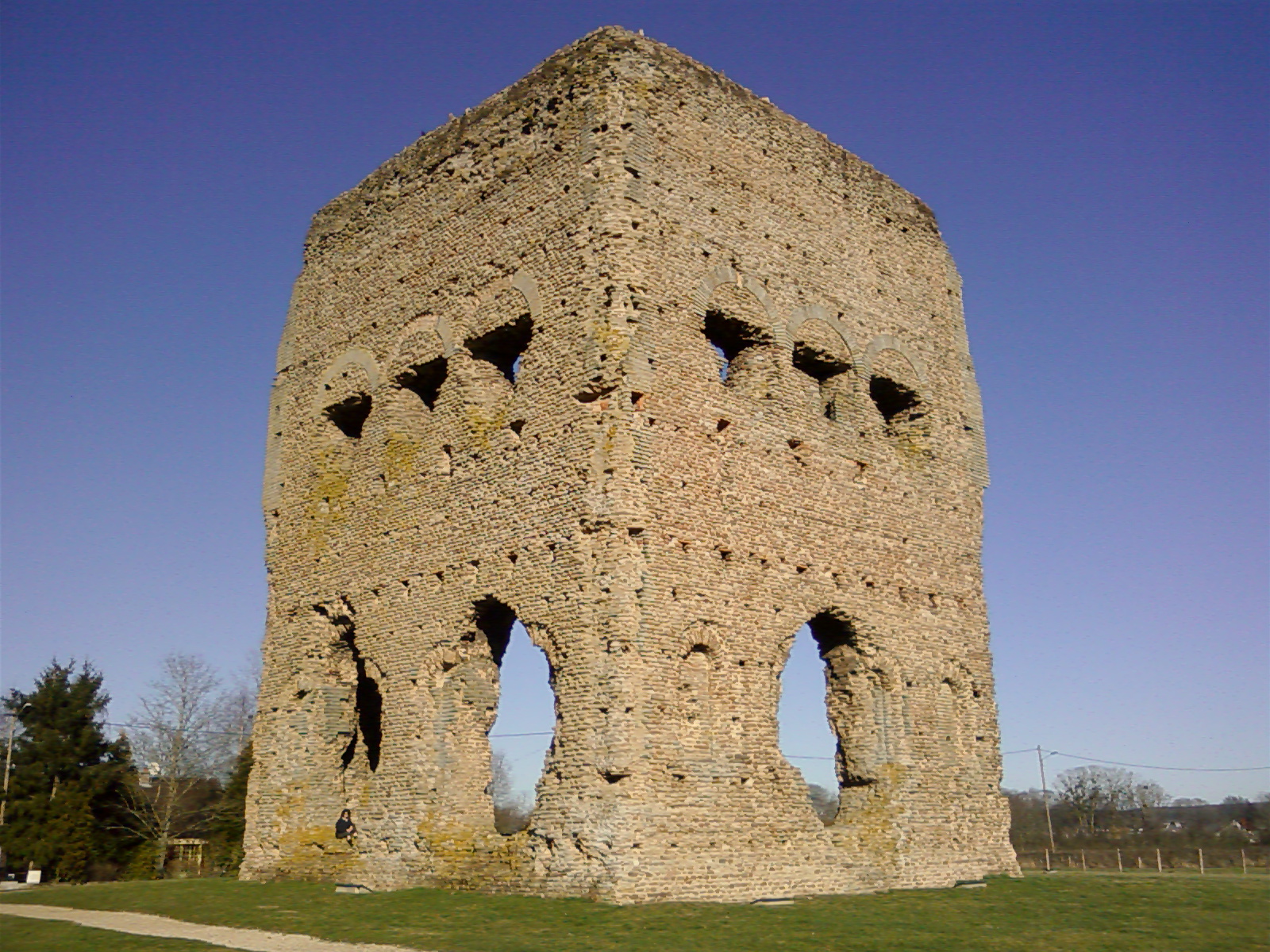
Autun
Autun () is a subprefecture of the Saône-et-Loire department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region of central-eastern France. It was founded during the Principate era of the early Roman Empire by Emperor Augustus as Augustodunum to give a Roman capital to the Gallic people Aedui, who had Bibracte as their political centre. In Roman times the city may have been home to 30,000 to 100,000 people, according to different estimates. Nowadays, the commune has a population of about 15,000. Geography The commune lies in the northwest of the department. History Early history Augustodunum was founded during the reign of the first Roman emperor, Augustus, after whom it was named. It was the civitas "tribal capital" of the Aedui, Continental Celts who had been allies and "brothers" (') of Rome since before Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. Augustodunum was a planned foundation replacing the original oppidum Bibracte, located some away. Several elements of Roman architecture such as wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |