|
Saint Lucy
Lucia of Syracuse (283–304), also called Saint Lucia ( la, Sancta Lucia) better known as Saint Lucy, was a Roman people, Roman Christian martyr who died during the Diocletianic Persecution. She is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church, Catholic, Anglicanism, Anglican, Lutheranism, Lutheran, and Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox churches. She is one of eight women (including Mary, mother of Jesus, the Virgin Mary) explicitly commemorated by Catholics in the Canon of the Mass. Her traditional feast day, known in Europe as Saint Lucy's Day, is observed by Western Christianity, Western Christians on 13 December. Lucia of Syracuse was honored in the Middle Ages and remained a well-known saint in early modern England. She is one of the best known virgin martyrs, along with Agatha of Sicily, Agnes of Rome, Saint Cecilia, Cecilia of Rome and Catherine of Alexandria. Sources The oldest record of her story comes from the fifth-century ''Acts of the Martyrs''. The single fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but some are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and consequently a public cult of veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. While the English word ''saint'' originated in Christianity, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special holiness that many religions attribute to certain people", referring to the Jewish tzadik, the Islamic walī, the Hindu rishi or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
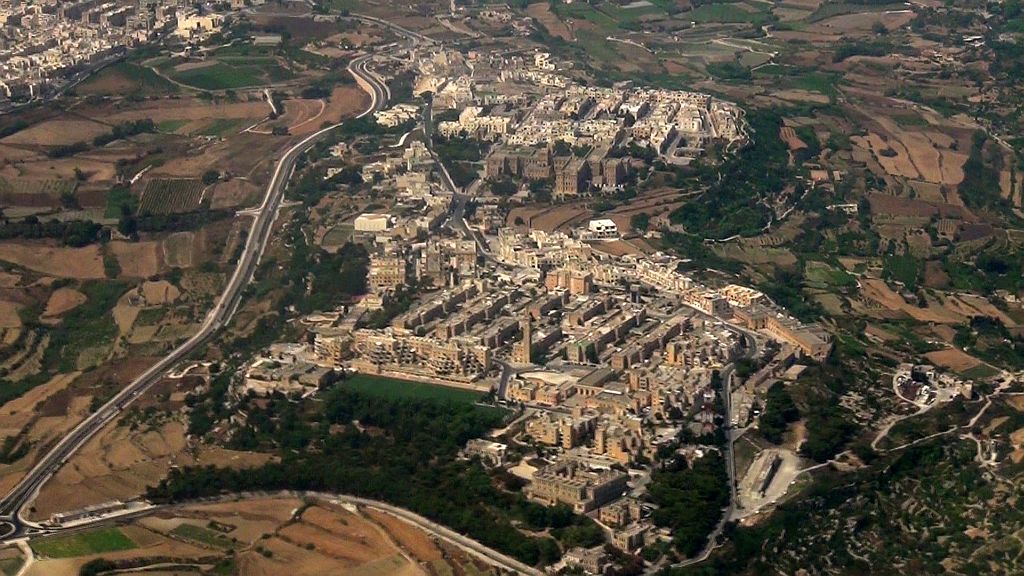
Mtarfa
Mtarfa ( mt, L-Imtarfa) is a small town in the Northern Region of Malta, with a population of 2,572 as of March 2014. It was considered to be a suburb of Rabat until 2000, when it became a separate local council. History A number of historic silos were discovered in Mtarfa in October 1973. In the Roman period, Mtarfa was a suburb of Melite, and it contained a Temple of Proserpina. The ruins of the temple were destroyed in the 17th and 18th centuries and the stones were reused in other buildings. Substantial remains of the suburb itself, including the arrangement of the streets and many tombs, survived until the late 19th century. In 1890, British military barracks began to be built in Mtarfa, destroying most of the Roman remains in the process. A chapel dedicated to St. Lucy was first recorded in 1460, and is still standing to date. It is not currently in regular use. A clock tower, now a prominent landmark of Mtarfa, was built in 1895. A naval hospital, RNH Mtarfa, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Christianity
Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ... (Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Protestantism, Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic Church, Independent Catholicism and Restorationism. The large majority of the world's 2.3 billion Christians are Western Christians (about 2 billion – 1.2 billion Latin Catholic and 800 million Protestant). The original and still major component, the Latin Church, developed under the bishop of Rome. Out of the Latin Church emerged a wide variety of independent Protestant denominations, including Lutheranism and Anglicanism, starting from the Protestant Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Lucy's Day
Saint Lucy's Day, also called the Feast of Saint Lucy, is a Christian feast day observed on 13 December. The observance commemorates Lucia of Syracuse, an early-fourth-century virgin martyr under the Diocletianic Persecution, who according to legend brought food and aid to Christians hiding in the Roman catacombs, wearing a candle lit wreath on her head to light her way and leave her hands free to carry as much food as possible.Barnhill, Carla. "St. Lucy's Day", ''Christian History'', issue 103 Her feast day, which coincided with the shortest day of the year prior to calendar reforms, is widely celebrated as a festival of light. Falling within the Advent season, Saint Lucy's Day is viewed as a precursor of Christmastide, pointing to the arrival of the Light of Christ in the calendar on Christmas Day. Saint Lucy's Day is celebrated most widely in Scandinavia and in Italy, with each emphasising a different aspect of her story. In Scandinavia, where Lucy is called Santa/San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon Of The Mass
The Canon of the Mass ( la, Canon Missæ), also known as the Canon of the Roman Mass and in the Mass of Paul VI as the Roman Canon or Eucharistic Prayer I, is the oldest anaphora used in the Roman Rite of Mass. The name ''Canon Missæ'' was used in the Tridentine Missal from the first typical edition of Pope Pius V in 1570 to that of Pope John XXIII in 1962 to describe the part of the Mass of the Roman Rite that began after the Sanctus with the words ''Te igitur''. All editions preceding that of 1962 place the indication ''"Canon Missae"'' at the head of each page from that point until the end of the Mass; that of 1962 does so only until the page preceding the Pater Noster and places the heading "Ordo Missae" on the following pages. Before 1962 there were divergent opinions about the point where the Canon of the Mass ended. Some considered that it ended where indicated in the 1962 Roman Missal, others where indicated in the earlier editions from 1570 onwards (the end of Mass), oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary, Mother Of Jesus
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jews, Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Saint Joseph, Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is a central figure of Christianity, venerated under titles of Mary, various titles such as virgin or queen, many of them mentioned in the Litany of Loreto. The Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern and Oriental Orthodox, Church of the East, Catholic, Anglican, and Lutheran churches believe that Mary, as mother of Jesus, is the Theotokos, Mother of God. Other Protestant views on Mary vary, with some holding her to have considerably lesser status. The New Testament of the Holy Bible, Bible provides the earliest documented references to Mary by name, mainly in the canonical Gospels. She is described as a young virgin who was chosen by God in Christianity, God to annunciation, conceive Jesus through the Holy Spirit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide . Adherents of Anglicanism are called ''Anglicans''; they are also called ''Episcopalians'' in some countries. The majority of Anglicans are members of national or regional ecclesiastical provinces of the international Anglican Communion, which forms the third-largest Christian communion in the world, after the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. These provinces are in full communion with the See of Canterbury and thus with the Archbishop of Canterbury, whom the communion refers to as its ''primus inter pares'' (Latin, 'first among equals'). The Archbishop calls the decennial Lambeth Conference, chairs the meeting of primates, and is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but some are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and consequently a public cult of veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. While the English word ''saint'' originated in Christianity, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special holiness that many religions attribute to certain people", referring to the Jewish tzadik, the Islamic walī, the Hindu rishi or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocletianic Persecution
The Diocletianic or Great Persecution was the last and most severe persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire. In 303, the emperors Diocletian, Maximian, Galerius, and Constantius issued a series of edicts rescinding Christians' legal rights and demanding that they comply with traditional religious practices. Later edicts targeted the clergy and demanded universal sacrifice, ordering all inhabitants to sacrifice to the gods. The persecution varied in intensity across the empire—weakest in Gaul and Britain, where only the first edict was applied, and strongest in the Eastern provinces. Persecutory laws were nullified by different emperors (Galerius with the Edict of Serdica in 311) at different times, but Constantine and Licinius' Edict of Milan in 313 has traditionally marked the end of the persecution. Christians had been subject to intermittent local discrimination in the empire, but emperors prior to Diocletian were reluctant to issue general laws against th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Martyr
In Christianity Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ..., a martyr is a person considered to have died because of their testimony for Jesus or faith in Christianity, faith in Jesus. In years of the early church, stories depict this often occurring through death by sawing, stoning, crucifixion, Execution by burning, burning at the stake or other forms of torture and capital punishment. The word ''martyr'' comes from the Koine word μάρτυς, ''mártys'', which means "witness" or "testimony". At first, the term applied to Apostles in the New Testament, Apostles. Once Christians started to undergo religious persecution, persecution, the term came to be applied to those who suffered hardships for their faith. Finally, it was restricted to those who had been killed for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman People
grc, Ῥωμαῖοι, , native_name_lang = , image = Pompeii family feast painting Naples.jpg , image_caption = 1st century AD wall painting from Pompeii depicting a multigenerational banquet , languages = , religions = Imperial cult, Roman religion, Hellenistic religion, Christianity , related = Other ancient Italic peoples (including other Latins and the Falisci), other ancient peoples of Italy, other Mediterranean Sea peoples, modern Romance peoples and Greeks The Romans ( la, Rōmānī; grc, Ῥωμαῖοι, Rhōmaîoi) were a cultural group, variously referred to as an ethnicity or a nationality, that in classical antiquity, from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD, came to rule large parts of Europe, the Near East and North Africa through conquests made during the Roman Republic and the later Roman Empire. Originally only referring to the Italic Latin citizens of Rome itself, the meaning of "Roman" underwent conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasmuan, Pampanga
Sasmuan, officially the Municipality of Sasmuan ( pam, Balen ning Sasmuan, tgl, Bayan ng Sasmuan), formerly known by its Spanish name Sexmoán, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 29,076 people. Etymology It was known as Sexmoan until January 15, 1991. The town's former name in Spanish was Sexmoán, as was initially transcribed by Spanish friars. In Spanish, the letter used to be pronounced as a voiceless postalveolar fricative /ʃ/, identical to the digraph in English. It was derived from the ancient Kapampangan rootword ''sasmo'', which means to meet, according to a 17th-century Kapampangan dictionary. ''Sasmuan'' therefore is synonymous with "''pitagmuan''" or "meeting place of the datus" or "meeting point". It was named "Sasmuan" because it is where the Pampangos meet when they were at war with the Chinese in Guagua. In 1991, it was unanimously changed into Sasmuan, since the previous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




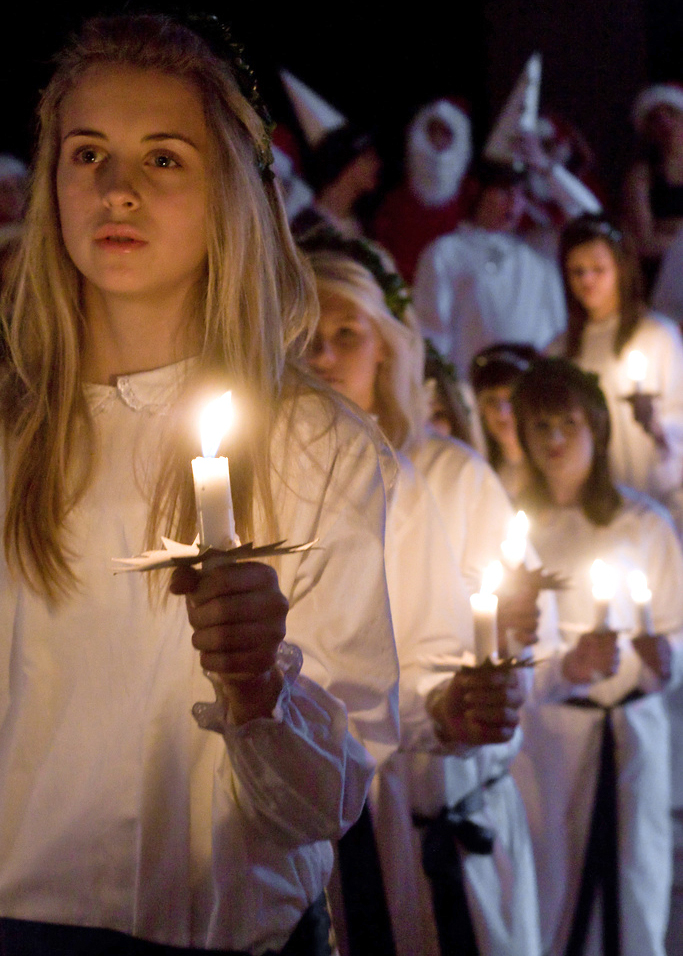



_-_Foto_G._Dall'Orto_28-5-2006.jpg)
.jpg)
