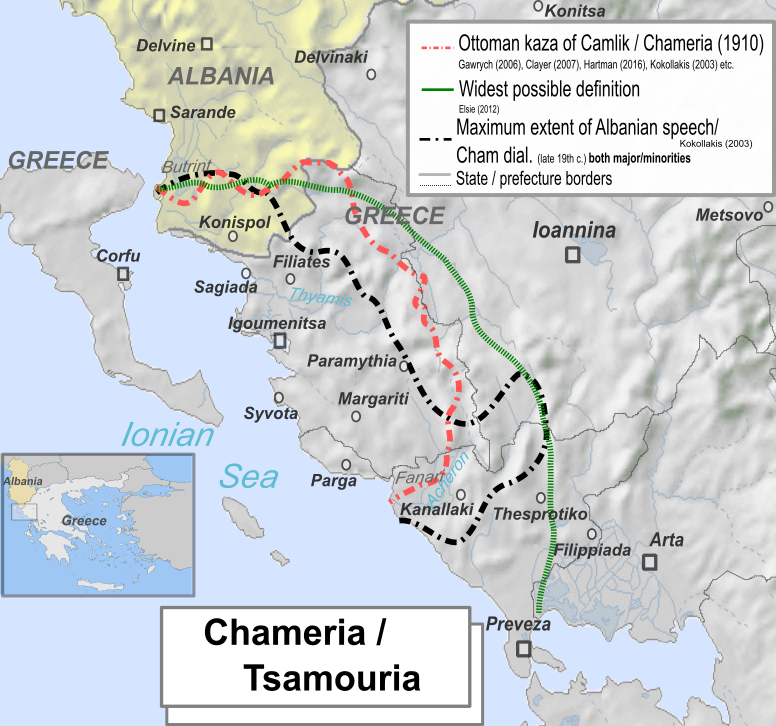
|
Sagiada
Sagiada ( el, Σαγιάδα) is a village and a former municipality in Thesprotia, Epirus, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Filiates, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 87.803 km2. In 2011 its population was 594 for the village and 1,740 for the municipal unit. The seat of the municipality was in Asprokklisi. Location Sagiada stretches between the Ionian Sea to the west and Albania to the north. It is the westernmost point of mainland Greece. The river Thyamis flows into sea 4 km south of the village Sagiada. There are plains in the southern part of the municipal unit, and mountains on the Albanian border. The village Sagiada is 10 km west of Filiates, 15 km northwest of the capital of Thesprotia, Igoumenitsa, and 4 km south of the Albanian town of Konispol. History In the late medieval era (14th century) the fort of Sagiada and its lucrative salt mines was contested among vario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cham Albanians
Cham Albanians or Chams ( sq, Çamë; el, Τσάμηδες, ''Tsámidhes''), are a sub-group of Albanians who originally resided in the western part of the region of Epirus in northwestern Greece, an area known among Albanians as Chameria. The Chams have their own particular cultural identity, which is a mixture of Albanian and Greek influences as well as many specifically Cham elements.See Hasluk, 'Christianity and Islam under the Sultans', London, 1927. A number of Chams contributed to the Albanian national identity and played an important role in starting the renaissance of the Albanian culture in the 19th century. The Chams speak their own dialect of the Albanian language, the Cham Albanian dialect, which is a Southern Tosk Albanian dialect and one of the two most conservative ones; the other being Arvanitika. During the late 1930s Chams suffered from intimidation and persecution under the dictatorship of General Metaxas. Following the Italian occupation of Albania in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filiates
Filiates ( el, Φιλιάτες; ) is a town and a municipality in Thesprotia, Greece. It is located in the northernmost part of the regional unit, bordering western Ioannina regional unit and southern Albania. Name The region of Filiates was known as Cestrine prior to the Ottoman period. The region is named for the ancient town of Cestria, in ancient Epirus, other ancient names for which were Cammania, Ilion, Epirus, Troy, Epirus and Troia and Epirusis; the site of ancient Cestria is probably over the Albanian frontier. The modern name Filiates is the result of the conversion of a surname. According to Eqrem Çabej, Idriz Ajeti and Ali Dhrimo, it contains the Albanian suffix -at, widely used to form toponyms from personal names and surnames. According to Konstantinos Giakoumis, it applies to a certain ''Filios'' with the addition of the Greek ending -άτες or -άταις. Filiates is known as Filat in Albanian, "Filiates (alb. Filat)" and as Filat in Ottoman Turkish. "Filat" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyamis
The Thyamis ( el, Θύαμις), also known as Glykys (Γλυκύς) or Kalamas (Καλαμάς), is a river in the Epirus region of Greece. It flows into the Ionian Sea. It is long, and its drainage area is about , over 99% of which on Greek territory. The names of the Chameria region (''Tsamouria'' in Greek), as well as the Chams, derive from the river's name. Thyamis in ancient Greece was mentioned by Pausanias as forming the boundary between Thesprotis and Kestrine. In addition, Suda and Ptolemaeus mentioned it. Some Renaissance scholars believed that the English River Thames owed its name to the River Thyamis, as early Celtic tribes were thought to have migrated from the Epirus region to England. While this belief influenced the modern spelling of the English river's name, it is no longer regarded as credible. Geography The source of the river is near the village Kalpaki, in the northwestern part of the Ioannina regional unit. It flows south at first, and turns southwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thesprotia
Thesprotia (; el, Θεσπρωτία, ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the Epirus region. Its capital and largest town is Igoumenitsa. Thesprotia is named after the Thesprotians, an ancient Greek tribe that inhabited the region in antiquity. History Thesprotia was part of the proto-Greek region in the late Bronze Age in which Greek archaic toponyms are were densely found. In antiquity, the territory of modern Thesprotia was inhabited by the ancient Greek tribe of Thesprotians and was bordered by the neighboring regions of Molossia to the north and Chaonia to the east. Thesprotia was part of the Epirote League before it was annexed by Rome where it became part of the Roman province of Epirus. After the fragmentation of the Roman Empire into East and West, it was part of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire until the late Middle Ages, except for a period of Bulgarian rule in the 9th-11th centuries. In c. 1430 it fell to the Ottomans. From the 8th-9th unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
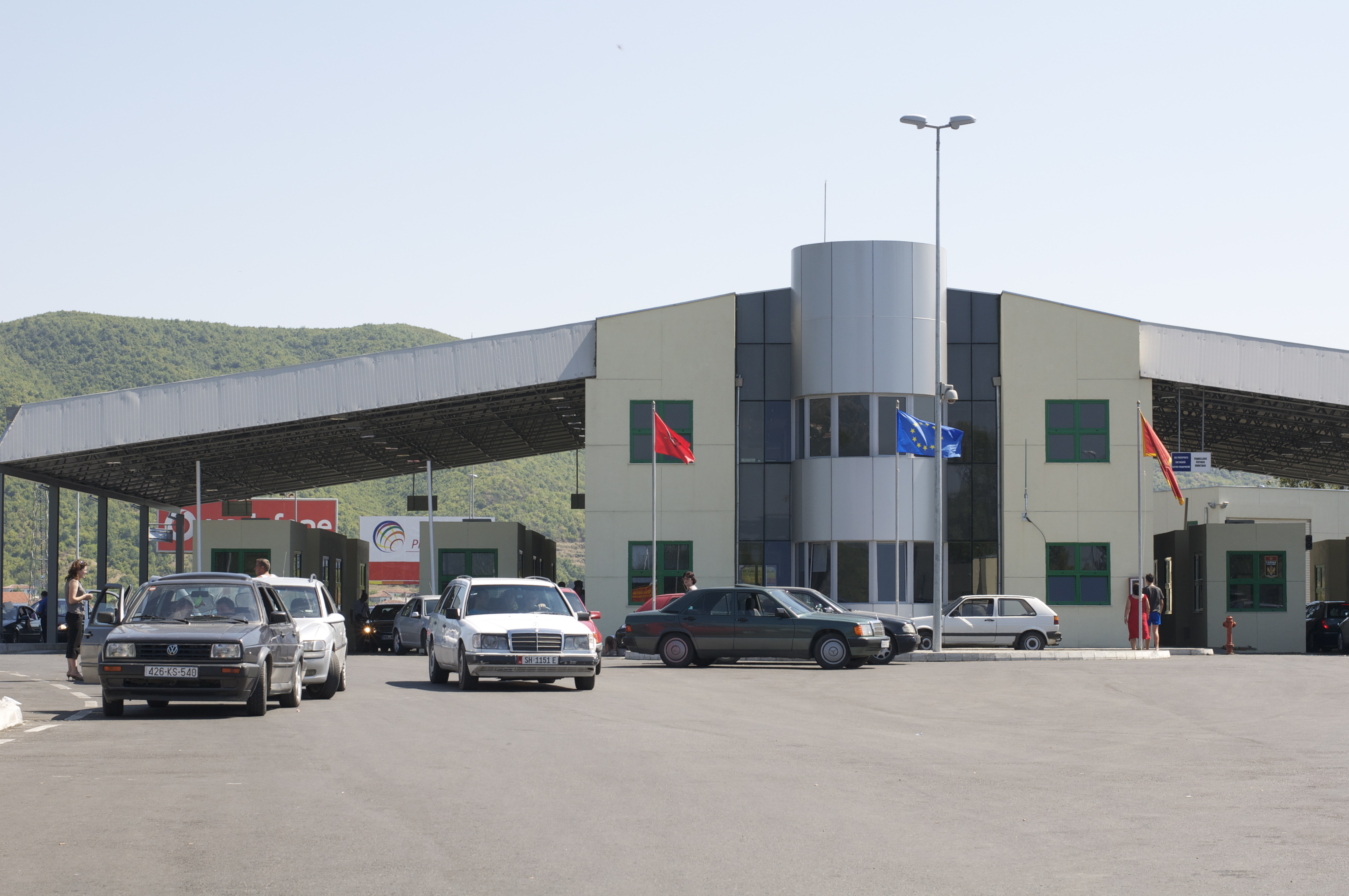
Border Crossings Of Albania
Border crossings ( sq, Vendkalimet kufitare) in the Republic of Albania are defined as boundary checkpoints that serve to control the flow of people and goods from neighbouring countries to and from Albania. These checkpoints are administered by the border police authorities that record the entry and exit of each person and vehicle followed by the customs authorities that record the entry and exit of goods and cash. Albania currently has 22 operational land border crossings and shares borders with Montenegro, Kosovo (116.3 km), North Macedonia (186.1 km), and Greece. This article outlines a complete list of Albania's international border crossings, including land, sea and air entry points. History During the communist period in Albania, very few people were allowed to leave the country (usually only diplomats) and would also be required to have written permission to do so. Visitors entering the country from outside for any reason, tourism or otherwise, were immediately suspect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konispol
Konispol ( sq-definite, Konispoli) is the southernmost town in Albania. It sits one kilometer away from the Border crossings of Albania, Albanian-Greek border. The settlement is inhabited by Muslim Cham Albanians. Konispol is the modern centre of the Cham Albanian community in Albania. The main economic interests of Konispol are agriculture and viticulture. The town is the seat of the southernmost administrative unit in Albania, the Municipality of Konispol ( sq, Bashkia Konispol). It was formed during the 2015 local government reform by the merger of the former municipalities of Konispol, Markat and Xarrë. The total population is 8,245 (2011 census), in a total area of 226.26 km2. The population of the former Konispol municipality at the 2011 census was 2,123. The former Konispol municipal unit (pre-2015) consisted of the town Konispol and the village Çiflik. The new larger municipality of Konispol contains settlements that are inhabited by Albanians who form the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expulsion Of Cham Albanians
The expulsion of Cham Albanians from Greece was the forced migration and ethnic cleansing of thousands of Cham Albanians from settlements of Chameria in Thesprotia, Greece - after the Second World War to Albania, at the hands of elements of the Greek Resistance: the National Republican Greek League (EDES) (1944) and EDES veteran resistance fighters (1945);Evergeti, Venetia; Hatziprokopiou, Panos and Nicolas Prevelakis (2014)Greece. In Cesari, Jocelyn (ed). ''The Oxford Handbook of European Islam''. Oxford University Press. p. 352. the expulsion was encouraged by the Allied mission under Colonel C.M. Woodhouse.Document 89/57/45 PRO/FO 371/48094. Cited in: Sozos Ioannis; Baltsiotis, Lambros (2018) ''Οι Τσάμηδες στην Ήπειρο (1940 - 1944)'' Panteion University The causes of the expulsion were multifaceted and remain a matter of debate among historians. Modern historiographical narratives argue that the causes involved the pre-existing Greek policies which tar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timar
A timar was a land grant by the sultans of the Ottoman Empire between the fourteenth and sixteenth centuries, with an annual tax revenue of less than 20,000 akçes. The revenues produced from the land acted as compensation for military service. A holder of a timar was known as a timariot. If the revenues produced from the timar were from 20,000 to 100,000 ''akçes'', the land grant was called a ''zeamet'', and if they were above 100,000 ''akçes'', the grant would be called a ''hass''.Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 99 Timar system In the Ottoman Empire, the timar system was one in which the projected revenue of a conquered territory was distributed in the form of temporary land grants among the Sipahis (cavalrymen) and other members of the military class including Janissaries and other kuls (slaves) of the sultan. These prebends were given as compensation for annual military service, for which they received no pay. In rare circumstances women could become timar holders. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athanasios Psalidas
Athanasios Psalidas ( el, Αθανάσιος Ψαλίδας; 1767–1829), was a Greek author, scholar and one of the most renowned figures of the modern Greek Enlightenment. Life Early years and diaspora Psalidas was born at 1767 in Ioannina, where he completed ground level education. He continued his studies in Russian Empire (now Ukraine, Poltava) in Slavic Poltava Seminary (1785–1787) and in Austria (1787–1795). In 1791 he published his first work, ''Real bliss'' (Αληθής Ευδαιμονία), written in both Greek and Latin. With this work he reestablished fundamental theoretical positions on the existence of God, immortality, afterlife, freedom of man, and the concept of the limits of freedom. During his studies, Psalidas worked in several Greek editorial companies and printing houses that were established in Vienna, notably the newspaper ''Ephimeris'' ( el, Εφημερίς, "newspaper" in Greek), published in Vienna since 1791. During the same period he published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Pasha Of Ioannina
Ali Pasha of Ioannina (1740 – 24 January 1822), was an Albanian ruler who served as pasha of a large part of western Rumelia, the Ottoman Empire's European territories, which was referred to as the Pashalik of Yanina. His court was in Ioannina, and the territory he governed incorporated central and southern Albania, most of Epirus and the western parts of Thessaly and Greek Macedonia. Ali had three sons: Muhtar Pasha, who served in the 1809 war against the Russians, Veli Pasha, who became Pasha of the Morea Eyalet and Salih Pasha, governor of Vlorë. Ali first appears in historical accounts as the leader of a band of brigands who became involved in many confrontations with Ottoman state officials in Albania and Epirus. He joined the administrative-military apparatus of the Ottoman Empire, holding various posts until 1788 when he was appointed pasha, ruler of the sanjak of Ioannina. His diplomatic and administrative skills, his interest in modernist ideas and concepts, his pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epirus (region)
Epirus (; el, Ήπειρος, translit=Ípiros, ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region in northwestern Greece.Π.Δ. 51/87 “Καθορισμός των Περιφερειών της Χώρας για το σχεδιασμό κ.λ.π. της Περιφερειακής Ανάπτυξης” (''Determination of the Regions of the Country for the planning etc. of the development of the regions, Efimeris tis Kyverniseos ΦΕΚ A 26/06.03.1987'' It borders the regions of Western Macedonia and Thessaly to the east, West Greece to the south, the Ionian Sea and Ionian Islands to the west and Albania to the north. The region has an area of about . It is part of the wider historical region of Epirus, which overlaps modern Albania and Greece but lies mostly within Greek territory. Geography and ecology Greek Epirus, like the region as a whole, is rugged and mountainous. It comprises the land of the ancient Molossians and Thesprotians and a small part of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Ioannina
The University of Ioannina (UoI; Greek: Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων, ''Panepistimio Ioanninon'') is a university located 5 km southwest of Ioannina, Greece. The university was founded in 1964, as a charter of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki and became an independent university in 1970. As of 2017, there is a student population of 25,000 enrolled at the university (21,900 at the undergraduate level and 3,200 at the postgraduate level) and 580 faculty members, while teaching is further supplemented by 171 Teaching Fellows and 132 Technical Laboratory staff. The university Administrative Services are staffed with 420 employees. University of Ioannina is one of the leading academic institutions in Greece.UniversityRankings.ch (SERI) 2015 - University of IoanninRetrieved in 2016-02-03. History The efforts for the establishment of a University in Ioannina and in the wider area were apparent in the last years before the revolution. At that time, promine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |