|
Sadz Dialect
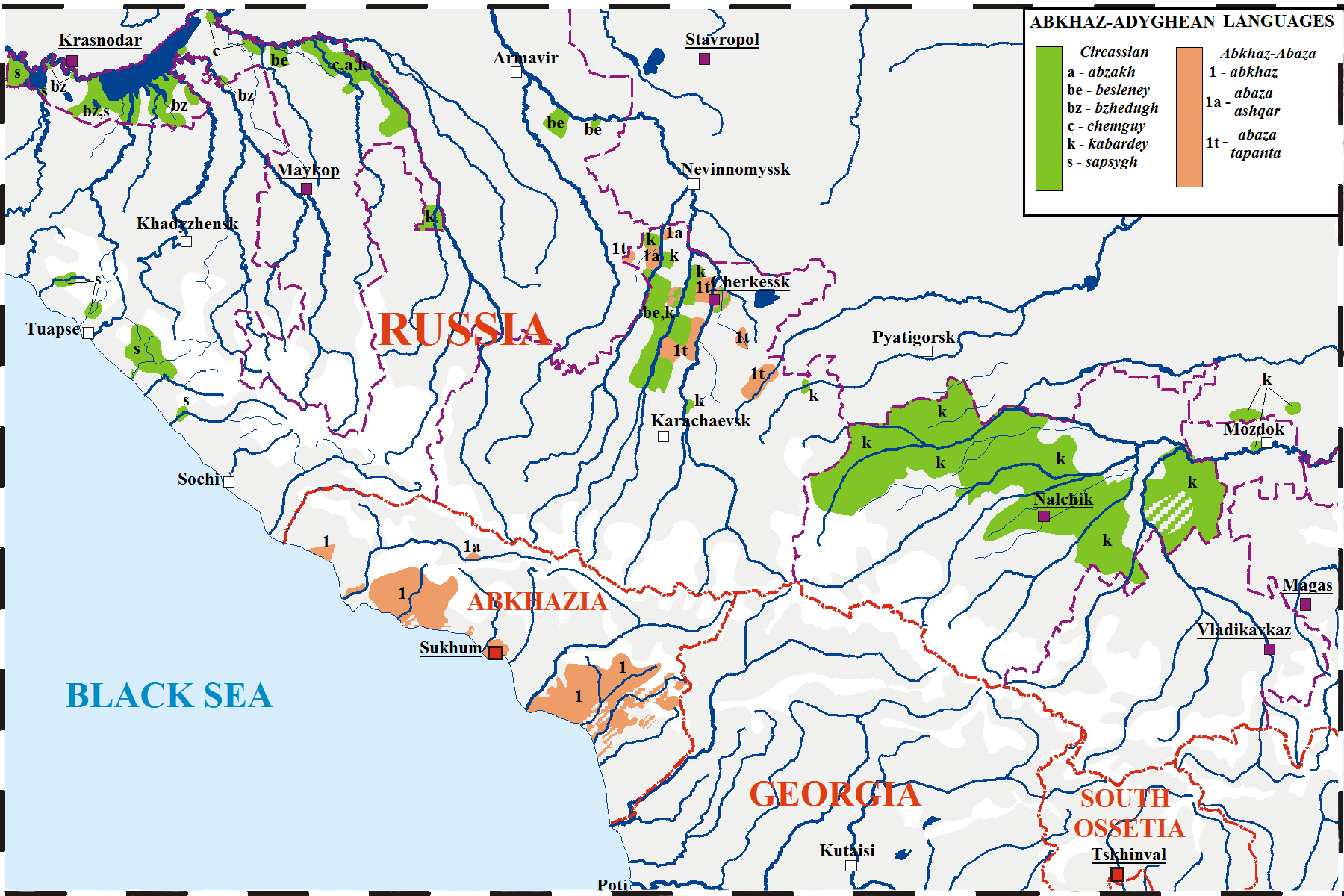
Abkhaz ( ; ), sometimes spelled Abxaz and also known as Abkhazian, is a Northwest Caucasian language most closely related to Abaza. It is spoken mostly by the Abkhaz people. It is one of the official languages of Abkhazia, where around 100,000 people speak it. Furthermore, it is spoken by thousands of members of the Abkhazian diaspora in Turkey, Georgia's autonomous republic of Adjara, Syria, Jordan, and several Western countries. 27 October is the day of the Abkhazian language in Georgia. Classification Abkhaz is a Northwest Caucasian language and is thus related to Adyghe. The language of Abkhaz is especially close to Abaza, and they are sometimes considered dialects of the same language,''B. G. Hewitt Abkhaz 1979;'' page 1. Abazgi, of which the literary dialects of Abkhaz and Abaza are simply two ends of a dialect continuum. Grammatically, the two are very similar; however, the differences in phonology are substantial, it also contains elements characteristic of Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abkhazians
Abkhazians (russian: Абхазы), or Abkhazs ( ab, Аԥсуаа, Aṕswaа, ), are a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian ethnic group, mainly living in Abkhazia, a disputed region on the northeastern coast of the Black Sea. A large Abkhaz diaspora population resides in Turkey, the origins of which lie in the population movements from the Caucasus in the late 19th century. Many Abkhaz also live in other parts of the former Soviet Union, particularly in Russia and Ukraine. Ethnology The Abkhaz language belongs to the isolate Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian language family, also known as Abkhaz–Adyghe or North Pontic family, which groups the dialectic continuum spoken by the Abazins, Abaza–Abkhaz (Abazgi) and Circassians, Adyghe ("Circassians" in English). Abkhazians are closely ethnically related to Circassians. Classical sources speak of several tribes dwelling in the region, but their exact identity and location remain controversial due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adyghe Language
Adyghe ( or ; ady, Адыгабзэ, Adygabzə, ), also known as West Circassian ( ady, link=no, кӏахыбзэ, khaxybzə), is a Northwest Caucasian language spoken by the western subgroups of Circassians. It is spoken mainly in Russia, as well as in Turkey, Jordan, Syria and Israel, where they settled after the Circassian genocide. It is closely related to the Kabardian (East Circassian) language, though some reject the distinction between the two languages in favor of both being dialects of a unitary Circassian language. The literary language is based on the Temirgoy dialect. Adyghe and Russian are the two official languages of the Republic of Adygea in the Russian Federation. There are around 128,000 speakers of Adyghe in Russia, almost all of them native speakers. In total, some 300,000 speak it worldwide. The largest Adyghe-speaking community is in Turkey, spoken by the diaspora from the Russian–Circassian War (–1864). In addition, the Adyghe language is spoke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hendek
Hendek is a town and a district of Sakarya Province in the Marmara region of Turkey. The municipality was founded in 1907. The mayor of the city is Ali İnci ( AKP). Notable natives * Gaffar Okkan (1952–2001), assassinated police chief * Süleyman Seba (1926–2014), former football player and long-time president of Beşiktaş J.K. See also *Hacıkışla, Hendek Hacıkışla is a village in Hendek district, Sakarya Province of Turkey, with a (2000) population of about 719. Population Most of the people in Hacıkışla are from the Black Sea The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the A ... * Elmayı Top Top Yapalım References External linksHendek Infos [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinop, Turkey
Sinop, historically known as Sinope (; gr, Σινώπη, Sinōpē), is a city on the isthmus of İnce Burun (İnceburun, Cape Ince), near Cape Sinope (Sinop Burnu, Boztepe Cape, Boztepe Burnu) which is situated on the northernmost edge of the Turkish side of the Black Sea coast, in the ancient region of Paphlagonia, in modern-day northern Turkey. The city serves as the capital of Sinop Province. History Over a period of approximately 2,500 years, Sinope has at various times been settled by Colchians, Greeks (in the late 7th, late 5th, and 4th–3rd centuries BC), by Romans in the mid-1st century BC, and by Turkic people beginning in the 12th century. In the 19th and 20th centuries it was also settled by the '' muhacir'' who immigrated from the Balkans and Caucasus. Evidence for Hittite Kingdom settlement along the Black Sea's southern shore remains murky. Researchers in the 1940s and 50s debated whether the "Great Sea", mentioned on the Boghazkoy tablets describing war b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Düzce
Düzce is the capital city of Düzce Province, the eighty-first Province in Turkey. The population is 367,087 and in 2009 was 125,240, an increase from 61,878 in 1990. Overview Düzce is the eighty-first and the newest province of Turkey. It is situated on the Black Sea between the Capital Ankara and Istanbul. It was greatly affected by both the Marmara and Düzce earthquakes of 1999. Ankara is 240 km to the east and Istanbul is 228 km to the west. Road D-100 passes through Düzce, while the TEM highway passes around it. Düzce is on the plateau of the West Black Sea coast. It is bordered to the west by Sakarya, to the northeast by Zonguldak, and to the east by Bolu. It opens to the Black Sea with the valley of Büyük Melen on the northwest. Düzce is 23 km across from east to west, and 20 km from north to south. Nearby are also some tourist centers and popular attractions such as Abant, Kartalkaya, Yedigoller, Golcuk and Akcakoca. The main agric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adapazarı
Adapazarı () is a city in northwestern Turkey and the central district of Sakarya Province. The province itself was originally named Adapazarı as well. Adapazarı is a part of the densely populated region of the country known as the Marmara Region. In 2014, the city had a population of 462,087. History The history of Adapazarı dates back to 378 BC, when it was called Agrilion (Ἀγρίλιον in Greek). Ancient settlers included Phrygians, Bithynians, Cimmerians, Lydians, Greeks, and Persians, but Adapazarı got its identity from the ancient Hellenistic, Romans, and Greek Byzantine rulers. After Alexander the Great's conquests, the Persians were forced out of the region. One of the most important remains of historical significance is the Justinianus Bridge ( tr, Beş Köprü) built by Byzantine Emperor Justinian in 533 AD. Historically, it was situated on the old military road from Constantinople (now Istanbul) to the east, connected in Late Antiquity by the important Sang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bzyp River
The Bzyb or Bzipi ( or ; ka, ბზიფი, Bzipi; ab, Бзыҧ, Bzyṗ; russian: Бзыбь, Bzybj) is one of the two largest rivers of Abkhazia, along with the Kodori, and the twelfth longest river in Georgia. The river valley has rich biodiversity of herbaceous garden plants, particularly in the gorge section in the upper reaches where the most prominent and colourful bellflower ' with profuse growth of 100 flowers per plant is given the name, the "Queen of the Abkhazian flora". During 1904-1917 it served as the border between Russian Empire's Sukhumi Okrug and Black Sea Governorate. Etymology It is significant, that "Bzipi" is a comparatively new name of the river. Until the 1820s it was called "Kapoetis Tskali" (literally meaning "Water of Kapoeti"). This is a Georgian name and comes from the name of the fish "Kapoeti". Fish Kapoeti belongs to the trout-salmon family. This large variety of trout dwells in this river. It has also been said that "Bzyp" is associated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhumi
Sukhumi (russian: Суху́м(и), ) or Sokhumi ( ka, სოხუმი, ), also known by its Abkhaz name Aqwa ( ab, Аҟәа, ''Aqwa''), is a city in a wide bay on the Black Sea's eastern coast. It is both the capital and largest city of the Republic of Abkhazia, which has controlled it since the Abkhazia war in 1992–93. However, internationally Abkhazia is considered part of Georgia. The city, which has an airport, is a port, major rail junction and a holiday resort because of its beaches, sanatoriums, mineral-water spas and semitropical climate. It is also a member of the International Black Sea Club. Sukhumi's history can be traced to the 6th century BC, when it was settled by Greeks, who named it Dioscurias. During this time and the subsequent Roman period, much of the city disappeared under the Black Sea. The city was named Tskhumi when it became part of the Kingdom of Abkhazia and then the Kingdom of Georgia. Contested by local princes, it became part of the Otto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubykh Language
Ubykh or Päkhy was a Northwest Caucasian language once spoken by the Ubykh tribe of Circassians who originally lived along the eastern coast of the Black Sea before being deported ''en masse'' to Turkey in the Circassian genocide. The Ubykh language was ergative and polysynthetic, with a high degree of agglutination, with polypersonal verbal agreement and a very large number of distinct consonants but only two phonemically distinct vowels. With around eighty consonants, it had one of the largest inventories of consonants in the world, and the largest number for any language without clicks. The name Ubykh is derived from (), its name in the Adyghe language. It is known in linguistic literature by many names: variants of Ubykh, such as ''Ubikh'', ( French); and its Germanised variant (from Ubykh ). Major features Ubykh is distinguished by the following features, some of which are shared with other Northwest Caucasian languages: * It is ergative, making no syntactic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Circassian Language
Proto-Circassian (or Proto-Adyghe–Kabardian) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Adyghean and Kabardian languages. Phonology Consonants The consonant system is reconstructed with a four-way phonation contrast in stops and affricates, and a two-way contrast in fricatives. Aspirated consonants to plain In the Proto-Circassian there was a series of aspirated consonants that survived in the Shapsug and Bzhedugh dialect while they became plain consonants in the other dialects. * → * → * → * → * → * → * → * → * → * → Plain voiceless consonants to voiced In the Proto-Circassian there was a series of tense consonants that became voiced in the eastern dialects. * → * → * → * → * → / * → * → / * → / Velar consonants to palato-alveolar In the Proto-Circassian language there exist a palatalized voiced velar stop , a palatalized aspirated voiceless velar stop , a palataliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Northwest Caucasian Language
Proto-Northwest Caucasian (sometimes abbreviated PNWC), also ''Proto-Adyghe-Abazgi'' or Proto-Adyghe-Abkhaz, is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Northwest Caucasian languages. Phonology Consonants # In Circassian and Abkhaz, gʷǝ is heart and in Ubykh it's gʲǝ. The most noticeable changes are: *The uvular consonants (/χ/ /ʁ/ /χʷ/ /ʁʷ/) become pharyngeal consonants (/ħ/ /ʕ/ /ħʷ/ /ʕʷ/) in the Proto-Abazgi language. Grammar Numbers Words See also * Proto-Circassian language * Proto-Abazgi language References {{Reflist *STAROSTIN, Sergei A.; NIKOLAYEV, Sergei L. (1994). A North Caucasian Etymological DictionaryPreface External links Abkhaz-Adyghe etymology Northwest Caucasian The Northwest Caucasian languages, also called West Caucasian, Abkhazo-Adyghean, Abkhazo-Circassian, Circassic, or sometimes ''Pontic languages'' (from the historical region of Pontus, in contrast to ''Caspian languages'' for the Northeast Cauc ... Northwest Caucasian l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





