|
Sacabaya
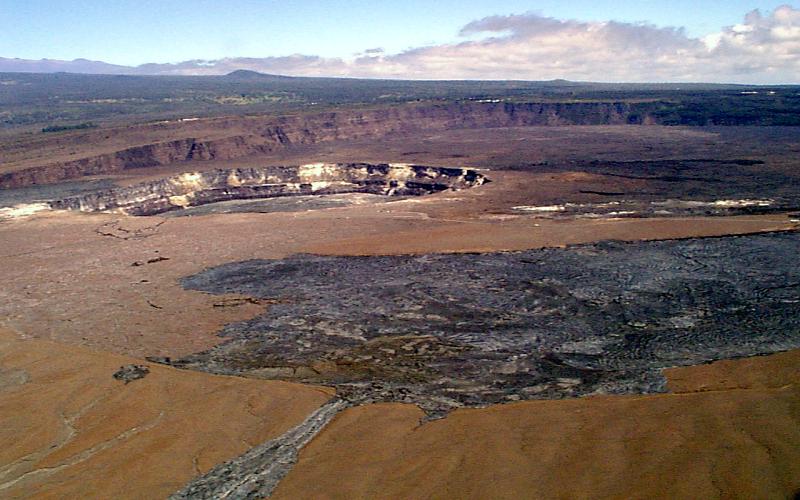
Sacabaya (also known as Tambo Quemado) is a pyroclastic shield in Bolivia. It is located on the Altiplano near to the Rio Lauca. The volcano is composed of ignimbrite, which has formed a shield. The shield is capped by an area of vents which has many overlapping craters, and is elongated in shape. At the southern end lies the youngest of the craters which has a lava dome within it. Sacabaya has a diameter of and rises to the summit; the edifice is covered by material produced during explosive activity. The summit contains a north-south row of several pit craters, each with a diameter of about , and one of which contains a lava dome In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on .... Material from the volcano has been transported away by wind. The volcano may be of Holocene age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Bolivia
The country of Bolivia hosts numerous activeIn vulcanology and this article active volcanoes are those with Holocene eruption, that means eruptions in the last 10,000 years. and extinct volcanoes across its territory. The active volcanoes are in western Bolivia making up the Cordillera Occidental, the western limit of the Altiplano plateau. Many of the active volcanoes are international mountains shared with Chile. All Cenozoic volcanoes of Bolivia are part of the Central Volcanic Zone (CVZ) of the Andean Volcanic Belt that results due to processes involved in the subduction of Nazca Plate under the South American Plate. The Central Volcanic Zone is a major upper Cenozoic volcanic province. Apart from Andean volcanoes the geology of Bolivia host the remnants of ancient volcanoes around the Precambrian Guaporé Shield in the eastern part of the country. Image:Nevado Sajama.jpg, Sajama, a stratovolcano considered extinct. Image:Licancabur Green Lake.jpg, View of Licancabur. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroclastic Shield
In volcanology, a pyroclastic shield or ignimbrite shield is an uncommon type of shield volcano. Unlike most shield volcanoes, pyroclastic shields are formed mostly of pyroclastic and highly explosive eruptions rather than relatively fluid basaltic lava issuing from vents or fissures on the surface of the volcano. They typically display low-angle flank slopes and often have a central caldera caused by large eruptions. Lava is commonly extruded after explosive activity has ended. The paucity of associated Plinian fall deposits indicates that pyroclastic shields are characterized by low Plinian columns. Pyroclastic shields are commonly known to form in the Central Andes of South America, as well as in Melanesia (the island of Bougainville alone has two). There are also pyroclastic shields in Africa, such as Emi Koussi in Chad. Examples * Ambrym, Vanuatu * Apoyeque, Nicaragua * Masaya, Nicaragua * Billy Mitchell, Bougainville, Papua New Guinea * Emi Koussi, Chad * Laguna Colora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroclastic Shield
In volcanology, a pyroclastic shield or ignimbrite shield is an uncommon type of shield volcano. Unlike most shield volcanoes, pyroclastic shields are formed mostly of pyroclastic and highly explosive eruptions rather than relatively fluid basaltic lava issuing from vents or fissures on the surface of the volcano. They typically display low-angle flank slopes and often have a central caldera caused by large eruptions. Lava is commonly extruded after explosive activity has ended. The paucity of associated Plinian fall deposits indicates that pyroclastic shields are characterized by low Plinian columns. Pyroclastic shields are commonly known to form in the Central Andes of South America, as well as in Melanesia (the island of Bougainville alone has two). There are also pyroclastic shields in Africa, such as Emi Koussi in Chad. Examples * Ambrym, Vanuatu * Apoyeque, Nicaragua * Masaya, Nicaragua * Billy Mitchell, Bougainville, Papua New Guinea * Emi Koussi, Chad * Laguna Colora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square patchwork with the (top left to bottom right) diagonals forming colored stripes (green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, white, green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, from top right to bottom left) , other_symbol = , other_symbol_type = Dual flag: , image_coat = Escudo de Bolivia.svg , national_anthem = " National Anthem of Bolivia" , image_map = BOL orthographic.svg , map_width = 220px , alt_map = , image_map2 = , alt_map2 = , map_caption = , capital = La Paz Sucre , largest_city = , official_languages = Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S latitude), and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto and La Paz. The Altiplano plateau is the world's second-highest after the Tibetan plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes. The Andes Mountains are the highest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altiplano
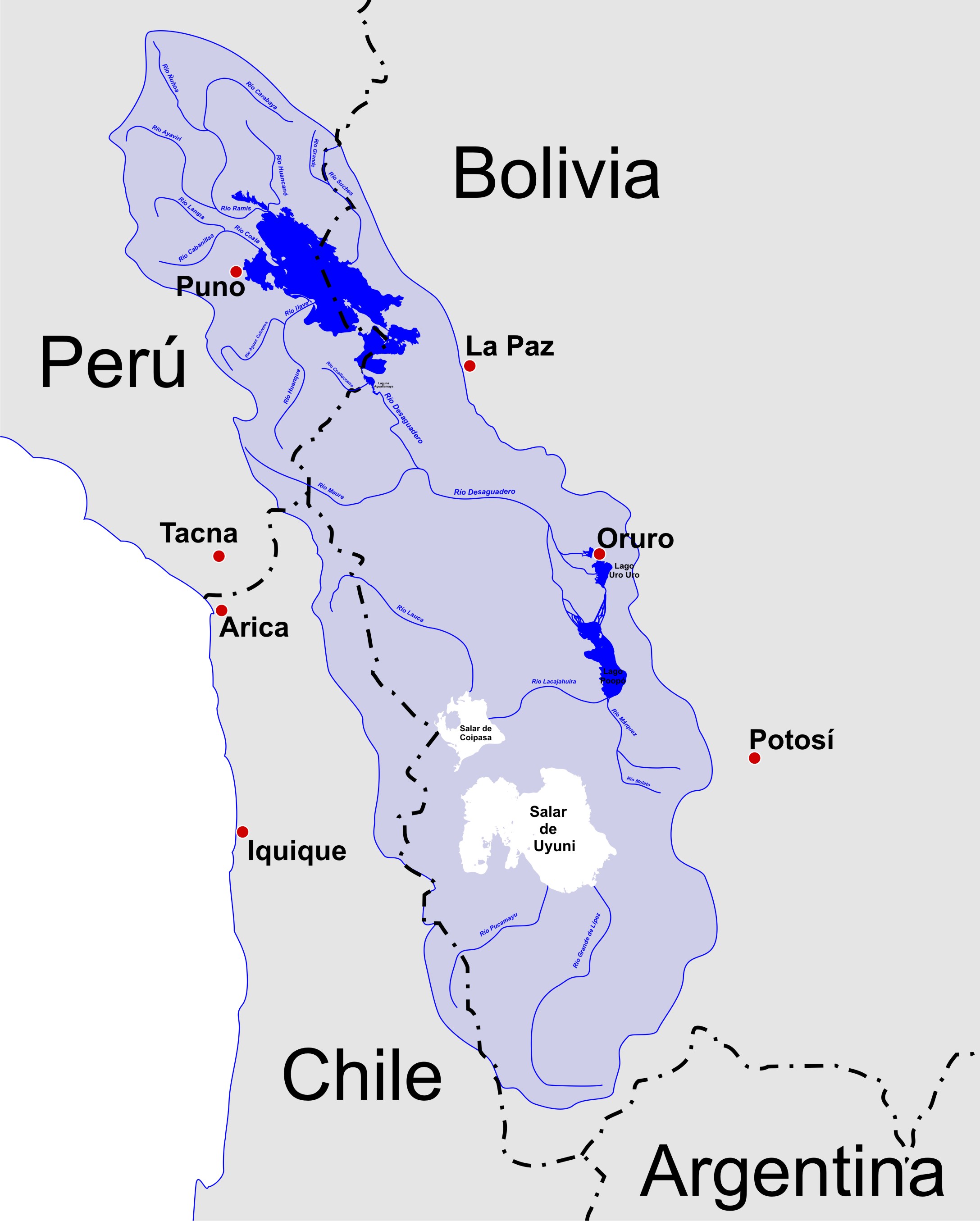
The Altiplano (Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechua and Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north-south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile. There are on the plateau several cities in each of these three nations, including El Alto, La Paz, Oruro, and Puno. The northeastern part of the Altiplano is more humid than the southwestern part, which has several salares (salt flats), due to its aridity. At the Bolivia–Peru border lies Lake Titicaca, the largest lake in South America. Farther south, in Bolivia, there was until recently a lake, Lake Poopó, but by December 2015 it had completely dried up, and was declared defunct. It is unclear whether that lake, which had been the second-largest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Lauca
The Lauca River is a binational river. It originates in the Chilean Altiplano of the Arica and Parinacota Region, crosses the Andes and empties into Coipasa Lake in Bolivia. The upper reach of the river lies within the boundaries of Lauca National Park in the Parinacota Province. Lauca River receives waters from a group of lakes known as Quta Qutani through the ''Desaguadero River''. In this area there is a type of marsh known as Parinacota wetlands, in which converge several streams, being the more important the river just mentioned, which has a variable flow rate ranging from 100 to 560 L/s, and an average of 260 L/s. From its source in the Parinacota wetlands the river flows west. The spurs of the ''Cordillera Central'' (also known as ''Chapiquiña'') form an obstacle impossible to pass through, forcing the river's course southward. In the vicinity of Wallatiri Guallatiri is a high volcano in Chile. It is located southwest of the Nevados de Quimsachata volcanic group a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignimbrite
Ignimbrite is a type of volcanic rock, consisting of hardened tuff. Ignimbrites form from the deposits of pyroclastic flows, which are a hot suspension of particles and gases flowing rapidly from a volcano, driven by being denser than the surrounding atmosphere. New Zealand geologist Patrick Marshall (1869-1950) coined the term ''ignimbrite'' from the Latin ''igni-'' [fire] and ''imbri-'' [rain]. Ignimbrites are made of a very poorly sorted mixture of volcanic ash (or tuff when Lithification, lithified) and pumice lapilli, commonly with scattered lithic fragments. The ash is composed of glass shards and crystal fragments. Ignimbrites may be loose and unconsolidated, or lithified (solidified) rock called lapilli-tuff. Near the volcanic source, ignimbrites often contain thick accumulations of lithic blocks, and distally, many show meter-thick accumulations of rounded cobbles of pumice. Ignimbrites may be white, grey, pink, beige, brown, or black depending on their composition and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lava Dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on Earth are lava dome forming. The geochemistry of lava domes can vary from basalt (e.g. Semeru, 1946) to rhyolite (e.g. Chaiten, 2010) although the majority are of intermediate composition (such as Santiaguito, dacite-andesite, present day) The characteristic dome shape is attributed to high viscosity that prevents the lava from flowing very far. This high viscosity can be obtained in two ways: by high levels of silica in the magma, or by degassing of fluid magma. Since viscous basaltic and andesitic domes weather fast and easily break apart by further input of fluid lava, most of the preserved domes have high silica content and consist of rhyolite or dacite. Existence of lava domes has been suggested for some domed structures on the Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pit Crater
A pit crater (also called a subsidence crater or collapse crater) is a depression formed by a sinking or collapse of the surface lying above a void or empty chamber, rather than by the eruption of a volcano or lava vent. Pit craters are found on Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, and the Moon. Pit craters are often found in a series of aligned or offset chains and in these cases, the features is called a pit crater chain. Pit crater chains are distinguished from catenae or crater chains by their origin. When adjoining walls between pits in a pit crater chain collapse, they become troughs. In these cases, the craters may merge into a linear alignment and are commonly found along extensional structures such as fractures, fissures and graben. Pit craters usually lack an elevated rim as well as the ejecta deposits and lava flows that are associated with impact craters.Okubo, Chris, and Stephen Martel. "Pit crater formation on Kilauea volcano, Hawaii." Journal of Volcanology and Geotherm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumarole
A fumarole (or fumerole) is a vent in the surface of the Earth or other rocky planet from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcanic activity, but fumarole activity can also precede a volcanic eruption and has been used for eruption prediction. Most fumaroles die down within a few days or weeks of the end of an eruption, but a few are persistent, lasting for decades or longer. An area containing fumaroles is known as a fumarole field. The predominant vapor emitted by fumaroles is steam, formed by the circulation of groundwater through heated rock. This is typically accompanied by volcanic gases given off by magma cooling deep below the surface. These volcanic gases include sulfur compounds, such as various sulfur oxides and hydrogen sulfide, and sometimes hydrogen chloride, hydrogen fluoride, and other gases. A fumarole that emits significant sulfur compounds is some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.jpg)