|
Saab Quantum
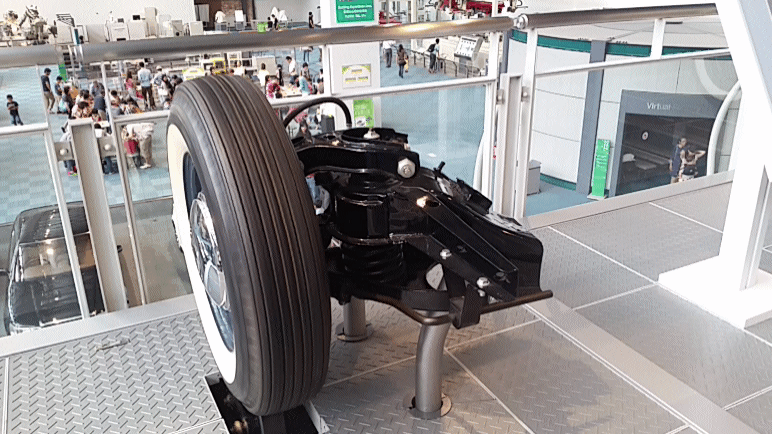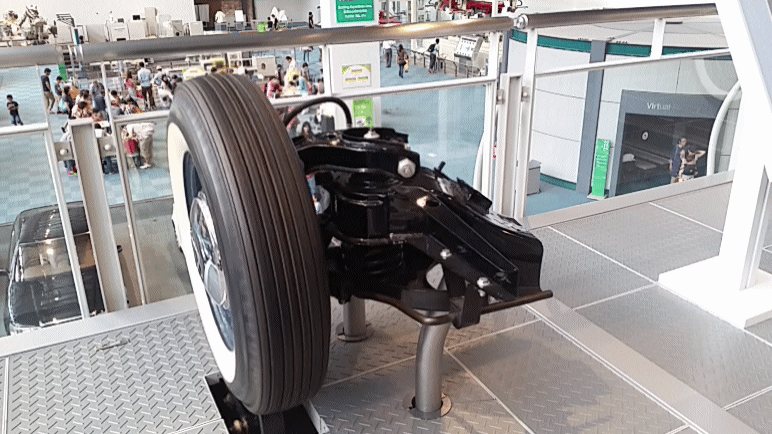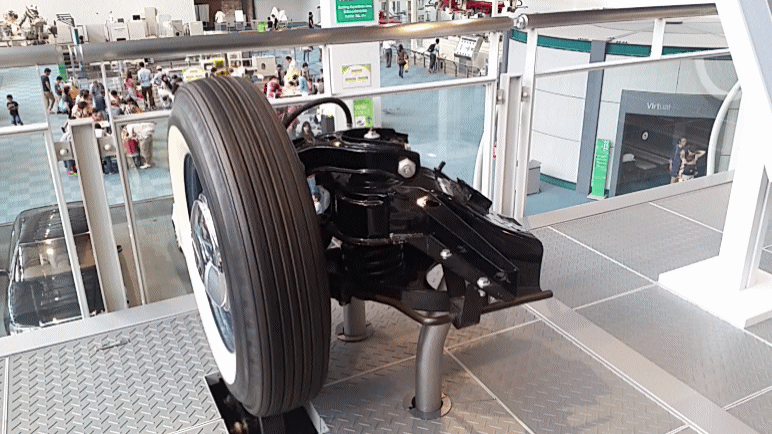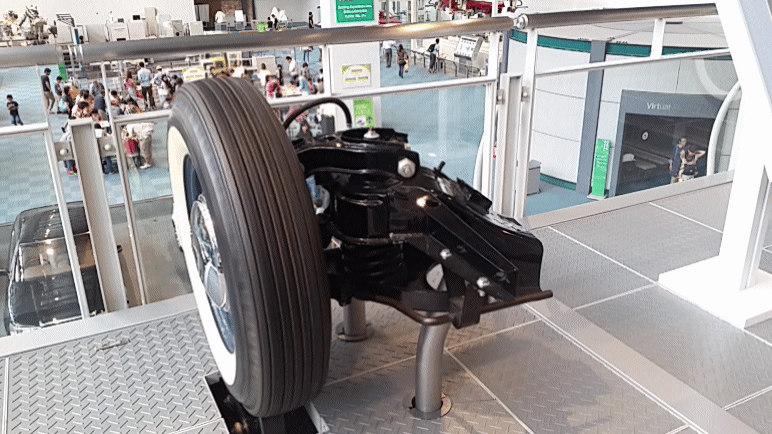
SAAB Quantum was a series of five privately designed and built automobiles using various Saab components. The earliest used Saab 93 two-stroke engines, transmissions and suspension. The later used Saab 96 drivetrains and suspension parts. All were built in the United States. The Quantum I was built in 1959, with a chassis computer engineered by Walter Kern at IBM in his spare time. It wore only the most basic bodywork at first. After initial testing and a race or two, it was replaced with moderately more complete bodywork which it still wears to this day. The Quantum II was nearly identical in every way, though built later. Both Quantums I and II were raced in the SCCA H-Modified class. They were pure prototypes and racing cars, never intended for production. The Quantum III was designed to be a production car and was first presented in 1962. Only a few copies were built. Due to a lack of quality it was turned down by Saab in Sweden and never went into production. * Quantum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saab Automobile
Saab Automobile AB () is a defunct automotive industry, car manufacturer that was founded in Sweden in 1945 when its parent company, Saab AB, began a project to design a small automobile. The first production model, the Saab 92, was launched in 1949. In 1968 the parent company merged with Scania-Vabis, and ten years later the Saab 900 was launched, in time becoming Saab's best-selling model. In the mid-1980s the new Saab 9000 model also appeared. In 1989, the automobile division of Saab-Scania was restructured into an independent company, Saab Automobile AB. The American manufacturer General Motors (GM) took 50 percent ownership. Two well-known models to come out of this period were the Saab 9-3 and the Saab 9-5. Then in 2000, GM exercised its option to acquire the remaining 50 percent. In 2010 GM sold Saab Automobile AB to the Dutch automobile manufacturer Spyker Cars N.V. After many years establishing a sound engineering reputation and ultimately a luxury car, luxury price t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saab 93
The Saab 93 (pronounced ''ninety-three'') is the second production automobile that was manufactured by Saab. Styled by Sixten Sason, it was first presented on December 1, 1955. The 93 was powered by a longitudinally-mounted three-cylinder 748 cc Saab two-stroke engine giving 33 hp (25 kW). The gearbox had three gears, the first unsynchronised. In order to overcome the problems of oil starvation on overrun (engine braking) for the two-stroke engine, a freewheel device was fitted. In 1957, two-point seatbelts were introduced as an option. The 93 was the first Saab to be exported from Sweden, with most exports going to the United States. A Saxomat clutch and a cabrio coach (large cloth sunroof) were available as options. On September 2, 1957, the 93B was introduced. The original two-piece windshield was also replaced with a one-piece windshield. In 1957, Erik Carlsson finished 1st in the Finland Rally in a Saab 93; in 1959, he was 1st in the Swedish Rally, also in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-stroke Cycle
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle during two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust (or scavenging) functions occurring at the same time. Two-stroke engines often have a high power-to-weight ratio, power being available in a narrow range of rotational speeds called the power band. Two-stroke engines have fewer moving parts than four-stroke engines. History The first commercial two-stroke engine involving cylinder compression is attributed to Scottish engineer Dugald Clerk, who patented his design in 1881. However, unlike most later two-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saab 96
The Saab 96 is an automobile manufactured and marketed by Saab from 1960 to January 1980, replacing the 93. The 96 featured aerodynamic two-door bodywork, four-passenger seating and at first a two-stroke, three-cylinder engine, later a four-stroke V4. Body design Compared with its predecessor, the Saab 93, the 96 featured greater and more easily accessible storage space and larger rear window. The front end was lengthened for 1965 models, in preparation for a new engine, and the radiator was placed ahead of the engine, rather than above and behind, a leftover from the thermosiphon cooling days. Both front and rear windows were enlarged slightly for 1968 models. Engine The Saab 96 had a longitudinally mounted engine layout. As first designed, it had an 841 cc displacement, three-cylinder Saab two-stroke engine. By 1965 this was increased to . An optional version of the engine, with triple carburetors and oil injection, was used in the Sport and Monte Carlo models. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-aided Design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software are helpful in protecting products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used. Its use in designing electronic systems is known as '' electronic design automation'' (''EDA''). In mechanical design it is known as ''mechanical design automation'' (''MDA''), which includes the process of creating a technical drawing with the use of computer software. CAD software for mechanical design uses either vector-based graphics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saab Two-stroke
The Saab two-stroke was a two-stroke cycle, inline, two cylinder, and later three cylinder engine manufactured by Swedish automotive manufacturer Saab that was based on a design by German manufacturer DKW. Two-cylinder The first version was a displacement straight-twin that was transversally mounted in the 1950–1956 Saab 92. It had with , and a top speed of . For the 1954 model year the engine received a new Solex 32BI carburetor and a new ignition coil which raised engine output to . It had some features only found in modern cars such as one ignition coil per cylinder. Three-cylinder The second type of Saab two stroke engine was a longitudinally placed inline-three cylinder of and initially . It was used in the Saabs 93, 94 (Sonett I, with an engine tuned to ), Saab Sonett II, 95, 96, Saab GT750, the Saab Formula Junior and the Saab Quantum. The engine had a combined belt driven DC dynamo and a coolant water pump. The Saab Formula Junior used a 'bored-out' hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kit Car
A kit car is an automobile available as a set of parts that a manufacturer sells and the buyer then assembles into a functioning car. Usually, many of the major mechanical systems such as the engine and transmission are sourced from donor vehicles or purchased new from other vendors. Kits vary in completeness, consisting of as little as a book of plans, or as much as a complete set with all components to assemble into a fully operational vehicle such as those from Caterham. Related terms There is also a sub-set of the kit car, commonly referred to as a "re-body", in which a commercially manufactured vehicle has a new (often fiberglass) body put on the running chassis. Most times, the existing drive gear and interior are retained. These kits require less technical knowledge from the builder, and because the chassis and mechanical systems were designed, built, and tested by a major automotive manufacturer, a re-body can lead to a much higher degree of safety and reliability. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sports Car Club Of America
The Sports Car Club of America (SCCA) is a non-profit American automobile club and sanctioning body supporting road racing, rallying, and autocross in the United States. Formed in 1944, it runs many programs for both amateur and professional racers. History The SCCA traces its roots to the Automobile Racing Club of America (not to be confused with the current stock car series of the same name). ARCA was founded in 1933 by brotherMilesand Sam Collier, and dissolved in 1941 at the outbreak of World War II. The SCCA was formed in 1944 as an enthusiast group. The SCCA began sanctioning road racing in 1948 with the inaugural Watkins Glen Grand Prix. Cameron Argetsinger, an SCCA member and local enthusiast who would later become Director of Pro Racing and Executive Director of the SCCA, helped organize the event for the SCCA. In 1951, the SCCA National Sports Car Championship was formed from existing marquee events around the nation, including Watkins Glen, Pebble Beach, and Elk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula S
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship between given quantities. The plural of ''formula'' can be either ''formulas'' (from the most common English plural noun form) or, under the influence of scientific Latin, ''formulae'' (from the original Latin). In mathematics In mathematics, a formula generally refers to an identity which equates one mathematical expression to another, with the most important ones being mathematical theorems. Syntactically, a formula (often referred to as a ''well-formed formula'') is an entity which is constructed using the symbols and formation rules of a given logical language. For example, determining the volume of a sphere requires a significant amount of integral calculus or its geometrical analogue, the method of exhaustion. However, having done thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ginetta
Ginetta Cars Limited is a British specialist builder of racing and sports cars based in Garforth, Leeds, West Yorkshire. History 20th century Ginetta was founded in 1958 by four Walklett brothers (Bob, Ivor, Trevers and Douglas) in Woodbridge, Suffolk. Their first product, the Fairlight, was a glass-fibre body shell priced at £49 for fitting to a Ford chassis. The first car, not destined for production, which subsequently became known as the Ginetta G1, was based on a pre-war Wolseley Hornet six. The four Walklett brothers each had their areas of expertise: Bob was the managing director, Douglas was the mechanical engineer and also handled the electrical work, Ivor was the designer and Trevers was the stylist, working closely with Ivor. From their original base, the company moved to Witham, Essex, in 1962, and between 1972 and 1974 operated from larger premises in Ballingdon Street adjacent to the railway bridge Sudbury, Suffolk, before returning to Witham. In 1988, the Walk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Wishbone Suspension
A double wishbone suspension is an independent suspension design for automobiles using two (occasionally parallel) wishbone-shaped arms to locate the wheel. Each wishbone or arm has two mounting points to the chassis and one joint at the knuckle. The shock absorber and coil spring mount to the wishbones to control vertical movement. Double wishbone designs allow the engineer to carefully control the motion of the wheel throughout suspension travel, controlling such parameters as camber angle, caster angle, toe pattern, roll center height, scrub radius, scuff and more. Implementation The double-wishbone suspension can also be referred to as "double A-arms", though the arms themselves can be A-shaped, L-shaped, or even a single bar linkage. A single wishbone or A-arm can also be used in various other suspension types, such as variations of the MacPherson strut. The upper arm is usually shorter to induce negative camber as the suspension jounces (rises), and often this arrangement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(crop).jpg)







.jpg)