|
STARAN
STARAN in the information technology industry might be the first commercially available computer designed around an associative memory. The STARAN computer was designed and built by Goodyear Aerospace Corporation. It is a content-addressable parallel processor (CAPP), a type of parallel processor which uses content-addressable memory. STARAN is . The STARAN machines became available in 1972. Goodyear Aerospace later developed the MPP based on similar principles but with a larger and wider processor array. See also * Index of computing articles *Outline of computers *Outline of computing The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to computing: Computing – activity of using and improving computer hardware and computer software. Branches of computing * Computer science (see also Outline of comp ... References * * * Goodyear Tire and Rubber Company One-of-a-kind computers {{computer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Content-addressable Memory
Content-addressable memory (CAM) is a special type of computer memory used in certain very-high-speed searching applications. It is also known as associative memory or associative storage and compares input search data against a table of stored data, and returns the address of matching data. CAM is frequently used in networking devices where it speeds up forwarding information base and routing table operations. This kind of associative memory is also used in cache memory. In associative cache memory, both address and content is stored side by side. When the address matches, the corresponding content is fetched from cache memory. History Dudley Allen Buck invented the concept of content-addressable memory in 1955. Buck is credited with the idea of ''recognition unit''. Hardware associative array Unlike standard computer memory, random-access memory (RAM), in which the user supplies a memory address and the RAM returns the data word stored at that address, a CAM is designed such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
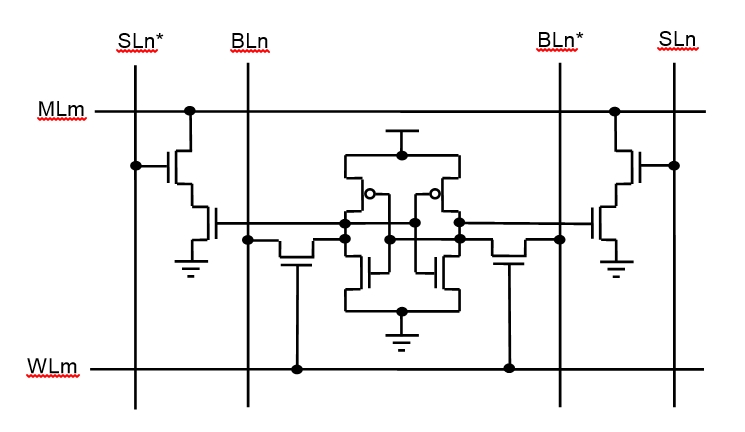
Content-addressable Parallel Processor
A content-addressable parallel processor (CAPP) also known as ''associative processor'' is a type of parallel processor which uses content-addressing memory (CAM) principles. CAPPs are intended for bulk computation. The syntactic structure of their computing algorithm are simple, whereas the number of concurrent processes may be very large, only limited by the number of locations in the CAM. The best-known CAPP may be STARAN, completed in 1972; several similar systems were later built in other countries. A CAPP is distinctly different from a Von Neumann architecture The von Neumann architecture — also known as the von Neumann model or Princeton architecture — is a computer architecture based on a 1945 description by John von Neumann, and by others, in the ''First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC''. The ... or classical computer that stores data in cells addressed individually by numeric address. The CAPP executes a stream of instructions that address memory based on the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Content-addressable Memory
Content-addressable memory (CAM) is a special type of computer memory used in certain very-high-speed searching applications. It is also known as associative memory or associative storage and compares input search data against a table of stored data, and returns the address of matching data. CAM is frequently used in networking devices where it speeds up forwarding information base and routing table operations. This kind of associative memory is also used in cache memory. In associative cache memory, both address and content is stored side by side. When the address matches, the corresponding content is fetched from cache memory. History Dudley Allen Buck invented the concept of content-addressable memory in 1955. Buck is credited with the idea of ''recognition unit''. Hardware associative array Unlike standard computer memory, random-access memory (RAM), in which the user supplies a memory address and the RAM returns the data word stored at that address, a CAM is designed such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goodyear MPP
The Goodyear Massively Parallel Processor (MPP) was a massively parallel processing supercomputer built by Goodyear Aerospace for the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. It was designed to deliver enormous computational power at lower cost than other existing supercomputer architectures, by using thousands of simple processing elements, rather than one or a few highly complex CPUs. Development of the MPP began circa 1979; it was delivered in May 1983, and was in general use from 1985 until 1991. It was based on Goodyear's earlier STARAN array processor, a 4x256 1-bit processing element (PE) computer. The MPP was a 128x128 2-dimensional array of 1-bit wide PEs. In actuality 132x128 PEs were configured with a 4x128 configuration added for fault tolerance to substitute for up to 4 rows (or columns) of processors in the presence of problems. The PEs operated in a single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) fashioneach PE performed the same operation simultaneously, on different data eleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology system (IT system) is generally an information system, a communications system, or, more specifically speaking, a computer system — including all hardware, software, and peripheral equipment — operated by a limited group of IT users. Although humans have been storing, retrieving, manipulating, and communicating information since the earliest writing systems were developed, the term ''information technology'' in its modern sense first appeared in a 1958 article published in the ''Harvard Business Review''; authors Harold J. Leavitt and Thomas L. Whisler commented that "the new technology does not yet have a single established name. We shall call it information technology (IT)." Their definition consists of three categories: techniques for pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goodyear Aerospace Corporation
Goodyear Aerospace Corporation (GAC) was the aerospace and defense subsidiary of the Goodyear Tire and Rubber Company. The company was originally operated as a division within Goodyear as the Goodyear Zeppelin Corporation, part of a joint project with Luftschiffbau Zeppelin, leading to the development of rigid airships in the United States. As part of the failing relationship between the US and Germany in the era prior to World War II, the division was spun off as Goodyear Aircraft Company in 1939. The company opened a new factory in Arizona in 1941 which produced subassemblies, including subcontracted airframe construction and the design of the Goodyear F2G Corsair and Goodyear Duck. In the post-war era, the division began to diversify and made major contributions to the development of synthetic aperture radar. In 1963 they became Goodyear Aerospace, with major product lines in radar, aircraft canopies, bulletproof glass, a number of spacecraft related products, and the unique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Computing
Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has gained broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling.S.V. Adve ''et al.'' (November 2008)"Parallel Computing Research at Illinois: The UPCRC Agenda" (PDF). Parallel@Illinois, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "The main techniques for these performance benefits—increased clock frequency and smarter but increasingly complex architectures—are now hitting the so-called power wall. The computer industry has accepted that future performance increases must largely come from increasing the number of processors (or cores) on a die, rather than m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD can be internal (part of the hardware design) and it can be directly accessible through an instruction set architecture (ISA), but it should not be confused with an ISA. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneously. Such machines exploit data level parallelism, but not concurrency: there are simultaneous (parallel) computations, but each unit performs the exact same instruction at any given moment (just with different data). SIMD is particularly applicable to common tasks such as adjusting the contrast in a digital image or adjusting the volume of digital audio. Most modern CPU designs include SIMD instructions to improve the performance of multimedia use. SIMD has three different subcategories in Flynn's 1972 Taxonomy, one of which is SIMT. SIMT should not be confused with software thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-bit Architecture
In computer architecture, 1-bit integers or other data units are those that are (1/8 octet) wide. Also, 1-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers of that size. There are no computers or microcontrollers of any kind that are exclusively 1-bit for all registers and address buses. A 1-bit register can only store 21 different values, i.e. 0 or 1 (off or on, respectively). This is very restrictive and therefore not enough for a program counter which, on modern systems, is implemented in an on-chip register, that isn't implemented on-chip in some 1-bit systems. Opcodes for at least one 1-bit processor architecture were 4-bit and the address bus was 8-bit. While 1-bit CPUs are obsolete, the first carbon nanotube computer from 2013 is a 1-bit one-instruction set computer (and has only 178 transistors). 1-bit A serial computer processes data a single bit at a time. For example, the PDP-8/S was a 12-bit co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Processing Element
This glossary of computer hardware terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related to computer hardware, i.e. the physical and structural components of computers, architectural issues, and peripheral devices. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P R S T U V W Z See also *List of computer term etymologies *Glossary of backup terms * Glossary of computer graphics * Glossary of computer science *Glossary of computer software terms This glossary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Computing Articles
Originally, the word ''computing'' was synonymous with counting and calculating, and the science and technology of mathematical calculations. Today, "computing" means using computers and other computing machines. It includes their operation and usage, the electrical processes carried out within the computing hardware itself, and the theoretical concepts governing them (computer science). ''See also:'' List of programmers, List of computing people, List of computer scientists, List of basic computer science topics, List of terms relating to algorithms and data structures. Topics on computing include: 0–9 1.TR.6 – 100BASE-FX – 100BASE-TX – 100BaseVG – 100VG-AnyLAN – 10BASE-2 – 10BASE-5 – 10BASE-T – 120 reset – 1-bit computing – 16-bit computing – 16-bit application – 16550 UART – 1NF – 1TBS – 20-GATE – 20-GATE – 28-bit – 2B1D – 2B1Q – 2D – 2NF – 3-tier (computing) – 32-bit application – 32-bit computing – 32 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outline Of Computers
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to computers: Computers – programmable machines designed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations. The sequences of operations can be changed readily, allowing computers to solve more than one kind of problem. What ''type'' of thing is a computer? Computers can be described as all of the following: * Tools – ** Machines – *** Business machines – * Systems – Types of computers * Mainframe computer – ** Super computer – * Midrange computer – * Personal computer – ** Desktop computer – ** Microcomputer – * Mobile computer and mobile device – ** Smartphone – ** Tablet computer – ** Laptop – * Computer appliance – ** Business machine – * Information appliance – ** Smartphone – ** Smart TV – Computer architecture Computer architecture – Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |