|
SSA22 Protocluster
The SSA22 Protocluster, also known as EQ J221734.0+001701, is a galaxy protocluster located at z=3.1 in the SSA 22 region. It is located at and was originally discovered in 1998.Astrophysical Journal, "A Large Structure of Galaxies at Redshift Z approximately 3 and Its Cosmological Implications", Steidel, Charles C.; Adelberger, Kurt L.; Dickinson, Mark; Giavalisco, Mauro; Pettini, Max; Kellogg, Melinda, v.492, p.428, 01/1998, , In 2006, a multifilamentary structure measuring 200 million light-years in width was announced, coinciding with the protocluster. Discovered in 2005 by Ryosuke Yamauchi from Tohoku University in Sendai, Japan, and his colleagues, the structure was found in a region of the universe known to contain large concentrations of gas. The structure is a very distant object; the astronomers that discovered it were actually looking at something from 12 billion years ago. This object is made up of lyman-break galaxies and large gas bubbles, such as lyman-alpha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giga-
Giga ( or ) is a unit prefix in the metric system denoting a factor of a short-scale billion or long-scale milliard (109 or ). It has the symbol G. ''Giga'' is derived from the Greek word (''gígas''), meaning "giant". The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' reports the earliest written use of ''giga'' in this sense to be in the Reports of the IUPAC 14th Conférence Internationale de Chimie in 1947: "The following prefixes to abbreviations for the names of units should be used: G giga 109×." When referring to information units in computing, such as gigabyte, giga may sometimes mean (230); this causes ambiguity. Standards organizations discourage this and use giga- to refer to 109 in this context too. ''Gigabit'' is only rarely used with the binary interpretation of the prefix. The binary prefix '' gibi'' has been adopted for 230, while reserving ''giga'' exclusively for the metric definition. Pronunciation In English, the prefix ''giga'' can be pronounced (a hard ''g'' as in ''gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. Defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Protocluster
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after galaxy filaments and were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. One of the key features of clusters is the intracluster medium (ICM). The ICM consists of heated gas between the galaxies and has a peak temperature between 2–15 keV that is dependent on the total mass of the cluster. Galaxy clusters should not be confused with ''galactic clusters'' (also known as open clusters), which are star clusters ''within'' galaxies, or with globular clusters, which typically orbit galaxies. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. The galaxy groups and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSA 22
The SSA22 Protocluster, also known as EQ J221734.0+001701, is a galaxy protocluster located at z=3.1 in the SSA 22 region. It is located at and was originally discovered in 1998.Astrophysical Journal, "A Large Structure of Galaxies at Redshift Z approximately 3 and Its Cosmological Implications", Steidel, Charles C.; Adelberger, Kurt L.; Dickinson, Mark; Giavalisco, Mauro; Pettini, Max; Kellogg, Melinda, v.492, p.428, 01/1998, , In 2006, a multifilamentary structure measuring 200 million light-years in width was announced, coinciding with the protocluster. Discovered in 2005 by Ryosuke Yamauchi from Tohoku University in Sendai, Japan, and his colleagues, the structure was found in a region of the universe known to contain large concentrations of gas. The structure is a very distant object; the astronomers that discovered it were actually looking at something from 12 billion years ago. This object is made up of lyman-break galaxies and large gas bubbles, such as lyman-alpha b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Geographic News
The National Geographic Society (NGS), headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, is one of the largest non-profit scientific and educational organizations in the world. Founded in 1888, its interests include geography, archaeology, and natural science, the promotion of environmental and historical conservation, and the study of world culture and history. The National Geographic Society's logo is a yellow portrait frame—rectangular in shape—which appears on the margins surrounding the front covers of its magazines and as its television channel logo. Through National Geographic Partners (a joint venture with The Walt Disney Company), the Society operates the magazine, TV channels, a website, worldwide events, and other media operations. Overview The National Geographic Society was founded on 13 January 1888 "to increase and diffuse geographic knowledge". It is governed by a board of trustees whose 33 members include distinguished educators, business executives, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyman-break Galaxies
Lyman-break galaxies are star-forming galaxies at high redshift that are selected using the differing appearance of the galaxy in several imaging filters due to the position of the Lyman limit. The technique has primarily been used to select galaxies at redshifts of ''z'' = 3–4 using ultraviolet and optical filters, but progress in ultraviolet astronomy and in infrared astronomy has allowed the use of this technique at lower and higher redshifts using ultraviolet and near-infrared filters. The Lyman-break galaxy selection technique relies on the fact that radiation at higher energies than the Lyman limit at 912 Å is almost completely absorbed by neutral gas around star-forming regions of galaxies. In the rest frame of the emitting galaxy, the emitted spectrum is bright at wavelengths longer than 912 Å, but very dim or imperceptible at shorter wavelengths—this is known as a " dropout", or "break", and can be used to find the position of the Lyman limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
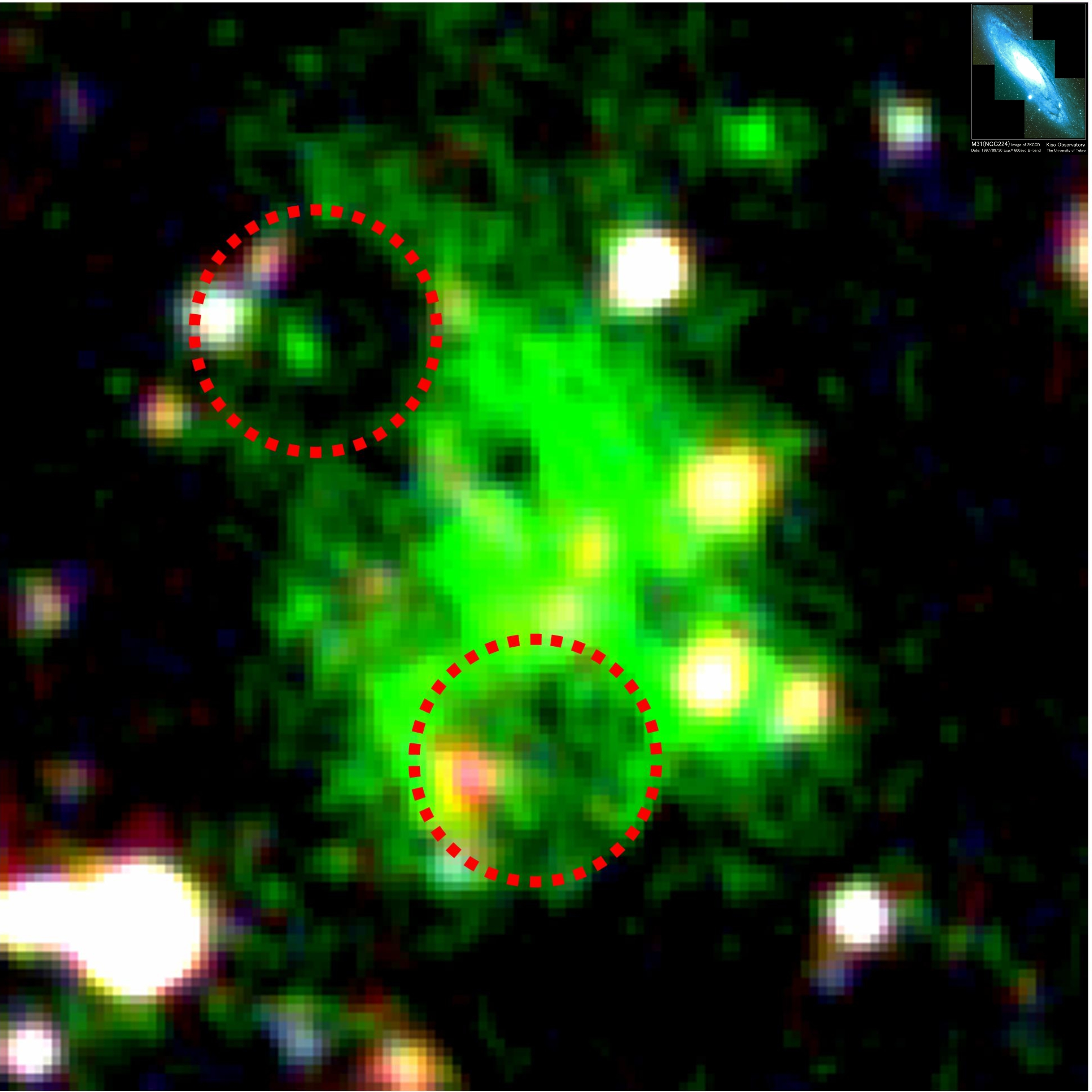
Lyman-alpha Blob
In astronomy, a Lyman-alpha blob (LAB) is a huge concentration of a gas emitting the Lyman-alpha emission line. LABs are some of the largest known individual objects in the Universe. Some of these gaseous structures are more than 400,000 light years across. So far they have only been found in the high-redshift universe because of the ultraviolet nature of the Lyman-alpha emission line. Since Earth's atmosphere is very effective at filtering out UV photons, the Lyman-alpha photons must be redshifted in order to be transmitted through the atmosphere. The most famous Lyman-alpha blobs were discovered in 2000 by Steidel et al. Matsuda et al., using the Subaru Telescope of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan extended the search for LABs and found over 30 new LABs in the original field of Steidel et al., although they were all smaller than the originals. These LABs form a structure which is more than 200 million light-years in extent. It is currently unknown whether LABs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyman-alpha Emitter
A Lyman-alpha emitter (LAE) is a type of distant galaxy that emits Lyman-alpha radiation from neutral hydrogen. Most known LAEs are extremely distant, and because of the finite travel time of light they provide glimpses into the history of the universe. They are thought to be the progenitors of most modern Milky Way type galaxies. These galaxies can be found nowadays rather easily in narrow-band searches by an excess of their narrow-band flux at a wavelength which may be interpreted from their redshift: : 1+z=\frac where z is the redshift, \lambda is the observed wavelength, and 1215.67 Å is the wavelength of Lyman-alpha emission. The Lyman-alpha line in most LAEs is thought to be caused by recombination of interstellar hydrogen that is ionized by an ongoing burst of star-formation. Such Lyman alpha emission was first suggested as a signature of young galaxies by Bruce Partridge and P. J. E. Peebles in 1967. Experimental observations of the redshift of LAEs are important in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as spacetime. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. Debates concerning the nature, essence and the mode of existence of space date back to antiquity; namely, to treatises like the ''Timaeus'' of Plato, or Socrates in his reflections on what the Greeks called ''khôra'' (i.e. "space"), or in the ''Physics'' of Aristotle (Book IV, Delta) in the definition of ''topos'' (i.e. place), or in the later "geometrical conception of place" as "spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy (IPA: ), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy with the diameter of about approximately from Earth and the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The galaxy's name stems from the area of Earth's sky in which it appears, the constellation of Andromeda, which itself is named after the princess who was the wife of Perseus in Greek mythology. The virial mass of the Andromeda Galaxy is of the same order of magnitude as that of the Milky Way, at . The mass of either galaxy is difficult to estimate with any accuracy, but it was long thought that the Andromeda Galaxy is more massive than the Milky Way by a margin of some 25% to 50%. This has been called into question by a 2018 study that cited a lower estimate on the mass of the Andromeda Galaxy, combined with preliminary reports on a 2019 study estimating a higher mass of the Milky Way. The Andromeda Galaxy has a diameter of about , making it the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale form. These models offer a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The overall uniformity of the Universe, known as the flatness problem, is explained through cosmic inflation: a sudden and very rapid expansion of space during the earliest moments. However, physics currently lacks a widely accepted theory of quantum gravity that can successfully model the earliest conditions of the Big Bang. Crucially, these models are compatible with the Hubble–Lemaître law—the observation that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |