|
SMBus
The System Management Bus (abbreviated to SMBus or SMB) is a single-ended simple two-wire bus for the purpose of lightweight communication. Most commonly it is found in computer motherboards for communication with the power source for ON/OFF instructions. It is derived from I²C for communication with low-bandwidth devices on a motherboard, especially power related chips such as a laptop's rechargeable battery subsystem (see Smart Battery System). Other devices might include temperature, fan or voltage sensors, lid switches, clock generator, and RGB lighting. PCI add-in cards may connect to an SMBus segment. A device can provide manufacturer information, indicate its model/part number, save its state for a suspend event, report different types of errors, accept control parameters and return status. The SMBus is generally not user configurable or accessible. Although SMBus devices usually can't identify their functionality, a new PMBus coalition has extended SMBus to include conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I²C
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit, ), alternatively known as I2C or IIC, is a synchronous, multi-controller/multi-target (master/slave), packet switched, single-ended, serial communication bus invented in 1982 by Philips Semiconductors. It is widely used for attaching lower-speed peripheral ICs to processors and microcontrollers in short-distance, intra-board communication. Several competitors, such as Siemens, NEC, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics, Motorola, Nordic Semiconductor and Intersil, have introduced compatible I2C products to the market since the mid-1990s. System Management Bus (SMBus), defined by Intel in 1995, is a subset of I2C, defining a stricter usage. One purpose of SMBus is to promote robustness and interoperability. Accordingly, modern I2C systems incorporate some policies and rules from SMBus, sometimes supporting both I2C and SMBus, requiring only minimal reconfiguration either by commanding or output pin use. Applications I2C is appropriate f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Management Bus
The Power Management Bus (PMBus) is a variant of the System Management Bus (SMBus) which is targeted at digital management of power supplies. Like SMBus, it is a relatively slow speed two wire communications protocol based on I²C. Unlike either of those standards, it defines a substantial number of domain-specific commands rather than just saying how to communicate using commands defined by the reader. Overview The first part gives an overview with particular reference to SMBus, while the second part goes into detail about all the commands defined for PMBus devices. There are both standardized commands and manufacturer specific commands. Conformance requirements for PMBus are minimal, and are described in Part I of the specification. See the PMBus 1.1 specification for full details. Comparison to SMBus At the lowest level, PMBus follows SMBus 1.1 with a few differences. This information is presented in more detail in Part I of the PMBus specification: * 400 kHz bus speed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
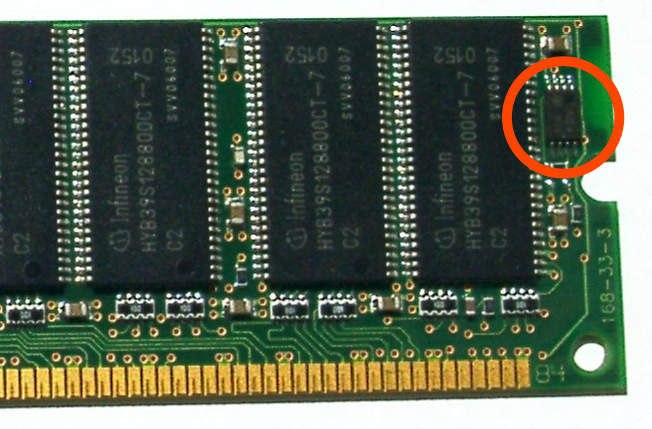
Serial Presence Detect
In computing, serial presence detect (SPD) is a standardized way to automatically access information about a memory module. Earlier 72-pin SIMMs included five pins that provided five bits of ''parallel presence detect'' (PPD) data, but the 168-pin DIMM standard changed to a serial presence detect to encode much more information. When an ordinary modern computer is turned on, it starts by doing a power-on self-test (POST). Since about the mid-1990s, this process includes automatically configuring the hardware currently present. SPD is a memory hardware feature that makes it possible for the computer to know what memory is present, and what memory timings to use to access the memory. Some computers adapt to hardware changes completely automatically. In most cases, there is a special optional procedure for accessing BIOS parameters, to view and potentially make changes in settings. It may be possible to control how the computer uses the memory SPD data—to choose settings, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Peripheral Interface
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a synchronous serial communication interface specification used for short-distance communication, primarily in embedded systems. The interface was developed by Motorola in the mid-1980s and has become a ''de facto'' standard. Typical applications include Secure Digital cards and liquid crystal displays. SPI devices communicate in full duplex mode using a master-slave architecture usually with a single master (though some Atmel and Silabs devices support changing roles on the fly depending on an external (SS) pin). The master (controller) device originates the frame for reading and writing. Multiple slave-devices may be supported through selection with individual chip select (CS), sometimes called slave select (SS) lines. Sometimes SPI is called a ''four-wire'' serial bus, contrasting with three-, two-, and one-wire serial buses. The SPI may be accurately described as a synchronous serial interface, but it is different from the Sync ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smart Battery System
Smart Battery System (SBS) is a specification for managing a smart battery, usually for a portable computer. It allows operating systems to perform power management operations via a smart battery charger based on remaining estimated run times by determining accurate state of charge readings. Through this communication, the system also controls the battery charge rate. Communication is carried over an SMBus two-wire communication bus. The specification originated with the Duracell and Intel companies in 1994, but was later adopted by several battery and semiconductor makers. Henk Jan Bergveld, Wanda S. Kruijt, Peter H. L. Notten '' Battery management systems: design by modelling'' Springer, 2002 pages 20-22 The Smart Battery System defines the SMBus connection, the data that can be sent over the connection (''Smart Battery Data'' or SBD), the Smart Battery Charger, and a computer BIOS interface for control. In principle, any battery operated product can use SBS. A special int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alert Standard Format
Alert Standard Format (ASF) (also sometimes referred to as ''Alert Standard Forum'', ''Alerting Specifications Forum'', ''Alert Specification Function'', etc.) is a DMTF standard for remote monitoring, management and control of computer systems in both OS-present and OS-absent environments. These technologies are primarily focused on minimizing on-site I/T maintenance, maximizing system availability and performance to the local user. ASF, unlike other DMTF standards, defines both external-facing network protocols (for use with Remote Management Consoles and Alert Sending Devices) and system-internal protocols and data models (for use in System Firmware, Remote Control Devices, Alert Sending Devices, and Sensors). ASF v1.0 (DSP0114) was published by the DMTF Pre-OS Working Group in June 2001. ASF v2.0 (DSP0136), adding secure remote authentication and data integrity, was published by the DMTF Pre-OS Working Group in April 2003. Network protocols * RMCP (Remote Management and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC-8
A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is an error-detecting code commonly used in digital networks and storage devices to detect accidental changes to digital data. Blocks of data entering these systems get a short ''check value'' attached, based on the remainder of a polynomial division of their contents. On retrieval, the calculation is repeated and, in the event the check values do not match, corrective action can be taken against data corruption. CRCs can be used for error correction (see bitfilters). CRCs are so called because the ''check'' (data verification) value is a ''redundancy'' (it expands the message without adding information) and the algorithm is based on ''cyclic'' codes. CRCs are popular because they are simple to implement in binary hardware, easy to analyze mathematically, and particularly good at detecting common errors caused by noise in transmission channels. Because the check value has a fixed length, the function that generates it is occasionally used as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bus (computing)
In computer architecture, a bus (shortened form of the Latin '' omnibus'', and historically also called data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This expression covers all related hardware components (wire, optical fiber, etc.) and software, including communication protocols. Early computer buses were parallel electrical wires with multiple hardware connections, but the term is now used for any physical arrangement that provides the same logical function as a parallel electrical busbar. Modern computer buses can use both parallel and bit serial connections, and can be wired in either a multidrop (electrical parallel) or daisy chain topology, or connected by switched hubs, as in the case of Universal Serial Bus (USB). Background and nomenclature Computer systems generally consist of three main parts: * The central processing unit (CPU) that processes data, * The memory that holds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embedded Controller
An Embedded Controller (EC) is a microcontroller in computers that handles various system tasks. Now it is usually merged with Super I/O, especially on mobile platforms (such as laptop). Tasks An embedded controller can have the following tasks: *Receiving and processing signals from the keyboardhttp://www.computer-engineering.org/ps2keyboard/ and the touchpad (including touchpad disable) *Other buttons and switches (e.g., power button, laptop lid switch (received from hall sensor)) *Controlling access to the A20 line *Thermal measurement (CPU, GPU, Motherboard) and response including fan control, CPU and GPU throttling, and emergency shutdown in response to rising temperatures *Controlling indicator LEDs (e.g. caps lock, scroll lock, num lock, battery, ac, power, wireless LAN, sleep) *Managing the battery charger and the battery *Allowing remote diagnostics and remediation over the network *Performing software-requested CPU reset *Controlling the watchdog timer *System Mana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Network Buses
List of electrical characteristics of single collision domain segment "slow speed" network buses: {, class="wikitable sortable" style="width:100%;" ! Name !! Multidrop !! Max nodes !! Electrical type !! Cable type !! data-sort-type="number", Max bitrate [ kbit/s] !data-sort-type="number", Length at max bitrate!! data-sort-type="number" , Max length [m] !data-sort-type="number", Bitrate at max length , - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , - , EIA-485 , , Y , , 256 , , EIA-485 , , Twisted pair , , , , , , , - , SCSI-1/2 , , Y , , 8 , , Open collector , , Ribbon cable , , , , , , , - , SCSI Ultra2 , , Y , , 16 , , EIA-485 , , Twisted pair , , , , , , , - , LIN, , Y , , 16 , , Open collector, , open collector with pull-up to 12V car supply , , , , , , - , SIOX , , Y , , 62 , , , , , , , , , , , - , I²C , , Y , , 127 or 1023 , , Open collector , , , , , , , , , - , SMBus , , Y , , 128 , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligent Platform Management Interface
The Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) is a set of computer interface specifications for an autonomous computer subsystem that provides management and monitoring capabilities independently of the host system's CPU, firmware ( BIOS or UEFI) and operating system. IPMI defines a set of interfaces used by system administrators for out-of-band management of computer systems and monitoring of their operation. For example, IPMI provides a way to manage a computer that may be powered off or otherwise unresponsive by using a network connection to the hardware rather than to an operating system or login shell. Another use case may be installing a custom operating system remotely. Without IPMI, installing a custom operating system may require an administrator to be physically present near the computer, insert a DVD or a USB flash drive containing the OS installer and complete the installation process using a monitor and a keyboard. Using IPMI, an administrator can mount an ISO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)