|
SLC25A46
Solute carrier family 25 member 46 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC25A46'' gene. This protein is a member of the SLC25 mitochondrial solute carrier family. It is a transmembrane protein located in the mitochondrial outer membrane involved in lipid transfer from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to mitochondria. Mutations in this gene result in neuropathy and optic atrophy. Structure The ''SLC25A46'' gene is located on the q arm of chromosome 5 in position 22.1 and spans 27,039 base pairs. The gene produces a 46.2 kDa protein composed of 418 amino acids. This gene has 8 exons and encodes a multi-pass integral membrane protein localized to the mitochondrial outer membrane. Function The encoded protein is an orphan transporter involved in lipid transfer from the endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria. It promotes mitochondrial fission and prevents the formation of hyperfilamentous mitochondria. This protein forms a complex with mitofilin (IMMT) on the inn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Complex
A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multienzyme complexes, in which multiple catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain. Protein complexes are a form of quaternary structure. Proteins in a protein complex are linked by non-covalent protein–protein interactions. These complexes are a cornerstone of many (if not most) biological processes. The cell is seen to be composed of modular supramolecular complexes, each of which performs an independent, discrete biological function. Through proximity, the speed and selectivity of binding interactions between enzymatic complex and substrates can be vastly improved, leading to higher cellular efficiency. Many of the techniques used to enter cells and isolate proteins are inherently disruptive to such large complexes, complicating the task of determining the components of a complex. Examples of protein complexes include the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
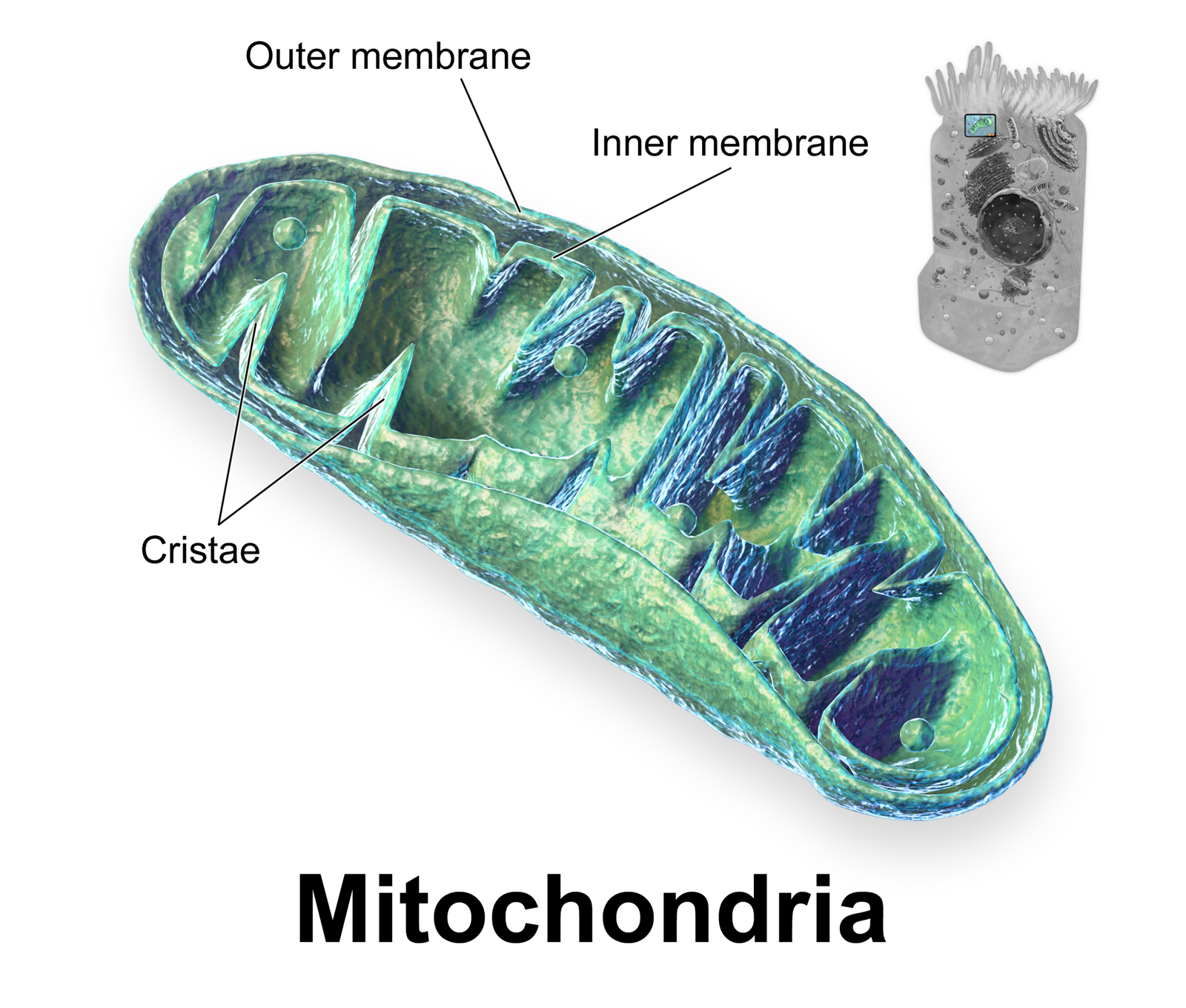
Crista
A crista (; plural cristae) is a fold in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. The name is from the Latin for ''crest'' or ''plume'', and it gives the inner membrane its characteristic wrinkled shape, providing a large amount of surface area for chemical reactions to occur on. This aids aerobic cellular respiration, because the mitochondrion requires oxygen. Cristae are studded with proteins, including ATP synthase and a variety of cytochromes. Background With the discovery of the dual-membrane nature of mitochondria, the pioneers of mitochondrial ultrastructural research proposed different models for the organization of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Three models proposed were: *Baffle model – According to Palade (1953), the mitochondrial inner membrane is convoluted in a baffle-like manner with broad openings towards the intra-cristal space. This model entered most textbooks and was widely believed for a long time. *Septa model – Sjöstrand (1953) suggested that she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy. Respiration is one of the key ways a cell releases chemical energy to fuel cellular activity. The overall reaction occurs in a series of biochemical steps, some of which are redox reactions. Although cellular respiration is technically a combustion reaction, it is an unusual one because of the slow, controlled release of energy from the series of reactions. Nutrients that are commonly used by animal and plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Senescence
Cellular senescence is a phenomenon characterized by the cessation of cell division. In their experiments during the early 1960s, Leonard Hayflick and Paul Moorhead found that normal human fetal fibroblasts in culture reach a maximum of approximately 50 cell population doublings before becoming senescent. This process is known as "replicative senescence", or the Hayflick limit. Hayflick's discovery of mortal cells paved the path for the discovery and understanding of cellular aging molecular pathways. Cellular senescence can be initiated by a wide variety of stress inducing factors. These stress factors include both environmental and internal damaging events, abnormal cellular growth, oxidative stress, autophagy factors, among many other things. The physiological importance for cell senescence has been attributed to prevention of carcinogenesis, and more recently, aging, development, and tissue repair. Senescent cells contribute to the aging phenotype, including frailty syndrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial Fusion
Mitochondria are dynamic organelles with the ability to fuse and divide ( fission), forming constantly changing tubular networks in most eukaryotic cells. These mitochondrial dynamics, first observed over a hundred years ago are important for the health of the cell, and defects in dynamics lead to genetic disorders. Through fusion, mitochondria can overcome the dangerous consequences of genetic malfunction. The process of mitochondrial fusion involves a variety of proteins that assist the cell throughout the series of events that form this process. Process overview When cells experience metabolic or environmental stresses, mitochondrial fusion and fission work to maintain functional mitochondria. An increase in fusion activity leads to mitochondrial elongation, whereas an increase in fission activity results in mitochondrial fragmentation. The components of this process can influence programmed cell death and lead to neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's disease. Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Knockdown
Gene knockdown is an experimental technique by which the expression of one or more of an organism's genes is reduced. The reduction can occur either through genetic modification or by treatment with a reagent such as a short DNA or RNA oligonucleotide that has a sequence complementary to either gene or an mRNA transcript. Versus transient knockdown If a DNA of an organism is genetically modified, the resulting organism is called a "knockdown organism." If the change in gene expression is caused by an oligonucleotide binding to an mRNA or temporarily binding to a gene, this leads to a temporary change in gene expression that does not modify the chromosomal DNA, and the result is referred to as a "transient knockdown". In a transient knockdown, the binding of this oligonucleotide to the active gene or its transcripts causes decreased expression through a variety of processes. Binding can occur either through the blocking of transcription (in the case of gene-binding), the degradati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three typesgroup A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or organ function depending on which nerves are affected; in other words, neuropathy affecting motor, sensory, or autonomic nerves result in different symptoms. More than one type of nerve may be affected simultaneously. Peripheral neuropathy may be acute (with sudden onset, rapid progress) or chronic (symptoms begin subtly and progress slowly), and may be reversible or permanent. Common causes include systemic diseases (such as diabetes or leprosy), hyperglycemia-induced glycation, vitamin deficiency, medication (e.g., chemotherapy, or commonly prescribed antibiotics including metronidazole and the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)), traumatic injury, ischemia, radiation therapy, excessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditary Motor And Sensory Neuropathy
Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies (HMSN) is a name sometimes given to a group of different neuropathies which are all characterized by their impact upon both afferent and efferent neural communication. HMSN are characterised by atypical neural development and degradation of neural tissue. The two common forms of HMSN are either hypertrophic demyelinated nerves or complete atrophy of neural tissue. Hypertrophic condition causes neural stiffness and a demyelination of nerves in the peripheral nervous system, and atrophy causes the breakdown of axons and neural cell bodies. In these disorders, a patient experiences progressive muscle atrophy and sensory neuropathy of the extremities. The term "hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy" was used mostly historically to denote the more common forms Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT). With the identification of a wide number of genetically and phenotypically distinct forms of CMT, the term HMSN is now used less frequently. Symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |