|
SK3
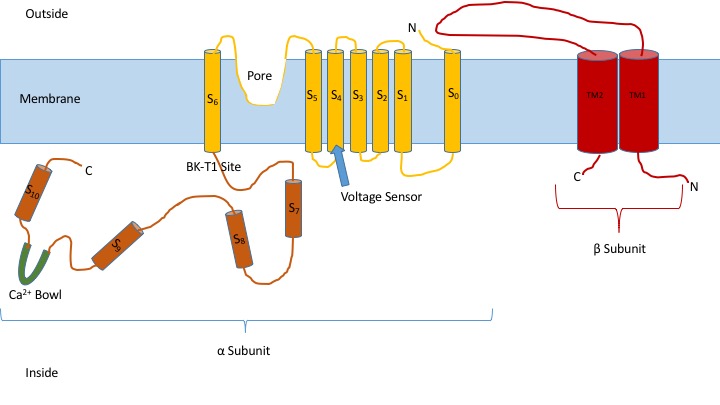
SK3 (small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel 3) also known as KCa2.3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNN3'' gene. SK3 is a small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel partly responsible for the calcium-dependent after hyperpolarisation current (IAHP). It belongs to a family of channels known as small-conductance potassium channels, which consists of three members – SK1, SK2 and SK3 (encoded by the KCNN1, 2 and 3 genes respectively), which share a 60-70% sequence identity. These channels have acquired a number of alternative names, however a NC-IUPHAR has recently achieved consensus on the best names, KCa2.1 (SK1), KCa2.2 (SK2) and KCa2.3 (SK3). Small conductance channels are responsible for the medium and possibly the slow components of the IAHP. Structure KCa2.3 contains 6 transmembrane domains, a pore-forming region, and intracellular N- and C- termini and is readily blocked by apamin. The gene for KCa2.3, KCNN3, is located on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SK Channel
SK channels (small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels) are a subfamily of calcium-activated potassium channels. They are so called because of their small single channel conductance in the order of 10 pS. SK channels are a type of ion channel allowing potassium cations to cross the cell membrane and are activated (opened) by an increase in the concentration of intracellular calcium through N-type calcium channels. Their activation limits the firing frequency of action potentials and is important for regulating afterhyperpolarization in the neurons of the central nervous system as well as many other types of electrically excitable cells. This is accomplished through the hyperpolarizing leak of positively charged potassium ions along their concentration gradient into the extracellular space. This hyperpolarization causes the membrane potential to become more negative. SK channels are thought to be involved in synaptic plasticity and therefore play important roles in l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNN2
Potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 2, also known as KCNN2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the KCNN2 gene. KCNN2 is an ion channel protein also known as KCa2.2. Function Action potentials in vertebrate neurons are followed by an afterhyperpolarization (AHP) that may persist for several seconds and may have profound consequences for the firing pattern of the neuron. Each component of the AHP is kinetically distinct and is mediated by different calcium-activated potassium channels. The KCa2.2 protein is activated before membrane hyperpolarization and is thought to regulate neuronal excitability by contributing to the slow component of synaptic AHP. KCa2.2 is an integral membrane protein that forms a voltage-independent calcium-activated channel with three other calmodulin-binding subunits. This protein is a member of the calcium-activated potassium channel family. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium-activated Potassium Channel
Calcium-activated potassium channels are potassium channels gated by calcium, or that are structurally or phylogenetically related to calcium gated channels. They were first discovered in 1958 by Gardos who saw that calcium levels inside of a cell could affect the permeability of potassium through that cell membrane. Then in 1970, Meech was the first to observe that intracellular calcium could trigger potassium currents. In humans they are divided into three subtypes: BK channel, large conductance or BK channels, which have very high conductance which range from 100 to 300 pS, intermediate conductance or IK channels, with intermediate conductance ranging from 25 to 100 pS, and small conductance or SK channels with small conductances from 2-25 pS. This family of ion channels is, for the most part, activated by intracellular Ca2+ and contains 8 members in the human genome. However, some of these channels (the KCa4 and KCa5 channels) are responsive instead to other intracellular ligan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNN1
Potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 1 , also known as KCNN1 is a human gene encoding the KCa2.1 protein. Action potentials in vertebrate neurons are followed by an afterhyperpolarization (AHP) that may persist for several seconds and may have profound consequences for the firing pattern of the neuron. Each component of the AHP is kinetically distinct and is mediated by different calcium-activated potassium channels. The protein encoded by this gene is activated before membrane hyperpolarization and is thought to regulate neuronal excitability by contributing to the slow component of synaptic AHP. The KCa2.1 protein is an integral membrane protein that forms a voltage-independent calcium-activated channel with three other calmodulin-binding subunits. The KCNN1 gene is a member of the KCNN family of potassium channel genes. See also * SK channel * Voltage-gated potassium channel Voltage-gated potassium channels (VGKCs) are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apamin
Apamin is an 18 amino acid globular peptide neurotoxin found in apitoxin ( bee venom). Dry bee venom consists of 2–3% of apamin. Apamin selectively blocks SK channels, a type of Ca2+-activated K+ channel expressed in the central nervous system. Toxicity is caused by only a few amino acids, in particular cysteine1, lysine4, arginine13, arginine14 and histidine18. These amino acids are involved in the binding of apamin to the Ca2+-activated K+ channel. Due to its specificity for SK channels, apamin is used as a drug in biomedical research to study the electrical properties of SK channels and their role in the afterhyperpolarizations occurring immediately following an action potential. Origin The first symptoms of apitoxin (bee venom), that are now thought to be caused by apamin, were described back in 1936 by Hahn and Leditschke. Apamin was first isolated by Habermann in 1965 from ''Apis mellifera'', the Western honey bee. Apamin was named after this bee. Bee venom contains many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic alcohol use and gallstones. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular
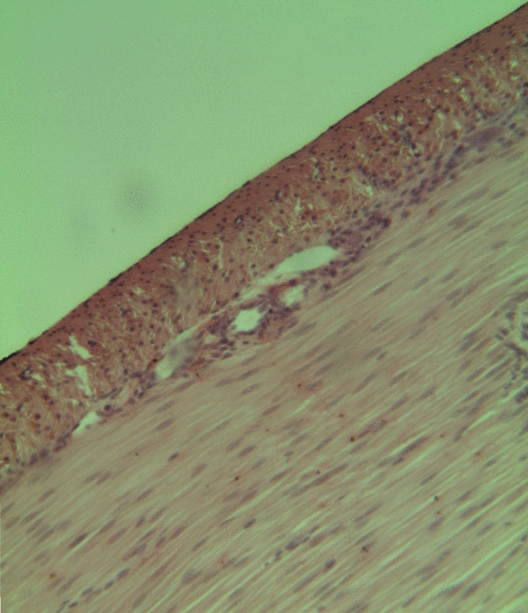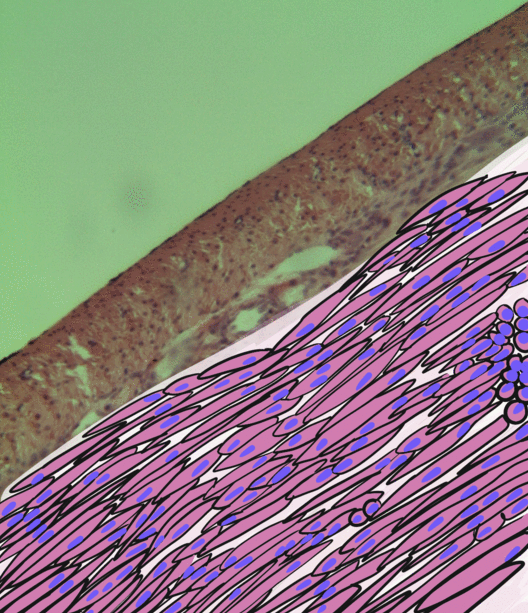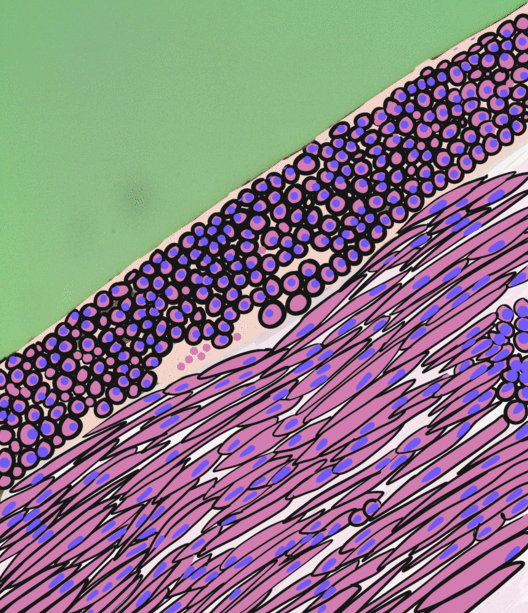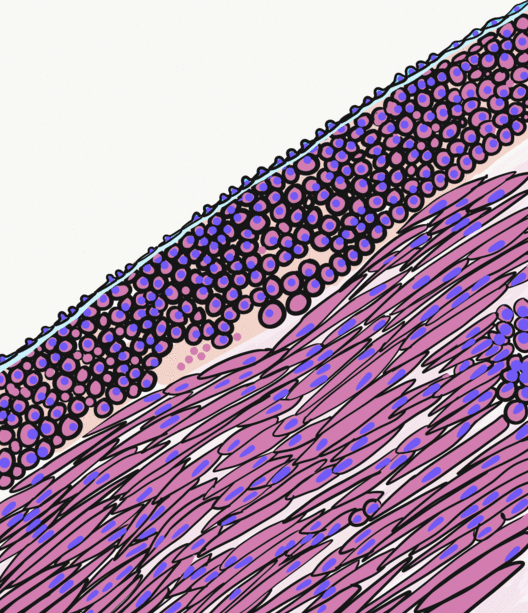
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning vessel. Some structures – such as cartilage, the epithelium, and the lens and cornea of the eye – do not contain blood vessels and are labeled ''avascular''. Etymology * artery: late Middle English; from Latin ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelium
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells form the barrier between vessels and tissue and control the flow of substances and fluid into and out of a tissue. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Cavernosum (other) in older texts.
{{Disambig ...
Corpus cavernosum may refer to: * Corpus cavernosum clitoridis * Corpus cavernosum penis * "Corpus cavernosum urethrae" was used for corpus spongiosum The corpus spongiosum is the mass of spongy tissue surrounding the male urethra within the penis. It is also called the corpus cavernosum urethrae in older texts. Anatomy The proximal part of the corpus spongiosum is expanded to form the uret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |