|
SERTAD1
SERTA domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SERTAD1'' gene. Interactions SERTAD1 has been shown to interact with: * CREB-binding protein, * Cyclin-dependent kinase 4, and * P16 p16 (also known as p16INK4a, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, CDKN2A, multiple tumor suppressor 1 and numerous other synonyms), is a protein that slows cell division by slowing the progression of the cell cycle from the G1 phase to the S p .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * {{gene-19-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin-dependent Kinase 4
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 also known as cell division protein kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CDK4'' gene. CDK4 is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein is highly similar to the gene products of ''S. cerevisiae'' cdc28 and ''S. pombe'' cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression. The activity of this kinase is restricted to the G1-S phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits D-type cyclins and CDK inhibitor p16INK4a. This kinase was shown to be responsible for the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product ( Rb). Ser/Thr-kinase component of cyclin D-CDK4 (DC) complexes that phosphorylate and inhibit members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulate the cell-cycle during G1/S transition. Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
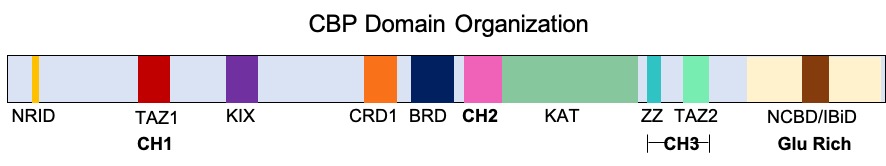
CREB-binding Protein
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the ''CREBBP'' gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively unique acetyltransferase activity is also seen in another transcription enzyme, EP300 (p300). Together, they are known as the p300-CBP coactivator family and are known to associate with more than 16,000 genes in humans; however, while these proteins share many structural features, emerging evidence suggests that these two co-activators may promote transcription of genes with different biological functions. For example, CBP alone has been implicated in a wide variety of pathophysiologies inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |