|
SCSI RDMA Protocol
In computing the SCSI RDMA Protocol (SRP) is a protocol that allows one computer to access SCSI devices attached to another computer via remote direct memory access (RDMA).ANSI T10 SRPr16a, www.t10.org ANSI T10 SRPr16a, web.archive.org /ref> The SRP protocol is also known as the SCSI Remote Protocol. The use of RDMA makes higher throughput and lower latency possible than what is generally available through e.g. the TCP/IP communication protocol. Though the SRP protocol has been designed to use RDMA networks efficiently, it is also possible to implement the SRP protocol over networks that do not support RDMA.
|
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISCSI Extensions For RDMA
The iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER) is a computer network protocol that extends the Internet Small Computer System Interface (iSCSI) protocol to use Remote Direct Memory Access ( RDMA). RDMA is provided by either the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) with RDMA services (iWARP) that uses existing Ethernet setup and therefore no need of huge hardware investment, RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) that does not need the TCP layer and therefore provides lower latency, or InfiniBand. It permits data to be transferred directly into and out of SCSI computer memory buffers (which connects computers to storage devices) without intermediate data copies and without much CPU intervention. History An RDMA consortium was announced on May 31, 2002, with a goal of product implementations by 2003. The consortium released their proposal in July, 2003. The protocol specifications were published as drafts in September 2004 in the Internet Engineering Task Force and issued as RFCs in October 2007. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCST
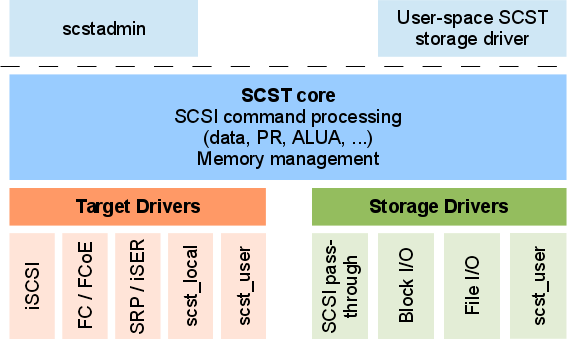
SCST is a GPL licensed SCSI target software stack. The design goals of this software stack are high performance, high reliability, strict conformance to existing SCSI standards, being easy to extend and easy to use. SCST does not only support multiple SCSI protocols (iSCSI, FC, SRP, ...) but also supports multiple local storage interfaces (SCSI pass-through, block I/O and file I/O) and also storage drivers implemented in user-space via the scst_user driver. In order to reach maximum performance SCST has been implemented as a set of kernel drivers. SCST is often combined with RAID, data deduplication and/or high-availability cluster software to augment its functionality. The SCST software stack is the basis software of many SAN systems. Several world records have been set with SAN systems based on SCST. SCST competes with LIO Target for the same purpose of providing a generic SCSI target module inside the Linux kernel. For the narrower purpose providing a Linux iSCSI target, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LIO Target
In computing, Linux-IO (LIO) Target is an open-source implementation of the SCSI target that has become the standard one included in the Linux kernel. Internally, LIO does not initiate sessions, but instead provides one or more Logical Unit Number In computer storage, a logical unit number, or LUN, is a number used to identify a logical unit, which is a device addressed by the SCSI protocol or by Storage Area Network protocols that encapsulate SCSI, such as Fibre Channel or iSCSI. A LUN m ...s (LUNs), waits for SCSI commands from a SCSI initiator, and performs required input/output data transfers. LIO supports common storage fabrics, including FCoE, Fibre Channel, IEEE 1394, iSCSI, iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER), SCSI RDMA Protocol (SRP) and Universal Serial Bus, USB. It is included in most Linux distributions; native support for LIO in QEMU/Kernel-based Virtual Machine, KVM, libvirt, and OpenStack makes LIO also a storage option for cloud deployments. LIO is maintained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mellanox
Mellanox Technologies Ltd. ( he, מלאנוקס טכנולוגיות בע"מ) was an Israeli-American multinational supplier of computer networking products based on InfiniBand and Ethernet technology. Mellanox offered adapters, switches, software, cables and silicon for markets including high-performance computing, data centers, cloud computing, computer data storage and financial services. On March 11, 2019, Nvidia announced its intent to acquire the company for $6.9 billion. Other companies willing to acquire Mellanox were Intel, Xilinx and Microsoft. The deal closed on April 27, 2020, with approval from the EU, U.S. and Chinese antitrust authorities. The company was integrated into Nvidia's networking division in 2020 and Nvidia stopped using the brand name "Mellanox" for its new networking products. History 1999–2009 Mellanox was founded in May 1999 by former Israeli executives of Intel Corporation and Galileo Technology (which was acquired by Marvell Technology Group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Networking
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies, based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies. The nodes of a computer network can include personal computers, servers, networking hardware, or other specialised or general-purpose hosts. They are identified by network addresses, and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes, rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the transmission medium used to carry signals, bandwidth, communications protocols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |