|
Szemerényi's Law
Szemerényi's law (or Szemerényi's lengthening) is both a sound change and a synchronic phonological rule that operated during an early stage of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). Though its effects are evident in many reconstructed as well as attested forms, it did not operate in late PIE, having become morphologized (with exceptions reconstructible via the comparative method). It is named for Hungarian linguist Oswald Szemerényi. Overview The rule deleted coda fricatives *s or laryngeals *h₁, *h₂ or *h₃ (cover symbol *H), with compensatory lengthening Compensatory lengthening in phonology and historical linguistics is the lengthening of a vowel sound that happens upon the loss of a following consonant, usually in the syllable coda, or of a vowel in an adjacent syllable. Lengthening triggered b ... occurring in a word-final position after resonants. In other words: : */-VRs/, */-VRH/ > *-VːR : */-VRH-/ > *-VR- (no examples of ''s''-deletion can be reconstructe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Change
A sound change, in historical linguistics, is a change in the pronunciation of a language. A sound change can involve the replacement of one speech sound (or, more generally, one phonetic feature value) by a different one (called phonetic change) or a more general change to the speech sounds that exist (phonological change), such as the merger of two sounds or the creation of a new sound. A sound change can eliminate the affected sound, or a new sound can be added. Sound changes can be environmentally conditioned if the change occurs in only some sound environments, and not others. The term "sound change" refers to diachronic changes, which occur in a language's sound system. On the other hand, " alternation" refers to changes that happen synchronically (within the language of an individual speaker, depending on the neighbouring sounds) and do not change the language's underlying system (for example, the ''-s'' in the English plural can be pronounced differently depending on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stang's Law
Stang's law is a Proto-Indo-European (PIE) phonological rule named after the Norwegian linguist Christian Stang. Overview The law governs the word-final sequences of a vowel, followed by a semivowel ( or ) or a laryngeal ( or ), followed by a nasal. According to the law these sequences are simplified such that laryngeals and semivowels are dropped, with compensatory lengthening of a preceding vowel. This rule is usually cited in more restricted form as: and ( denoting a vowel and a long vowel). Often the rules and also are added: * PIE 'sky' (accusative singular) > > Sanskrit ''dyā́m'', acc. sg. of ''dyaús'', Latin ''diem'' (which served as the basis for Latin ''diēs'' 'day'), Greek Ζῆν (''Zên'') (reformed after Homeric Greek to Ζῆνα ''Zêna'', subsequently Δία ''Día''), acc. of Ζεύς (''Zeús'') * PIE 'cow' (acc. sg.) > > Sanskrit ''gā́m'', acc. sg. of ''gaús'', Greek (Homeric and dialectal) βών (''bṓn''), acc. sg. of βοῦς (''boûs' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
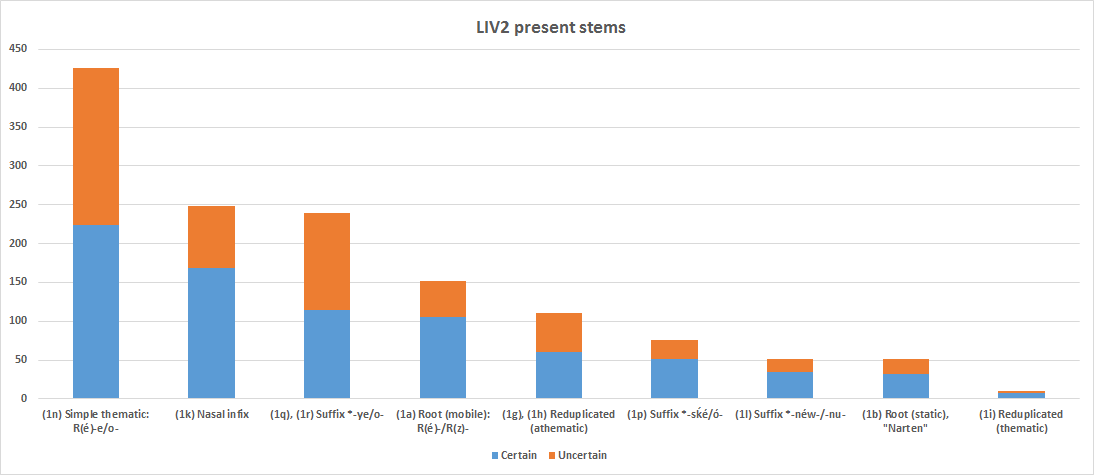
PIE Verb
Proto-Indo-European verbs reflect a complex system of morphology, more complicated than the substantive, with verbs categorized according to their aspect, using multiple grammatical moods and voices, and being conjugated according to person, number and tense. In addition to finite forms thus formed, non-finite forms such as participles are also extensively used.Beekes, 18.1.1. The verbal system is clearly represented in Ancient Greek and Vedic Sanskrit, which closely correspond, in nearly all aspects of their verbal systems, and are two of the most well-understood of the early daughter languages of Proto-Indo-European. Basics Verb conjugation in Proto-Indo-European involves the interplay of six dimensions (number, person, voice, mood, aspect and tense) with the following variables identified under the ''Cowgill-Rix'' system, which is one of the methodologies proposed and applies only to certain subfamilies: Further, participles can be considered part of the verbal syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |