|
Sverdrup Transport
The Sverdrup balance, or Sverdrup relation, is a theoretical relationship between the wind stress exerted on the surface of the open ocean and the vertically integrated meridional (north-south) transport of ocean water. History Aside from the oscillatory motions associated with tidal flow, there are two primary causes of large scale flow in the ocean: ''(1)'' thermohaline processes, which induce motion by introducing changes at the surface in temperature and salinity, and therefore in seawater density, and ''(2)'' wind forcing. In the 1940s, when Harald Sverdrup was thinking about calculating the gross features of ocean circulation, he chose to consider exclusively the wind stress component of the forcing. As he says in his 1947 paper, in which he presented the Sverdrup relation, this is probably the more important of the two. After making the assumption that frictional dissipation is negligible, Sverdrup obtained the simple result that the meridional mass transport (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wind Stress
In physical oceanography and fluid dynamics, the wind stress is the shear stress exerted by the wind on the free surface, surface of large bodies of water – such as oceans, seas, estuary, estuaries and lakes. When wind is blowing over a water surface, the wind applies a wind force on the water surface. The wind stress is the component of this wind force that is parallel to the surface per unit area. Also, the wind stress can be described as the flux of horizontal momentum applied by the wind on the water surface. The wind stress causes a deformation of the water body whereby wind waves are generated. Also, the wind stress drives ocean currents and is therefore an important driver of the large-scale ocean circulation. The wind stress is affected by the wind speed, the shape of the wind waves and the atmospheric stratification. It is one of the components of the air–sea interaction, with others being the atmospheric pressure on the water surface, as well as the exchange of energy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Barotropic Vorticity Equation
The barotropic vorticity equation assumes the atmosphere is nearly barotropic, which means that the direction and speed of the geostrophic wind are independent of height. In other words, there is no vertical wind shear of the geostrophic wind. It also implies that thickness contours (a proxy for temperature) are parallel to upper level height contours. In this type of atmosphere, high and low pressure areas are centers of warm and cold temperature anomalies. Warm-core highs (such as the subtropical ridge and the Bermuda-Azores high) and cold-core lows have strengthening winds with height, with the reverse true for cold-core highs (shallow Arctic highs) and warm-core lows (such as tropical cyclones). A simplified form of the vorticity equation for an inviscid, divergence-free flow (solenoidal velocity field), the barotropic vorticity equation can simply be stated as :\frac = 0, where is the material derivative and :\eta = \zeta + f is ''absolute vorticity'', with ''ζ'' bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
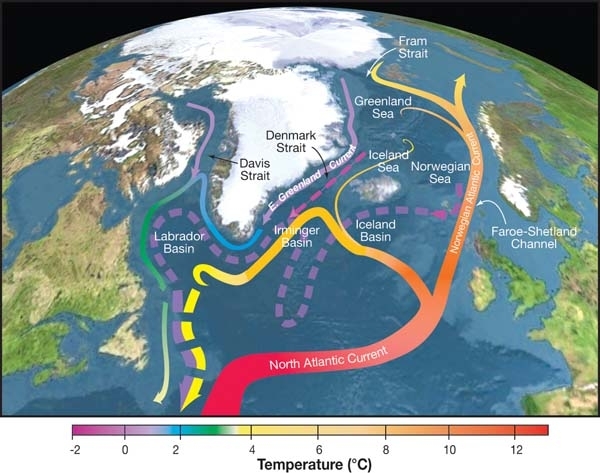
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is the main ocean current system in the Atlantic Ocean.IPCC, 2021Annex VII: Glossary [Matthews, J.B.R., V. Möller, R. van Diemen, J.S. Fuglestvedt, V. Masson-Delmotte, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, A. Reisinger (eds.)]. IClimate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2215–2256, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.022. It is a component of Earth's ocean circulation system and plays an important role in the climate system. The AMOC includes Atlantic currents at the surface and at great depths that are driven by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carl-Gustaf Rossby
Carl-Gustaf Arvid Rossby ( 28 December 1898 – 19 August 1957) was a Swedish-born American meteorologist who first explained the large-scale motions of the atmosphere in terms of fluid mechanics. He identified and characterized both the jet stream and the long waves in the westerlies that were later named Rossby waves. Biography Carl-Gustaf Rossby was born in Stockholm, Sweden. He was the first of five children born to Arvid and Alma Charlotta (Marelius) Rossby. He attended Stockholm University, where he developed his first interest in mathematical physics. Rossby came into meteorology and oceanography while studying geophysics under Vilhelm Bjerknes at the Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen in Bergen, Norway, during 1919, where Bjerknes' group was developing the groundbreaking concepts that became known as the Bergen School of Meteorology, including theory of the polar front. He also studied at the University of Leipzig and at the Lindenberg Observatory (''Mete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Walter Munk
Walter Heinrich Munk (October 19, 1917 – February 8, 2019) was an American physical oceanographer. He was one of the first scientists to bring statistical methods to the analysis of oceanographic data. Munk worked on a wide range of topics, including surface waves, geophysical implications of variations in the Earth's rotation, tides, internal waves, deep-ocean drilling into the sea floor, acoustical measurements of ocean properties, sea level rise, and climate change. His work won awards including the National Medal of Science, the Kyoto Prize, and induction to the French Legion of Honour. Munk's career began before the outbreak of World War II and ended nearly 80 years later with his death in 2019. The war interrupted his doctoral studies at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography (Scripps), and led to his participation in U.S. military research efforts. Munk and his doctoral advisor Harald Sverdrup developed methods for forecasting wave conditions which were used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ocean Basin
In hydrology, an oceanic basin (or ocean basin) is anywhere on Earth that is covered by seawater. Geologically, most of the ocean basins are large geologic basins that are below sea level. Most commonly the ocean is divided into basins following the continents distribution: the North and South Atlantic (together approximately 75 million km2/ 29 million mi2), North and South Pacific (together approximately 155 million km2/ 59 million mi2), Indian Ocean (68 million km2/ 26 million mi2) and Arctic Ocean (14 million km2/ 5.4 million mi2). Also recognized is the Southern Ocean (20 million km2/ 7 million mi2). All ocean basins collectively cover 71% of the Earth's surface, and together they contain almost 97% of all water on the planet. They have an average depth of almost 4 km (about 2.5 miles). Definitions of boundaries Boundaries based on continents ''" Limits of Oceans and Seas"'',International Hydrographic Organization (IHO), (1953): Limits of Oceans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Western Boundary Current
Boundary currents are ocean currents with dynamics determined by the presence of a coastline, and fall into two distinct categories: western boundary currents and eastern boundary currents. Eastern boundary currents Eastern boundary currents are relatively shallow, broad and slow-flowing. They are found on the eastern side of oceanic basins (adjacent to the western coasts of continents). Subtropical eastern boundary currents flow equatorward, transporting cold water from higher latitudes to lower latitudes; examples include the Benguela Current, the Canary Current, the Humboldt (Peru) Current, and the California Current. Coastal upwelling often brings nutrient-rich water into eastern boundary current regions, making them productive areas of the ocean. Western boundary currents Western boundary currents may themselves be divided into sub-tropical or low-latitude western boundary currents. Sub-tropical western boundary currents are warm, deep, narrow, and fast-flowing currents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coriolis Effect
In physics, the Coriolis force is a pseudo force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motion of the object. In one with anticlockwise (or counterclockwise) rotation, the force acts to the right. Deflection of an object due to the Coriolis force is called the Coriolis effect. Though recognized previously by others, the mathematical expression for the Coriolis force appeared in an 1835 paper by French scientist Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis, in connection with the theory of water wheels. Early in the 20th century, the term ''Coriolis force'' began to be used in connection with meteorology. Newton's laws of motion describe the motion of an object in an inertial (non-accelerating) frame of reference. When Newton's laws are transformed to a rotating frame of reference, the Coriolis and centrifugal accelerations appear. When applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Henry Stommel
Henry Melson Stommel (September 27, 1920 – January 17, 1992) was a major contributor to the field of physical oceanography. Beginning in the 1940s, he advanced theories about global ocean circulation patterns and the behavior of the Gulf Stream that form the basis of physical oceanography today. Widely recognized as one of the most influential and productive oceanographers of his time, Stommel was both a groundbreaking theoretician and an astute, seagoing observer. Early life and education Stommel was born in Wilmington, Delaware. An anomaly among modern scientists, Stommel became a full professor without an earned doctorate. He received his B.S. in astronomy from Yale University (1942) and served there as instructor in mathematics and astronomy (1942–44). Academic posts He was research associate at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution from 1944 to 1959 where the Office of Naval Research generously supported his projects. He became professor of oceanography at Harv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ekman Transport
Ekman transport is part of Ekman motion theory, first investigated in 1902 by Vagn Walfrid Ekman. Winds are the main source of energy for ocean circulation, and Ekman transport is a component of wind-driven ocean current. Ekman transport occurs when ocean surface waters are influenced by the friction force acting on them via the wind. As the wind blows it casts a friction force on the ocean surface that drags the upper 10-100m of the water column with it. However, due to the influence of the Coriolis force, Coriolis effect, as the ocean water moves it is subject to a force at a 90° angle from the direction of motion causing the water to move at an angle to the wind direction. The direction of transport is dependent on the hemisphere: in the Northern Hemisphere, northern hemisphere, transport veers clockwise from wind direction, while in the Southern Hemisphere, southern hemisphere it veers anticlockwise.Colling, pp 42-44 This phenomenon was first noted by Fridtjof Nansen, who reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ekman Layer
Ekman transport is part of Ekman motion theory, first investigated in 1902 by Vagn Walfrid Ekman. Winds are the main source of energy for ocean circulation, and Ekman transport is a component of wind-driven ocean current. Ekman transport occurs when ocean surface waters are influenced by the friction force acting on them via the wind. As the wind blows it casts a friction force on the ocean surface that drags the upper 10-100m of the water column with it. However, due to the influence of the Coriolis effect, as the ocean water moves it is subject to a force at a 90° angle from the direction of motion causing the water to move at an angle to the wind direction. The direction of transport is dependent on the hemisphere: in the northern hemisphere, transport veers clockwise from wind direction, while in the southern hemisphere it veers anticlockwise.Colling, pp 42-44 This phenomenon was first noted by Fridtjof Nansen, who recorded that ice transport appeared to occur at an angle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Unit Vector
In mathematics, a unit vector in a normed vector space is a Vector (mathematics and physics), vector (often a vector (geometry), spatial vector) of Norm (mathematics), length 1. A unit vector is often denoted by a lowercase letter with a circumflex, or "hat", as in \hat (pronounced "v-hat"). The term ''normalized vector'' is sometimes used as a synonym for ''unit vector''. The normalized vector û of a non-zero vector u is the unit vector in the direction of u, i.e., :\mathbf = \frac=(\frac, \frac, ... , \frac) where ‖u‖ is the Norm (mathematics), norm (or length) of u and \, \mathbf\, = (u_1, u_2, ..., u_n). The proof is the following: \, \mathbf\, =\sqrt=\sqrt=\sqrt=1 A unit vector is often used to represent direction (geometry), directions, such as normal directions. Unit vectors are often chosen to form the basis (linear algebra), basis of a vector space, and every vector in the space may be written as a linear combination form of unit vectors. Orthogonal coordinates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |