|
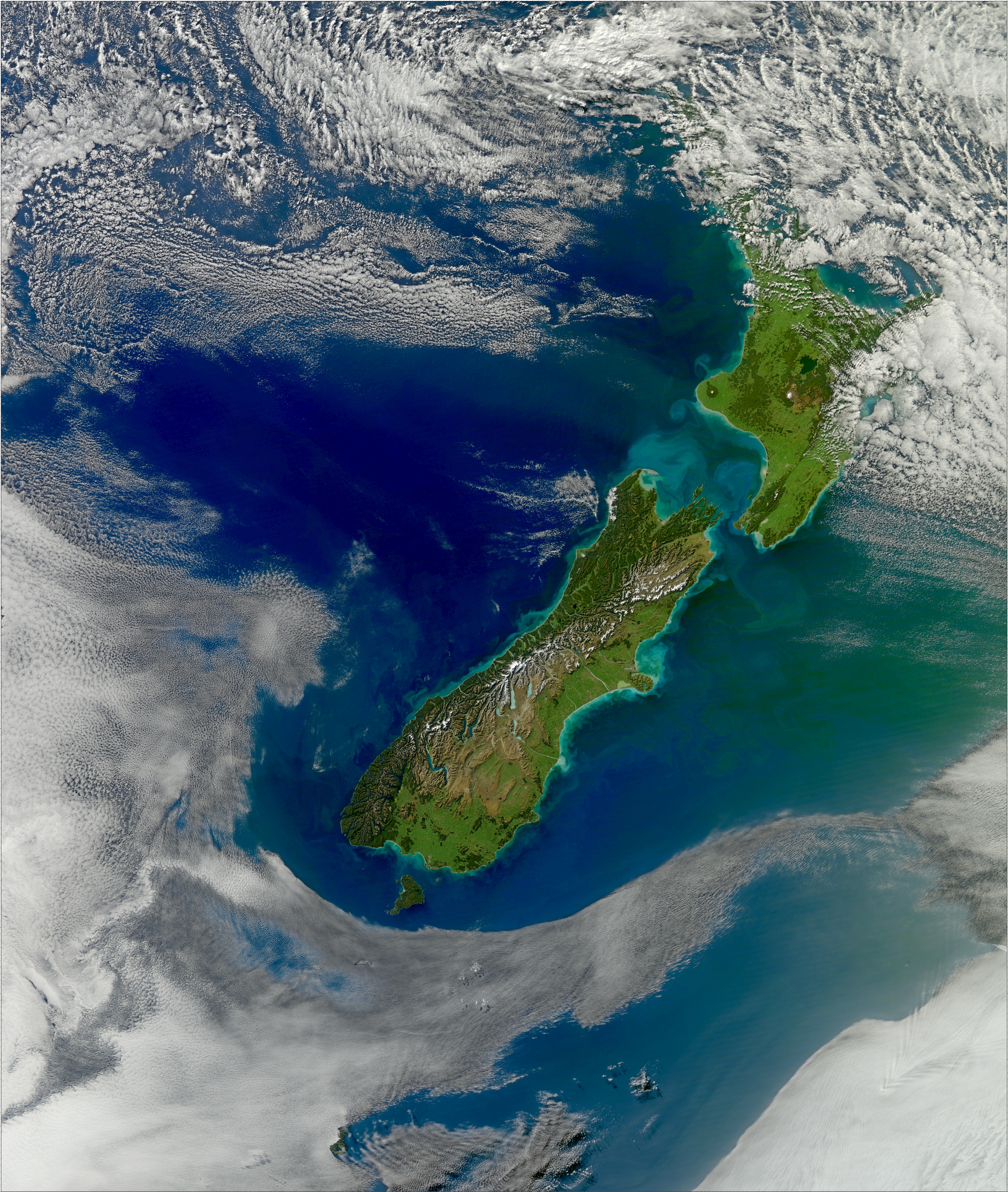
Sustainability In New Zealand
Sustainability in New Zealand is being increasingly recognised as being good practice and the government has made some moves toward this goal. History Over the relatively short human occupation of New Zealand, huge changes had been made to the natural environment. Although efforts were made by a small number of individuals and organisations in highlighting environmental issues, only ad-hoc measures were made by the government at central and local level. Sustainability became a concept that emerged from the environmental movement which become a social and political movement of its own right in the 1960s. In 1972 the Values Party formed, being the first national-level Green party. The New Zealand government has enacted legislation to enshrine sustainability principles in law, notably the Resource Management Act 1991. It was a landmark piece of legislation, being the first to adopt the principle of sustainability. In 2003 the government announced the Sustainable Development Prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainability Govt Nz Logo
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable living). Sustainability is commonly described as having three dimensions (also called pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many publications state that the environmental dimension (also called "planetary integrity" or "ecological integrity") is the most important, and, in everyday usage, "sustainability" is often focused on countering major environmental problems, such as climate change, loss of biodiversity, loss of ecosystem services, land degradation, and air and water pollution. Humanity is now exceeding several "planetary boundaries". A closely related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used synonymously. However, UNESCO distinguishes the two thus: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Growth
Green growth is a term to describe a hypothetical path of economic growth that is environmentally sustainable. It is based on the understanding that as long as economic growth remains a predominant goal, a decoupling of economic growth from resource use and adverse environmental impacts is required. As such, green growth is closely related to the concepts of green economy and low-carbon or sustainable development. A main driver for green growth is the transition towards sustainable energy systems. Advocates of green growth policies argue that well-implemented green policies can create opportunities for employment in sectors such as renewable energy, green agriculture, or sustainable forestry. Several countries and international organizations, such as the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), World Bank, and United Nations, have developed strategies on green growth; others, such as the Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI), are specifically dedicated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Centre For Sustainable Cities
The New Zealand Centre for Sustainable Cities states that it is an inter-disciplinary research centre "dedicated to providing the research base for innovative solutions to the economic, social, environmental and cultural development" of New Zealand urban centres. It states "87% of New Zealanders live in cities. The health and well-being of a significant proportion of (New Zealand) population is reliant on developing environments that take into account the connections between transport, design, energy, health and governance and other issues." Professor Philippa Howden-Chapman of the University of Otago is the director and states: :"The centre builds on a strong existing network of expertise. It is a partnership, led by the University of Otago, of six universities - Otago, Canterbury, Victoria, Massey, Waikato and Auckland - two Crown Research Institutes, Landcare and NIWA and BRANZ. It is positioned to work with regional councils, territorial local authorities and national agenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Building In New Zealand
This article is intended to give an overview of green building in New Zealand. Green Building Council The New Zealand Green Building Council formed in July 2005. An establishment board was formed later in 2005 and with formal organisational status granted on 1 February 2006. That month Jane Henley was appointed as the CEO and activity to gain membership of the World Green Building Council began. In July 2006 the first full board was appointed with 12 members reflecting wide industry involvement. The several major milestones were achieved in 2006/2007; becoming a member of the international green building council, the launch of the Green Star NZ — Office Design Tool, and welcoming of member companies. Green Star The Green Star rating system is a tool implemented by the NZGBC to measure the environmental attributes and performance of buildings. The system is voluntary and similar to that of other countries. See also * Sustainability in New Zealand * Environment of New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generation Zero (organisation)
Generation Zero is a youth-led organisation in New Zealand focused on transitioning society away from its dependency on fossil fuels and combating climate change. Generation Zero "was founded with the central purpose of providing solutions for New Zealand to cut carbon pollution through smarter transport, liveable cities & independence from fossil fuels." The group believes that young people must be at the forefront of tackling climate change, and that "young people are the inheritors of humanity’s response". Campaigns Power Shift conference In December 2012, the first New Zealand Power Shift conference was held at Auckland University, attracting over 700 people. Modelled off an international phenomenon, over 40 workshops, speakers, and participants combined to produce a festive atmosphere for the three days of learning and upskilling about climate change. The flash mob dancing at the end of the conference attracted media attention. 50/50 campaign Generation Zero's 50/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Of New Zealand
The environment of New Zealand is characterised by an endemic flora and fauna which has evolved in near isolation from the rest of the world. The main islands of New Zealand span two biomes, temperate and subtropical, complicated by large mountainous areas above the tree line.Walter, H. & Breckle, S-W. (2002). ''Walter's Vegetation of the Earth: The Ecological Systems of the Geo-Biosphere''. New York: Springer-Verlag, p. 86 There are also New Zealand Subantarctic Islands, numerous smaller islands which extend into the subantarctic. The prevailing weather systems bring significantly more rain to the west of the country. New Zealand's territorial waters cover a much larger area than its landmass and extend over the continental shelf and abyssal plateau in the South Pacific Ocean, Tasman Sea and Southern ocean. Historically having an isolated and endemic ecosystem far into modernity, the arrival of Polynesians about 1300 AD and then later European settlers began to have significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Efficiency And Conservation Authority
Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority (EECA) is a New Zealand government/Crown agency responsible for promoting energy efficiency and conservation. The EECA was set up by the Fourth National Government of New Zealand in 1992 to encourage, support and promote energy efficiency, energy conservation, and the use of renewable sources of energy. The EECA, by promoting energy efficiency, helps to reduce climate change and GHG emissions through energy efficiency measures. History In 2000 EECA became a Crown entity, established under the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Act 2000. It is subject to the Crown Entities Act 2004. The passing of the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Act meant that for the first time, New Zealand had a legislative basis for promoting energy efficiency, energy conservation, and renewable energy. The Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority is responsible for preparing a national energy efficiency and conservation strategy for approval by the admin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation In New Zealand
Conservation in New Zealand has a history associated with both Māori and Europeans. Both groups of people caused a loss of species and both altered their behaviour to a degree after realising their effect on indigenous flora and fauna. Protected areas New Zealand has thirteen national parks, forty four marine reserves and many other protected areas for the conservation of biodiversity. The introduction of many invasive species is threatening the indigenous biodiversity, since the geographical isolation of New Zealand led to the evolution of plants and animals that did not have traits to protect against predation. New Zealand has a high proportion of endemic species, so pest control is generally regarded as a high priority. The New Zealand Department of Conservation administers approximately 30% of New Zealand's land, along with less than 1% of the country's marine environment, for conservation and recreational purposes. It has published lists, under the New Zealand Threat C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Footprint
The ecological footprint is a method promoted by the Global Footprint Network to measure human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people or an economy. It tracks this demand through an ecological accounting system. The accounts contrast the biologically productive area people use for their consumption to the biologically productive area available within a region or the world (biocapacity, the productive area that can regenerate what people demand from nature). In short, it is a measure of human impact on the environment. Footprint and biocapacity can be compared at the individual, regional, national or global scale. Both footprint and biocapacity change every year with number of people, per person consumption, efficiency of production, and productivity of ecosystems. At a global scale, footprint assessments show how big humanity's demand is compared to what Earth can renew. Global Footprint Network estimates that, as of 2014, humanity has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Performance Index
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale from microscopic to global in extent. It can also be subdivided according to its attributes. Examples include the marine environment, the atmospheric environment and the terrestrial environment. The number of biophysical environments is countless, given that each living organism has its own environment. The term ''environment'' can refer to a singular global environment in relation to humanity, or a local biophysical environment, e.g. the UK's Environment Agency. Life-environment interaction All life that has survived must have adapted to the conditions of its environment. Temperature, light, humidity, soil nutrients, etc., all influence the species within an environment. However, life in turn modifies, in various forms, its conditions. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Economic Development (New Zealand)
The Ministry of Economic Development ( mi, Manatū Ōhanga) was a New Zealand public sector organisation tasked with promoting development of New Zealand's economy. Known as the Ministry of Commerce until 2000, it was renamed in 2000 under the Fifth Labour Government, then replaced with the Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment on 1 July 2012 by the subsequent National Government. The Ministry dealt with policy in a wide range of different areas including energy, communications, the radio spectrum, industry and regional development, intellectual property, consumer issues, tourism, international trade, and the regulatory environment. At the time of its disestablishment, the Ministry supported eight ministerial portfolios: the Minister of Economic Development (Lead Minister for the Ministry of Economic Development), the Minister of Commerce, the Minister for Communications and Information Technology, the Minister of Consumer Affairs, the Minister of Energy and Resour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Herald
''The New Zealand Herald'' is a daily newspaper published in Auckland, New Zealand, owned by New Zealand Media and Entertainment, and considered a newspaper of record for New Zealand. It has the largest newspaper circulation of all newspapers in New Zealand, peaking at over 200,000 copies in 2006, although circulation of the daily ''Herald'' had declined to 100,073 copies on average by September 2019. Its main circulation area is the Auckland region. It is also delivered to much of the upper North Island including Northland, Waikato and King Country. History ''The New Zealand Herald'' was founded by William Chisholm Wilson, and first published on 13 November 1863. Wilson had been a partner with John Williamson in the ''New Zealander'', but left to start a rival daily newspaper as he saw a business opportunity with Auckland's rapidly growing population. He had also split with Williamson because Wilson supported the war against the Māori (which the ''Herald'' termed "the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)