|
Surface Activated Bonding
Surface activated bonding (SAB) is a low-temperature wafer bonding technology with atomically clean and activated surfaces. Surface activation prior to bonding by using fast atom bombardment is typically employed to clean the surfaces. High-strength bonding of semiconductor, metal, and dielectric can be obtained even at room temperature. Overview In the standard SAB method, wafer surfaces are activated by argon fast atom bombardment in ultra-high vacuum Ultra-high vacuum (UHV) is the vacuum regime characterised by pressures lower than about . UHV conditions are created by pumping the gas out of a UHV chamber. At these low pressures the mean free path of a gas molecule is greater than approximatel ... (UHV) of 10−4–10−7 Pa. The bombardment removes adsorbed contaminants and native oxides on the surfaces. The activated surfaces are atomically clean and reactive for formation of direct bonds between wafers when they are brought into contact even at room temperature. Researche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafer Bonding
Wafer bonding is a packaging technology on Wafer (electronics), wafer-level for the fabrication of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), microelectronics and optoelectronics, ensuring a mechanically stable and hermetically sealed encapsulation. The wafers' diameter range from 100 mm to 200 mm (4 inch to 8 inch) for MEMS/NEMS and up to 300 mm (12 inch) for the production of microelectronic devices. Smaller wafers were used in the early days of the microelectronics industry, with wafers being just 1 inch in diameter in the 1950s. Overview In microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), the package protects the sensitive internal structures from environmental influences such as temperature, moisture, high pressure and oxidizing species. The long-term stability and reliability of the functional elements depend on the encapsulation process, as does the overall device cost. The package has to fulfil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
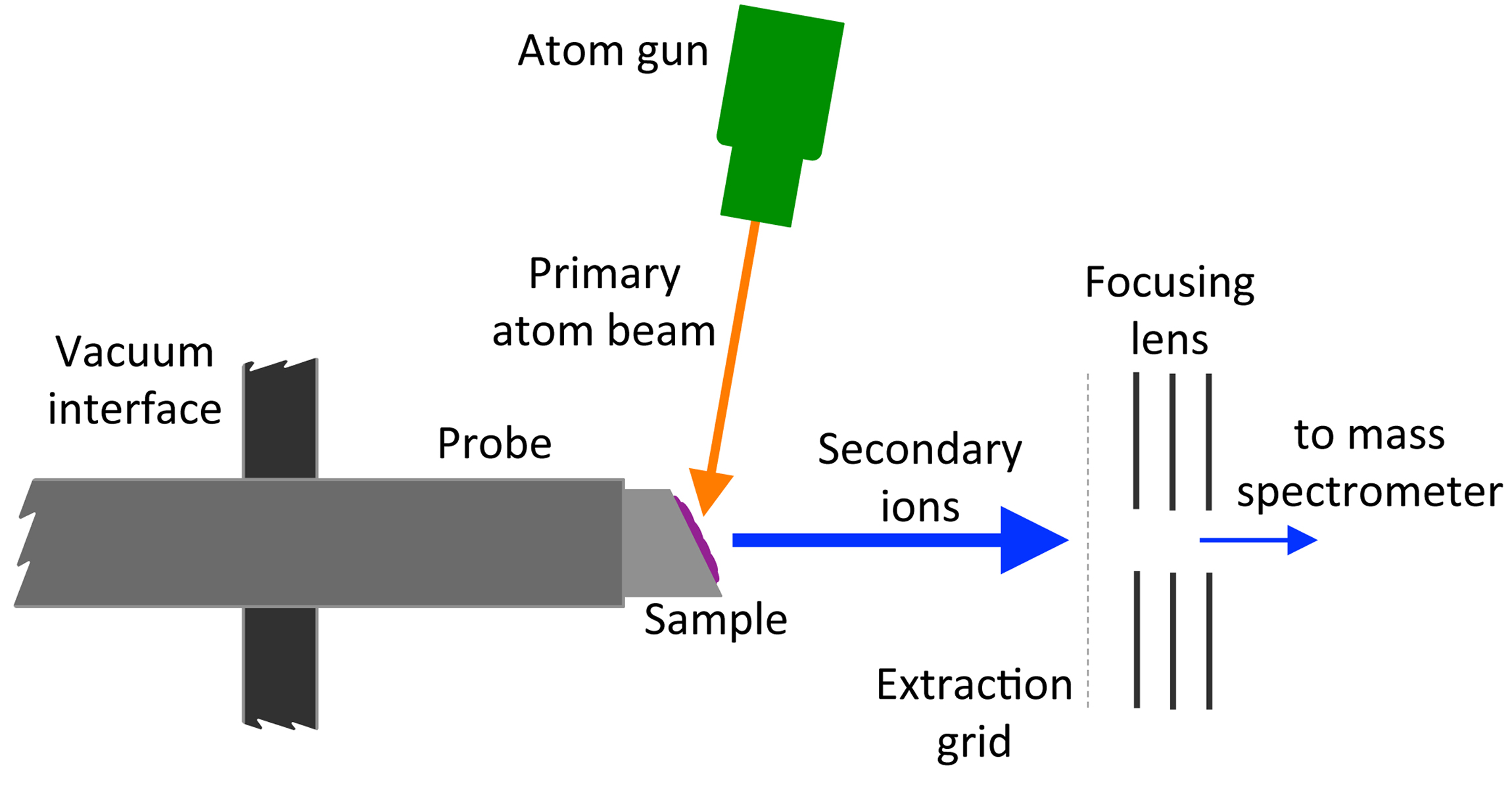
Fast Atom Bombardment
Fast atom bombardment (FAB) is an ionization technique used in mass spectrometry in which a beam of high energy atoms strikes a surface to create ions. It was developed by Michael Barber at the University of Manchester in 1980. When a beam of high energy ions is used instead of atoms (as in secondary ion mass spectrometry), the method is known as liquid secondary ion mass spectrometry (LSIMS). In FAB and LSIMS, the material to be analyzed is mixed with a non-volatile chemical protection environment, called a matrix, and is bombarded under vacuum with a high energy (4000 to 10,000 electron volts) beam of atoms. The atoms are typically from an inert gas such as argon or xenon. Common matrices include glycerol, thioglycerol, 3-nitrobenzyl alcohol (3-NBA), 18-crown-6 ether, 2-nitrophenyloctyl ether, sulfolane, diethanolamine, and triethanolamine. This technique is similar to secondary ion mass spectrometry and plasma desorption mass spectrometry. Ionization mechanism FAB is a rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glass. Its electrical resistivity and conductivity, resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping (semiconductor), doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into wires) and malleable (they can be hammered into thin sheets). These properties are the result of the ''metallic bond'' between the atoms or molecules of the metal. A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polymeric sulfur nitride. In physics, a metal is generally regarded as any substance capable of conducting electricity at a temperature of absolute zero. Many elements and compounds that are not normally classified as metals become metallic under high pressures. For example, the nonmetal iodine gradually becomes a metal at a pressure of between 40 and 170 thousand times atmospheric pressure. Equally, some materials regarded as metals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in an electrical conductor, because they have no loosely bound, or free, electrons that may drift through the material, but instead they shift, only slightly, from their average equilibrium positions, causing dielectric polarisation. Because of dielectric polarisation, positive charges are displaced in the direction of the field and negative charges shift in the direction opposite to the field (for example, if the field is moving parallel to the positive ''x'' axis, the negative charges will shift in the negative ''x'' direction). This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polaris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra-high Vacuum
Ultra-high vacuum (UHV) is the vacuum regime characterised by pressures lower than about . UHV conditions are created by pumping the gas out of a UHV chamber. At these low pressures the mean free path of a gas molecule is greater than approximately 40 km, so the gas is in free molecular flow, and gas molecules will collide with the chamber walls many times before colliding with each other. Almost all molecular interactions therefore take place on various surfaces in the chamber. UHV conditions are integral to scientific research. Surface science experiments often require a chemically clean sample surface with the absence of any unwanted adsorbates. Surface analysis tools such as X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and low energy ion scattering require UHV conditions for the transmission of electron or ion beams. For the same reason, beam pipes in particle accelerators such as the Large Hadron Collider are kept at UHV. Overview Maintaining UHV conditions requires the use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafer Bonding
Wafer bonding is a packaging technology on Wafer (electronics), wafer-level for the fabrication of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), microelectronics and optoelectronics, ensuring a mechanically stable and hermetically sealed encapsulation. The wafers' diameter range from 100 mm to 200 mm (4 inch to 8 inch) for MEMS/NEMS and up to 300 mm (12 inch) for the production of microelectronic devices. Smaller wafers were used in the early days of the microelectronics industry, with wafers being just 1 inch in diameter in the 1950s. Overview In microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), the package protects the sensitive internal structures from environmental influences such as temperature, moisture, high pressure and oxidizing species. The long-term stability and reliability of the functional elements depend on the encapsulation process, as does the overall device cost. The package has to fulfil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Technology
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities (" doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabricat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics Manufacturing
Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) is a term used for companies that design, manufacture, test, distribute, and provide return/repair services for electronic components and assemblies for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). The concept is also referred to as Electronics Contract Manufacturing (ECM). Many consumer electronics are built in China, due to maintenance cost, availability of materials, and speed as opposed to other countries such as the United States. Cities such as Shenzhen and Penang have become important production centres for the industry, attracting many consumer electronics companies such as Apple Inc. Some companies such as Flex (company), Flex and Wistron are Original design manufacturers and providers of Electronics manufacturing services. History The EMS industry was initially established in 1961 by SCI Systems of Huntsville Alabama. The industry realized its most significant growth in the 1980s; at the time, most electronics manufacturing for large-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packaging (microfabrication)
In electronics manufacturing, integrated circuit packaging is the final stage of semiconductor device fabrication, in which the block of semiconductor material is encapsulated in a supporting case that prevents physical damage and corrosion. The case, known as a " package", supports the electrical contacts which connect the device to a circuit board. In the integrated circuit industry, the process is often referred to as packaging. Other names include semiconductor device assembly, assembly, encapsulation or sealing. The packaging stage is followed by testing of the integrated circuit. The term is sometimes confused with electronic packaging, which is the mounting and interconnecting of integrated circuits (and other components) onto printed-circuit boards. Design considerations Electrical The current-carrying traces that run out of the die, through the package, and into the printed circuit board (PCB) have very different electrical properties compared to on-chip signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Device Fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are present in everyday electrical and electronics, electronic devices. It is a multiple-step sequence of Photolithography, photolithographic and chemical processing steps (such as surface passivation, thermal oxidation, planar process, planar diffusion and p–n junction isolation, junction isolation) during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer (electronics), wafer made of pure semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications. The entire manufacturing process takes time, from start to packaged chips ready for shipment, at least six to eight weeks (tape-out only, not including the circuit design) and is performed in highly specialized semiconduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |