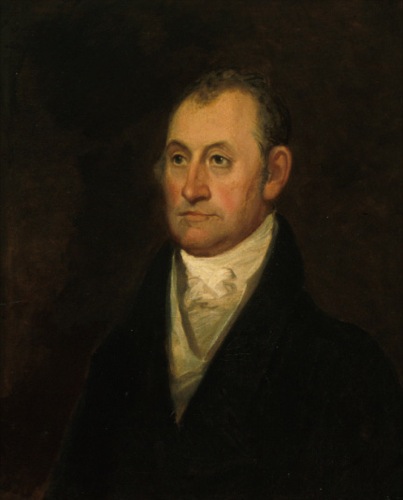|
Supreme Court Justice
The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest-ranking judicial body in the United States. Its membership, as set by the Judiciary Act of 1869, consists of the chief justice of the United States and eight Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, associate justices, any six of whom constitute a quorum. Appointments Clause, Article II, Section 2, Clause 2 of the Constitution grants plenary power to the President of the United States to nominate, and with the advice and consent of the United States Senate, appoint justices to the Supreme Court; justices have life tenure. Background The Supreme Court was created by Article Three of the United States Constitution, Article III of the Constitution of the United States, United States Constitution, which stipulates that the "judicial power of the United States, shall be vested in one Supreme Court," and was organized by the 1st United States Congress. Through the Judiciary Act of 1789, Congress specified the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Of The United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point of federal law. It also has original jurisdiction over a narrow range of cases, specifically "all Cases affecting Ambassadors, other public Ministers and Consuls, and those in which a State shall be Party." The court holds the power of judicial review, the ability to invalidate a statute for violating a provision of the Constitution. It is also able to strike down presidential directives for violating either the Constitution or statutory law. However, it may act only within the context of a case in an area of law over which it has jurisdiction. The court may decide cases having political overtones, but has ruled that it does not have power to decide non-justiciable political questions. Established by Article Three of the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Original Jurisdiction
In common law legal systems original jurisdiction of a court is the power to hear a case for the first time, as opposed to appellate jurisdiction, when a higher court has the power to review a lower court's decision. India In India, the Supreme Court has original, appellate and advisory jurisdiction. Its exclusive original jurisdiction extends to all cases between the Government of India and the States of India or between Government of India and states on one side and one or more states on other side or cases between different states. Original jurisdiction is related to cases directly brought to the Supreme Court. Cases that require the interpretation of the constitution or cases relating to the denial of fundamental rights are heard in the Supreme Court. In case there is a dispute between two or more states or between the union and the states, the Supreme Court decides such cases. In addition, Article 131 of the Constitution of India grants original jurisdiction to the Supr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clarence Thomas
Clarence Thomas (born June 23, 1948) is an American jurist who serves as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. He was nominated by President George H. W. Bush to succeed Thurgood Marshall and has served since 1991. After Marshall, Thomas is the second African American to serve on the Court and its longest-serving member since Anthony Kennedy's retirement in 2018. Thomas was born in Pin Point, Georgia. After his father abandoned the family, he was raised by his grandfather in a poor Gullah community near Savannah. Growing up as a devout Catholic, Thomas originally intended to be a priest in the Catholic Church but was frustrated over the church's insufficient attempts to combat racism. He abandoned his aspiration of becoming a clergyman to attend the College of the Holy Cross and, later, Yale Law School, where he was influenced by a number of conservative authors, notably Thomas Sowell, who dramatically shifted his worldview from progressive to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Roberts
John Glover Roberts Jr. (born January 27, 1955) is an American lawyer and jurist who has served as the 17th chief justice of the United States since 2005. Roberts has authored the majority opinion in several landmark cases, including ''National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius,'' '' Shelby County v. Holder'', and '' Riley v. California''. He has been described as having a conservative judicial philosophy but, above all, is an institutionalist. He has shown a willingness to work with the Supreme Court's liberal bloc, and after the retirement of Anthony Kennedy in 2018, he has been regarded as the primary swing vote on the Court. However, Roberts is no longer regarded as the Court's median vote following the replacement of Ruth Bader Ginsburg by Amy Coney Barrett in 2020. Roberts grew up in northwestern Indiana and was educated in a series of Catholic schools. He studied history at Harvard University and then attended Harvard Law School, where he was managing e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CBS News
CBS News is the news division of the American television and radio service CBS. CBS News television programs include the ''CBS Evening News'', ''CBS Mornings'', news magazine programs '' CBS News Sunday Morning'', '' 60 Minutes'', and '' 48 Hours'', and Sunday morning political affairs program ''Face the Nation''. CBS News Radio produces hourly newscasts for hundreds of radio stations, and also oversees CBS News podcasts like '' The Takeout Podcast''. CBS News also operates a 24-hour digital news network. Up until April 2021, the president and senior executive producer of CBS News was Susan Zirinsky, who assumed the role on March 1, 2019. Zirinsky, the first female president of the network's news division, was announced as the choice to replace David Rhodes on January 6, 2019. The announcement came amid news that Rhodes would step down as president of CBS News "amid falling ratings and the fallout from revelations from an investigation into sexual misconduct allegations" ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visiting Judge
A visiting judge is a judge appointed to hear a case as a member of a court to which he or she does not ordinarily belong. In United States federal courts, this is referred to as an assignment "by designation" of the Chief Justice of the United States (for inter- circuit assignments) or the Circuit Chief Judge (for intra-circuit assignments), and is authorized by (for active district judges) or (for retired justices and judges). In many United States Courts of Appeals it is not uncommon for a district judge to sit on a panel as a visiting judge; less frequently it is a judge from another circuit (in active service or, more commonly, in senior status). Retired Supreme Court justices have done the same, including Justices Sandra Day O'Connor and David Souter, and very unusually, sitting justices (in 1984, for example, Justice William Rehnquist served as a visiting judge for a jury trial in the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Virginia). This is someti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Code
In the law of the United States, the Code of Laws of the United States of America (variously abbreviated to Code of Laws of the United States, United States Code, U.S. Code, U.S.C., or USC) is the official compilation and codification of the general and permanent federal statutes. It contains 53 titles (Titles 1–54, excepting Title 53, which is reserved for a proposed title on small business). The main edition is published every six years by the Office of the Law Revision Counsel of the House of Representatives, and cumulative supplements are published annually.About United States Code Gpo.gov. Retrieved on 2013-07-19. The official version of these laws appears in the '' |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judicial Circuits Act
The Judicial Circuits Act of 1866 (ch. 210, ) reorganized the United States circuit courts and provided for the gradual elimination of several seats on the Supreme Court of the United States. It was signed into law on July 23, 1866, by President Andrew Johnson. It in effect denied him the opportunity of appointing any justices to the Supreme Court. It was the first major legislation dealing with the judiciary following the American Civil War. The Act redrew the boundaries of the judicial circuits and reduced the number of circuits from ten to nine. It also provided for the gradual reduction in the number of seats on the Supreme Court from the ten that had been authorized in 1863 to seven and established in large measure the geographical outlines of the circuits ever since. As it happened, only two seats, those of John Catron and James Moore Wayne, were abolished during the brief three-year interval of the Act's efficacy, before being superseded by the Judiciary Act of 1869. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenth Circuit Act Of 1863
The Tenth Circuit Act of 1863 () was a federal statute which increased the size of the Supreme Court of the United States from nine justices to ten, and which also reorganized the circuit courts of the federal judiciary. The newly created Tenth Circuit consisted of California and Oregon, and addressed the judicial needs of the newly created western states. The Act became effective on March 3, 1863, during the Lincoln administration. History The period of the American Civil War and the immediate aftermath of Reconstruction saw shakeups in the Court and in legislation concerning its size. This culminated in the Judiciary Act of 1869, the last piece of legislation which altered the size of the Supreme Court. Pursuant to the Tenth Circuit 1863 Act, Stephen Johnson Field was installed in the newly created Associate Justice seat. Shortly thereafter, Salmon P. Chase replaced Roger B. Taney as Chief Justice of the United States, and in 1865 Associate Justice John Catron died; Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighth And Ninth Circuits Act Of 1837
The Eighth and Ninth Circuits Act of 1837 () was a federal statute which increased the size of the Supreme Court of the United States from seven justices to nine, and which also reorganized the circuit courts of the federal judiciary. The newly created Eighth and Ninth circuits were designed to alleviate the judicial needs of newly-created western states. The Act became law on March 3, 1837, at the end of the Jackson administration. History The period from 1834-1838 saw a major shakeup in the Court. During this period, Chief Justice John Marshall died and was replaced by Roger B. Taney, Associate Justice William Johnson died and was replaced by James Moore Wayne, and Associate Justice Gabriel Duvall resigned, being replaced by Philip P. Barbour. Further, the 1837 Act came into effect shortly after these replacements. John Catron and John McKinley were the first justices appointed to these newly created seats. File:John Catron - Brady-Handy.jpg, John Catron, first ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh Circuit Act Of 1807
The Seventh Circuit Act of 1807 (formally, "An Act establishing Circuit Courts, and abridging the jurisdiction of the district courts in the districts of Kentucky, Tennessee and Ohio", ; 9th Congress, ch. 16; enacted February 24, 1807) was a federal statute which increased the size of the Supreme Court of the United States from six Justices to seven, and which also reorganized the circuit courts of the federal judiciary. The Act became law on February 24, 1807, during the Jefferson administration. Text Effect The Act created a new seat on the U.S. Supreme Court and required the new Associate Justice to reside in the seventh circuit. Under the Act, the new seventh circuit consisted of Ohio, Kentucky and Tennessee. In early 1807, the Act became law, and the justice first appointed to the new seat was Thomas Todd Thomas Todd (January 23, 1765 – February 7, 1826) was an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1807 to 1826. Raised in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.png)