|
Supraorbital Nerve
The supraorbital nerve is one of two branches of the frontal nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve. The other branch of the frontal nerve is the supratrochlear nerve. Structure The supraorbital nerve branches from the frontal nerve midway between the base and apex of the orbit. It travels anteriorly above the levator palpebrae superioris and exits the orbit through the supraorbital foramen (or notch) in the superior margin orbit. It exits the orbit lateral to the supratrochlear nerve. It then ascends onto the forehead beneath the corrugator supercilii and frontalis muscles and divides into a medial branch and lateral branch. Function The supraorbital nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin of the lateral forehead and upper eyelid, as well as the conjunctiva of the upper eyelid and mucosa of the frontal sinus The frontal sinuses are one of the four pairs of paranasal sinuses that are situated behind the brow ridges. Sinuses are mucosa-lined airspaces within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunctiva
The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium (depending on the zone). The conjunctiva is highly vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies. Structure The conjunctiva is typically divided into three parts: Blood supply Blood to the bulbar conjunctiva is primarily derived from the ophthalmic artery. The blood supply to the palpebral conjunctiva (the eyelid) is derived from the external carotid artery. However, the circulations of the bulbar conjunctiva and palpebral conjunctiva are linked, so both bulbar conjunctival and palpebral conjunctival vessels are supplied by both the ophthalmic artery and the external carotid artery, to varying extents. Nerve supply Sensory innervation of the conjunctiva is divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
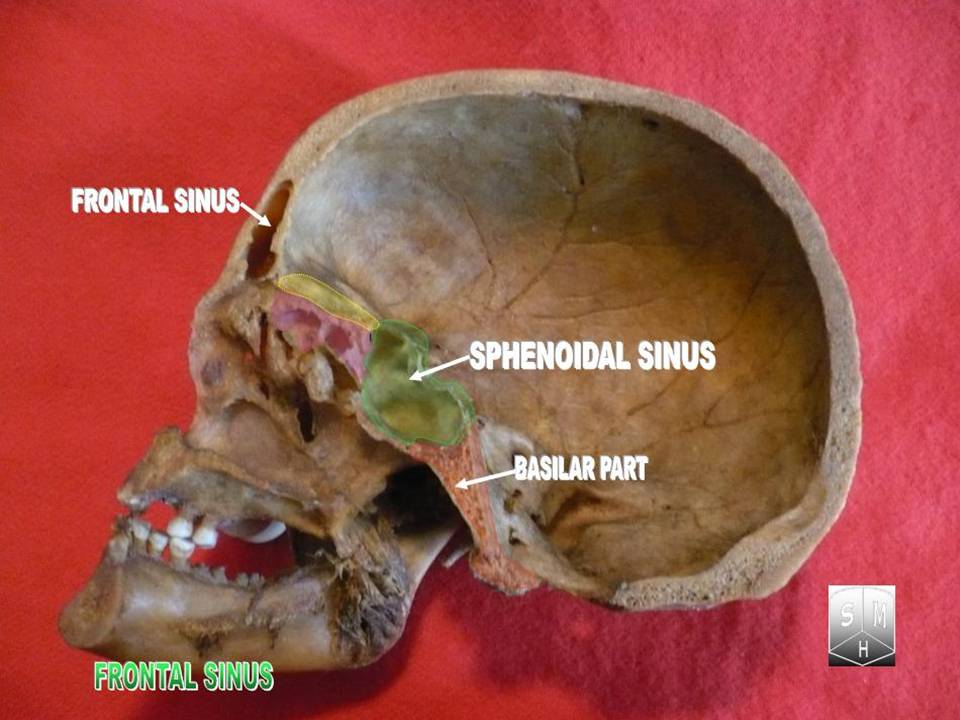
Frontal Sinus
The frontal sinuses are one of the four pairs of paranasal sinuses that are situated behind the brow ridges. Sinuses are mucosa-lined airspaces within the bones of the face and skull. Each opens into the anterior part of the corresponding middle nasal meatus of the nose through the frontonasal duct which traverses the anterior part of the labyrinth of the ethmoid. These structures then open into the semilunar hiatus in the middle meatus. Structure Each frontal sinus is situated between the external and internal plates of the frontal bone.Frontal sinuses are rarely symmetrical. Their average measurements are as follows: height 28 mm, breadth 24 mm, depth 20 mm, creating a space of 6-7 ml. Blood supply The mucous membrane of the frontal sinuses receives arterial supply via the supraorbital artery, and anterior ethmoidal artery. Innervation The mucous membrane in this sinus is innervated by the supraorbital nerve, which contains the postganglionic parasympathetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Nerve
The frontal nerve is the largest branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It supplies sensation to the skin of the forehead, the mucosa of the frontal sinus, and the skin of the upper eyelid. It may be affected by schwannoma. Structure The frontal nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). The frontal nerve branches immediately before entering the superior orbital fissure. In then travels superolateral to the annulus of Zinn between the lacrimal nerve and inferior ophthalmic vein. After entering the orbit it travels anteriorly between the roof periosteum and the levator palpebrae superioris. Midway between the apex and base of the orbit it divides into two branches, the supratrochlear nerve and supraorbital nerve. Functions The two branches of the frontal nerve provide sensory innervation to the skin of the forehead, mucosa of the frontal sinus (an air sinus), and the skin of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmic Nerve
The ophthalmic nerve (V1) is a sensory nerve of the face. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It has three branches that provide sensory innervation to the eye, the skin of the upper face, and the skin of the anterior scalp. Structure The ophthalmic nerve is the first branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It is joined by filaments from the cavernous plexus of the sympathetic, and communicates with the oculomotor, trochlear, and abducent nerves. It gives off a recurrent (meningeal) filament which passes between the layers of the tentorium. Branches The ophthalmic nerve divides into three major branches as it passes through the superior orbital fissure. *The nasociliary nerve gives off several sensory branches to the orbit. It then continues out through the anterior ethmoidal foramen, where it enters the nasal cavity. It provides innervation for much of the anterior nasal mucosa. It also gives off a branch which exits through the nasal bones to form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supratrochlear Nerve
The supratrochlear nerve is a branch of the frontal nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) from the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the forehead and the upper eyelid. Structure The supratrochlear nerve is a branch of the frontal nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) from the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It is smaller than the supraorbital nerve from the frontal nerve. It branches midway between the base and apex of the orbit. It passes above the Trochlea of superior oblique, trochlea of the superior oblique muscle. It then travels anteriorly above the levator palpebrae superioris muscle. It exits the orbit through the frontal notch in the superomedial margin of the orbit. It then ascends onto the forehead beneath the corrugator supercilii muscle and frontalis muscle. It then divides into sensory branches. The supratrochlear nerve travels with the supratrochlear artery, a branch of the ophthalmic artery. Func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraorbital Foramen
The supraorbital foramen, is a bony elongated opening located above the orbit (eye socket) and under the forehead. It is part of the frontal bone of the skull. The supraorbital foramen lies directly under the eyebrow. In some people this foramen is incomplete and is then known as the supraorbital notch. Structure The supraorbital foramen is a small groove at superior and medial margin of the orbit in the frontal bone. It is part of the frontal bone of the skull. It arches transversely below the superciliary arches and is the upper part of the brow ridge. It is thin and prominent in its lateral two-thirds, but rounded in its medial third. Between these two parts, the supraorbital nerve, the supraorbital artery, and the supraorbital vein pass. The supraorbital nerve divides into superficial and deep branches after it has left the supraorbital foramen. Additional images File:Gray135.png, Frontal bone. Inner surface. File:Gray1193.svg, Side view of head, showing surface relations of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrugator Supercilii
The corrugator supercilii muscle is a small, narrow, pyramidal muscle close to the eye. It arises from the medial end of the superciliary arch, and inserts into the deep surface of the skin of the eyebrow. It draws the eyebrow downward and medially, producing the vertical wrinkles of the forehead. Structure The corrugator supercilii muscle is located at the medial end of the eyebrow, beneath the frontalis muscle and just above the orbicularis oculi muscle. It arises from the medial end of the superciliary arch. Its fibers pass upward and laterally, between the palpebral and orbital portions of the orbicularis oculi muscle. It inserts into the deep surface of the skin of the eyebrow, above the middle of the orbital arch. Relations The supratrochlear nerve passes by the corrugator supercilii muscle between it and the frontalis muscle. Function The corrugator supercilii muscle draws the eyebrow downward and medially, producing the vertical wrinkles of the forehead. It is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontalis Muscles
The frontalis muscle () is a muscle which covers parts of the forehead of the skull. Some sources consider the frontalis muscle to be a distinct muscle. However, Terminologia Anatomica currently classifies it as part of the occipitofrontalis muscle along with the occipitalis muscle. In humans, the frontalis muscle only serves for facial expressions. The frontalis muscle is supplied by the facial nerve and receives blood from the supraorbital and supratrochlear arteries. Structure The frontalis muscle is thin, of a quadrilateral form, and intimately adherent to the superficial fascia. It is broader than the occipitalis and its fibers are longer and paler in color. It is located on the front of the head. The muscle has no bony attachments. Its medial fibers are continuous with those of the procerus; its intermediate fibers blend with the corrugator and orbicularis oculi muscles, thus attached to the skin of the eyebrows; and its lateral fibers are also blended with the latter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Eyelid
An eyelid is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. The human eyelid features a row of eyelashes along the eyelid margin, which serve to heighten the protection of the eye from dust and foreign debris, as well as from perspiration. "Palpebral" (and "blepharal") means relating to the eyelids. Its key function is to regularly spread the tears and other secretions on the eye surface to keep it moist, since the cornea must be continuously moist. They keep the eyes from drying out when asleep. Moreover, the blink reflex protects the eye from foreign bodies. The appearance of the human upper eyelid often varies between different populations. The prevalence of an epicanthic fold covering the inner corner of the eye account for the majority of East Asian and Southeast Asian populations, and is also found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |