|
Superposition Theorem
The superposition theorem is a derived result of the superposition principle suited to the network analysis of electrical circuits. The superposition theorem states that for a linear system (notably including the subcategory of time-invariant linear systems) the response (voltage or current) in any branch of a bilateral linear circuit having more than one independent source equals the algebraic sum of the responses caused by each independent source acting alone, where all the other independent sources are replaced by their internal impedances. To ascertain the contribution of each individual source, all of the other sources first must be "turned off" (set to zero) by: * Replacing all other independent voltage sources with a short circuit (thereby eliminating difference of potential i.e. ''V''=0; internal impedance of ideal voltage source is zero (short circuit)). * Replacing all other independent current sources with an open circuit (thereby eliminating current i.e. ''I''=0; int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superposition Principle
The superposition principle, also known as superposition property, states that, for all linear systems, the net response caused by two or more stimuli is the sum of the responses that would have been caused by each stimulus individually. So that if input ''A'' produces response ''X'' and input ''B'' produces response ''Y'' then input (''A'' + ''B'') produces response (''X'' + ''Y''). A function F(x) that satisfies the superposition principle is called a linear function. Superposition can be defined by two simpler properties: additivity F(x_1+x_2)=F(x_1)+F(x_2) \, and homogeneity F(a x)=a F(x) \, for scalar . This principle has many applications in physics and engineering because many physical systems can be modeled as linear systems. For example, a beam can be modeled as a linear system where the input stimulus is the load on the beam and the output response is the deflection of the beam. The importance of linear systems is that they are easier to analyze mathematically; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norton Equivalent
In direct-current circuit theory, Norton's theorem, also called the Mayer–Norton theorem, is a simplification that can be applied to networks made of linear time-invariant resistances, voltage sources, and current sources. At a pair of terminals of the network, it can be replaced by a current source and a single resistor in parallel. For alternating current (AC) systems the theorem can be applied to reactive impedances as well as resistances. The Norton equivalent circuit is used to represent any network of linear sources and impedances at a given frequency. Norton's theorem and its dual, Thévenin's theorem, are widely used for circuit analysis simplification and to study circuit's initial-condition and steady-state response. Norton's theorem was independently derived in 1926 by Siemens & Halske researcher Hans Ferdinand Mayer (1895–1980) and Bell Labs engineer Edward Lawry Norton (1898–1983). To find the equivalent, the Norton current ''I''no is calculated as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics. The requirement of zero interaction can often be relaxed if, for example, the interaction is perfectly elastic or regarded as point-like collisions. Under various conditions of temperature and pressure, many real gases behave qualitatively like an ideal gas where the gas molecules (or atoms for monatomic gas) play the role of the ideal particles. Many gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, noble gases, some heavier gases like carbon dioxide and mixtures such as air, can be treated as ideal gases within reasonable tolerances over a considerable parameter range around standard temperature and pressure. Generally, a gas behaves more like an ideal gas at higher temperature and lower pressu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
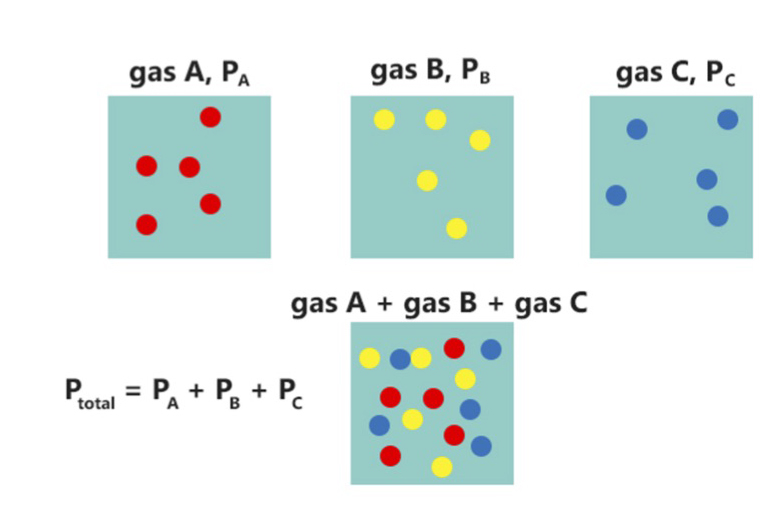
Partial Pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture (Dalton's Law). The partial pressure of a gas is a measure of thermodynamic activity of the gas's molecules. Gases dissolve, diffuse, and react according to their partial pressures but not according to their concentrations in gas mixtures or liquids. This general property of gases is also true in chemical reactions of gases in biology. For example, the necessary amount of oxygen for human respiration, and the amount that is toxic, is set by the partial pressure of oxygen alone. This is true across a very wide range of different concentrations of oxygen present in various inhaled breathing gases or dissolved in blood; consequently, mixture ratios, like that of breathab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton's Law
Dalton's law (also called Dalton's law of partial pressures) states that in a mixture of non-reacting gases, the total pressure exerted is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases. This empirical law was observed by John Dalton in 1801 and published in 1802.J. Dalton (1802)"Essay IV. On the expansion of elastic fluids by heat,"''Memoirs of the Literary and Philosophical Society of Manchester'', vol. 5, pt. 2, pages 595–602; see page 600. Dalton's law is related to the ideal gas laws. Formula Mathematically, the pressure of a mixture of non-reactive gases can be defined as the summation: p_\text = \sum_^n p_i = p_1+p_2+p_3+\cdots+p_n where ''p''1, ''p''2, ..., ''pn'' represent the partial pressures of each component. p_ = p_\text x_i where ''xi'' is the mole fraction of the ''i''th component in the total mixture of ''n'' components . Volume-based concentration The relationship below provides a way to determine the volume-based concentration of any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core, which induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction, discovered in 1831, describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil. Transformers are used to change AC voltage levels, such transformers being termed step-up or step-down type to increase or decrease voltage level, respectively. Transformers can also be used to provide galvanic isolation between circuits as well as to couple stages of signal-processing circuits. Since the invention of the first constant-potential transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the ''condenser microphone''. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a coil. When the current flowing through the coil changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces an electromotive force (''emf'') (voltage) in the conductor, described by Faraday's law of induction. According to Lenz's law, the induced voltage has a polarity (direction) which opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors oppose any changes in current through them. An inductor is characterized by its inductance, which is the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of inductance is the henry (H) named for 19th century American scientist Joseph Henry. In the measurement of magnetic circuits, it is equivalent to . Inductors have values that typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependent Source
In the theory of electrical networks, a dependent source is a voltage source or a current source whose value depends on a voltage or current elsewhere in the network.I. D. Mayergoyz, Wes Lawson ''Basic electric circuit theory: a one-semester text'' Gulf Professional Publishing, 1996 , Chapter 8 "Dependent sources and operational amplifiers" Dependent sources are useful, for example, in modeling the behavior of amplifiers. A bipolar junction transistor can be modeled as a dependent current source whose magnitude depends on the magnitude of the current fed into its controlling base terminal. An operational amplifier can be described as a voltage source dependent on the differential input voltage between its input terminals. Practical circuit elements have properties such as finite power capacity, voltage, current, or frequency limits that mean an ideal source is only an approximate model. Accurate modeling of practical devices requires using several idealized elements in combinatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Circuit
Open circuit may refer to: *Open-circuit scuba, a type of SCUBA-diving equipment where the user breathes from the set and then exhales to the surroundings without recycling the exhaled air *Open-circuit test, a method used in electrical engineering to determine the impedance in the excitation branch of a real transformer *Open-circuit voltage, the difference of electrical potential between two terminals of a device when there is no external load connected *An electrical circuit is an "open circuit" if it lacks a complete path between the terminals of its power source See also *Closed-circuit (other) *Short circuit (other) A short circuit is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or a very low electrical impedance. Short Circuit may also refer to: Film * ''Short Circuit'' (1943 film), an Italian film * ''Short Circu ... * Open system (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)