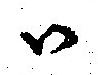|
Sundanese Script
Standard Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Baku'', ) is a writing system which is used by the Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Kuno'') which was used by the ancient Sundanese between the 14th and 18th centuries. Currently the standard Sundanese script is also commonly referred to as the Sundanese script. History Old Sundanese was developed based on the Pallava script of India, and was used from the 14th until the 18th centuries. The last manuscript written in Old Sundanese script was ''Carita Waruga Guru.'' From the 17th to the 19th centuries, Sundanese was mostly spoken and not written. Javanese and Pegon scripts were used to write Sundanese during this period. In 1996, the government of West Java announced a plan to introduce an official Sundanese script, and in October 1997, Old Sundanese script was chosen and renamed to ''Aksara Sunda.'' Typology The standardized script has 32 basic characters, consists of 7 ''aksara swara'' (in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Sundanese Script
Old Sundanese script () is a script that developed in West Java in the 14th–18th centuries which was originally used to write Old Sundanese language. The Old Sundanese script is a development of the Pallava script which has reached the stage of modifying its distinctive form as used in lontar texts in the 16th century. History The use of Old Sundanese script in its earliest form is found in the inscriptions found in Astana Gede, Kawali District, Ciamis Regency, and the Kebantenan Inscription in Jatiasih District, Bekasi City. Edi S. Ekajati revealed that the existence of the Old Sundanese script had been displaced for a long time due to the expansion of the Islamic Mataram Kingdom into the Priangan region, except for Cirebon and Banten. At that time the Sundanese conquerors made Javanese culture their role model and ideal type. As a result, Sundanese culture was displaced by Javanese culture. In fact, many Sundanese writers and cultural observers use Javanese writi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Sundanese Language
Old Sundanese (Sundanese script: , Old Sundanese script: , Buda script: , ) is the earliest recorded stage of the Sundanese language which is spoken in the western part of Java. The evidence is recorded in inscriptions from around the 12th to 14th centuries and ancient palm-leaf manuscripts from the 15th to 17th centuries AD. Old Sundanese is no longer used today, but has developed into its descendant, modern Sundanese. Written Evidence Old Sundanese is recorded in stone inscriptions such as the Kawali Inscription in Ciamis, and the Batutulis inscription in Bogor, as well as in inscriptions made from copper plates such as the Kabantenan inscription from the Bekasi area. Other remains documenting the use of Old Sundanese are palm-leaf manuscripts from the Bandung, Garut, and Bogor regions. The manuscripts are now stored in several institutions, including Kabuyutan Ciburuy in Bayongbong Garut, Sri Baduga Museum in Bandung, the National Library of Indonesia in Jakarta, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Kawi
The Kawi or or Old Javanese script is a Brahmic script found primarily in Java and used across much of Maritime Southeast Asia between the 8th century and the 16th century.Aditya Bayu Perdana and Ilham Nurwansah 2020Proposal to encode Kawi/ref> The script is an abugida meaning that characters are read with an inherent vowel. Diacritics are used, either to suppress the vowel and represent a pure consonant, or to represent other vowels.De Casparis, J. G. ''Indonesian Palaeography: A History of Writing in Indonesia from the beginnings to c. AD 1500'', Leiden/Koln, 1975, pp. 35-42 with footnotes History The Kawi script is related to the Nagari or old-Devanagari script in India. Also called the Prae-Nagari in Dutch publications after the classic work of F.D.K. Bosch on early Indonesian scripts, the early-Nagari form of script was primarily used in the Kawi script form to write southeast Asian Sanskrit and Old Javanese language in central and eastern Java. Kawi is the ancestor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abugida
An abugida (, from Ge'ez language, Ge'ez: ), sometimes known as alphasyllabary, neosyllabary or pseudo-alphabet, is a segmental Writing systems#Segmental writing system, writing system in which consonant-vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is secondary. This contrasts with a full alphabet, in which vowels have status equal to consonants, and with an abjad, in which vowel marking is absent, Abjad#Impure abjads, partial, or optional (although in less formal contexts, all three types of script may be termed alphabets). The terms also contrast them with a syllabary, in which the symbols cannot be split into separate consonants and vowels. Related concepts were introduced independently in 1948 by James Germain Février (using the term ) and David Diringer (using the term ''semisyllabary''), then in 1959 by Fred Householder (introducing the term ''pseudo-alphabet''). The Ethiopian Semitic languages, Ethiopic term "abugi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lontar Manuscript
Palm-leaf manuscripts are manuscripts made out of dried palm leaves. Palm leaves were used as writing materials in the Indian subcontinent and in Southeast Asia reportedly dating back to the 5th century BCE. Their use began in South Asia and spread to other regions, as texts on dried and smoke-treated palm leaves of Palmyra palm or the talipot palm. Their use continued till the 19th century, when printing presses replaced hand-written manuscripts. One of the oldest surviving palm leaf manuscripts of a complete treatise is a Sanskrit Shaivism text from the 9th-century, discovered in Nepal, now preserved at the Cambridge University Library.Pārameśvaratantra (MS Add.1049.1) with images , Puṣkarapārameśvaratantra, University of Cambridge (2015) The [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, which is maintained by the Unicode Consortium, defines as of the current version (15.0) 149,186 characters covering 161 modern and historic scripts, as well as symbols, emoji (including in colors), and non-visual control and formatting codes. Unicode's success at unifying character sets has led to its widespread and predominant use in the internationalization and localization of computer software. The standard has been implemented in many recent technologies, including modern operating systems, XML, and most modern programming languages. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Universal Coded Character Set, ISO/IEC 10646, each being code-for-code identical with the other. ''The Unicode Standard'', however, includes more th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virama
Virama ( ्) is a Sanskrit phonological concept to suppress the inherent vowel that otherwise occurs with every consonant letter, commonly used as a generic term for a codepoint in Unicode, representing either # halanta, hasanta or explicit virāma, a diacritic in many Brahmic scripts, including the Devanagari and Bengali scripts, or # saṃyuktākṣara (Sanskrit: संयुक्ताक्षर) or implicit virama, a conjunct consonant or ligature. Unicode schemes of scripts writing Mainland Southeast Asia languages, such as that of Burmese script and of Tibetan script, generally don't group the two functions together. Names The name is Sanskrit for "cessation, termination, end". As a Sanskrit word, it is used in place of several language-specific terms, such as: }, ''sukun'' , ް◌ , Derives from Arabic "sukun" , - , ''Srog med'' , Tibetan , ''Srog med'' , ྄ , Only used when transcribing Sanskrit Usage In Devanagari and many other Indic scripts, a virama is use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visarga
Visarga ( sa, विसर्गः, translit=visargaḥ) means "sending forth, discharge". In Sanskrit phonology ('' ''), ' (also called, equivalently, ' by earlier grammarians) is the name of a phone voiceless glottal fricative, , written as: Visarga is an allophone of and in pausa (at the end of an utterance). Since is a common inflectional suffix (of nominative singular, second person singular, etc.), visarga appears frequently in Sanskrit texts. In the traditional order of Sanskrit sounds, visarga and anusvāra appear between vowels and stop consonants. The precise pronunciation of visarga in Vedic texts may vary between Śākhās. Some pronounce a slight echo of the preceding vowel after the aspiration: will be pronounced , and will be pronounced . Visarga is not to be confused with colon. Types The visarga is commonly found in writing, resembling the punctuation mark of colon or as two tiny circles one above the other. This form is retained by most India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Close Back Unrounded Vowel
The close back unrounded vowel, or high back unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is . Typographically, it is a turned letter ; given its relation to the sound represented by the letter , it can be considered a with an extra "bowl". Features Occurrence See also *Index of phonetics articles A * Acoustic phonetics * Active articulator * Affricate * Airstream mechanism * Alexander John Ellis * Alexander Melville Bell * Alfred C. Gimson * Allophone * Alveolar approximant () * Alveolar click () * Alveolar consonant * Alveolar ejecti ... * Ɯ Notes References * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{IPA navigation Close vowels Back vowels Unrounded vowels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |