|
Sulfonamide Antibiotics
Sulfonamide is a functional group (a part of a molecule) that is the basis of several groups of drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic (nonantibiotic) antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides. Allergies to sulfonamides are common. The overall incidence of adverse drug reactions to sulfa antibiotics is approximately 3%, close to penicillin; hence medications containing sulfonamides are prescribed carefully. Sulfonamide drugs were the first broadly effective antibacterials to be used systemically, and paved the way for the antibiotic revolution in medicine. Function In bacteria, antibacterial sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase (DH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
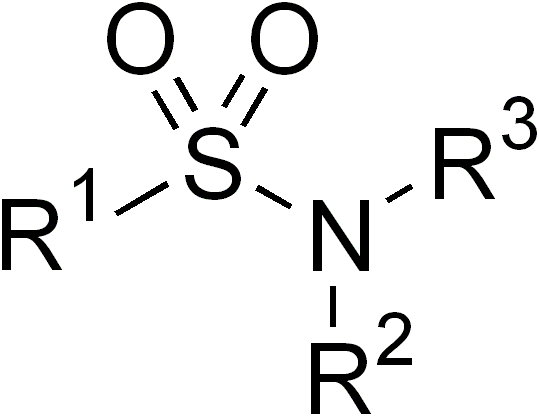
Sulfonamide
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for sulfa drug, a derivative or var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydropteroate Synthase
Dihydropteroate synthase is an enzyme classified under . It produces dihydropteroate in bacteria, but it is not expressed in most eukaryotes including humans. This makes it a useful target for sulfonamide antibiotics, which compete with the PABA precursor. * (2-amino-4-hydroxy-7,8-dihydropteridin-6-yl)methyl diphosphate + 4-aminobenzoate (PABA) \rightleftharpoons diphosphate + dihydropteroate. All organisms require reduced folate cofactors for the synthesis of a variety of metabolites. Most microorganisms must synthesize folate de novo because they lack the active transport system of higher vertebrate cells that allows these organisms to use dietary folates. Proteins containing this domain include dihydropteroate synthase () as well as a group of methyltransferase enzymes including methyltetrahydrofolate, corrinoid iron-sulphur protein methyltransferase (MeTr) that catalyses a key step in the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway of carbon dioxide fixation. Dihydropteroate synthase () (D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas (UK: sulphonylurea) are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture, for example as antidiabetic drugs widely used in the management of diabetes mellitus type 2. They act by increasing insulin release from the beta cells in the pancreas. A number of sulfonylureas are also used as herbicides, because they can interfere with plant biosynthesis of certain amino acids. Sulfonylureas are also used experimentally to inhibit interleukin 1 beta release from the NALP3 (or NLRP3) inflammasome. Drugs * First-generation drugs include acetohexamide, carbutamide, chlorpropamide, glycyclamide (tolcyclamide), metahexamide, tolazamide and tolbutamide. * Second-generation drugs include glibenclamide (glyburide), glibornuride, gliclazide, glipizide, gliquidone, glisoxepide and glyclopyramide. * Third-generation drugs include glimepiride, although it is sometimes considered a second-generation agent. Medical uses Sulfonylureas are used primarily for the treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetazolamide
Acetazolamide, sold under the trade name Diamox among others, is a medication used to treat glaucoma, epilepsy, altitude sickness, periodic paralysis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension (raised brain pressure of unclear cause), urine alkalinization, and heart failure. It may be used long term for the treatment of open angle glaucoma and short term for acute angle closure glaucoma until surgery can be carried out. It is taken Oral administration, by mouth or intravenous, injection into a vein. Acetazolamide is a first generation carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and it decreases the ocular fluid and osmolality in the eye to decrease intraocular pressure. Common side effects include numbness, tinnitus, ringing in the ears, loss of appetite, vomiting, and sleepiness. It is not recommended in those with significant kidney problems, liver problems, or who are sulfonamide allergy, allergic to sulfonamides. Acetazolamide is in the diuretic and carbonic anhydrase inhibitor families of me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsemide
Torasemide, also known as torsemide, is a diuretic medication used to treat fluid overload due to heart failure, kidney disease, and liver disease and high blood pressure. It is a less preferred treatment for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. Common side effects include headache, increased urination, diarrhea, cough, and dizziness. Other side effects may include hearing loss and low blood potassium. Torasemide is a sulfonamide and loop diuretic. Use is not recommended in pregnancy or breastfeeding. It works by decreasing the reabsorption of sodium by the kidneys. Torasemide was patented in 1974 and came into medical use in 1993. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 213th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2million prescriptions. Medical uses It is used to treat fluid overload due to heart failure. It is someti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bumetanide
Bumetanide, sold under the brand name Bumex among others, is a medication used to treat swelling and high blood pressure. This includes swelling as a result of heart failure, liver failure, or kidney problems. It may work for swelling when other medications have not. For high blood pressure it is not a preferred treatment. It is taken by mouth, or by injection into a vein or muscle. Effects generally begin within an hour and lasts for about six hours. Common side effects include dizziness, low blood pressure, low blood potassium, muscle cramps, and kidney problems. Other serious side effects may include hearing loss and low blood platelets. Blood tests are recommended regularly for those on treatment. Safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding is unclear. Bumetanide is a loop diuretic and works by decreasing the reabsorption of sodium by the kidneys. Bumetanide was patented in 1968 and came into medical use in 1972. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furosemide
Furosemide is a loop diuretic medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken by injection into a vein or by mouth. When taken by mouth, it typically begins working within an hour, while intravenously, it typically begins working within five minutes. Common side effects include feeling lightheaded while standing, ringing in the ears, and sensitivity to light. Potentially serious side effects include electrolyte abnormalities, low blood pressure, and hearing loss. Blood tests are recommended regularly for those on treatment. Furosemide is a type of loop diuretic that works by decreasing the reabsorption of sodium by the kidneys. Common side effects of furosemide injection include hypokalemia (low potassium level), hypotension (low blood pressure), and dizziness. Furosemide was patented in 1959 and approved for medical use in 1964. It is on the Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indapamide
Indapamide is a thiazide-like diuretic drug used in the treatment of hypertension, as well as decompensated heart failure. Combination preparations with perindopril (an ACE inhibitor antihypertensive) are available. The thiazide-like diuretics (indapamide and chlorthalidone) reduce risk of major cardiovascular events and heart failure in hypertensive patients compared with hydrochlorothiazide with a comparable incidence of adverse events. Both thiazide diuretics and thiazide-like diuretics are effective in reducing risk of stroke. Both drug classes appear to have comparable rates of adverse effects as other antihypertensives such as angiotensin II receptor blockers and dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers and lesser prevalence of side-effects when compared to ACE-inhibitors and non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers. It was patented in 1968 and approved for medical use in 1977. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Its in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metolazone
Metolazone is a thiazide-like diuretic marketed under the brand names Zytanix, Metoz, Zaroxolyn, and Mykrox. It is primarily used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure. Metolazone indirectly decreases the amount of water reabsorbed into the bloodstream by the kidney, so that blood volume decreases and urine volume increases. This lowers blood pressure and prevents excess fluid accumulation in heart failure. Metolazone is sometimes used together with loop diuretics such as furosemide or bumetanide, but these highly effective combinations can lead to dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities. It was patented in 1966 and approved for medical use in 1974. Medical uses One of the primary uses of metolazone is for treating edema (fluid retention) associated with congestive heart failure (CHF). In mild heart failure, metolazone or another diuretic may be used alone, or combined with other diuretics for moderate or severe heart failure. In addition to preventing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic medication often used to treat high blood pressure and swelling due to fluid build-up. Other uses include treating diabetes insipidus and renal tubular acidosis and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in those with a high calcium level in the urine. Hydrochlorothiazide is less effective than chlortalidone for prevention of heart attack or stroke. Hydrochlorothiazide is taken by mouth and may be combined with other blood pressure medications as a single pill to increase effectiveness. Potential side effects include poor kidney function; electrolyte imbalances, including low blood potassium, and, less commonly, low blood sodium, gout, high blood sugar, and feeling lightheaded with standing. While allergies to hydrochlorothiazide are reported to occur more often in those with allergies to sulfa drugs, this association is not well supported. It may be used during pregnancy, but it is not a first-line medication in this group. It is in the th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin ( antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine. Medical uses In medicine, diuretics are used to treat heart failure, liver cirrhosis, hypertension, influenza, water poisoning, and certain kidney diseases. Some diuretics, such as acetazolamide, help to make the urine more alkaline, and are helpful in increasing excretion of substances such as aspirin in cases of overdose or poisoning. Diuretics are sometimes abused by people with an eating disorder, especially people with bulimia nervosa, with the goa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiazide
Thiazide () refers to both a class of sulfur-containing organic molecules and a class of diuretics based on the chemical structure of benzothiadiazine. The thiazide drug class was discovered and developed at Merck and Co. in the 1950s. The first approved drug of this class, chlorothiazide, was marketed under the trade name Diuril beginning in 1958. In most countries, thiazides are the least expensive antihypertensive drugs available. Thiazide organic molecules are bi-cyclic structures that contain adjacent sulfur and nitrogen atoms on one ring. Confusion sometimes occurs because thiazide-like diuretics such as indapamide are referred to as thiazides despite not having the thiazide chemical structure. When used this way, "thiazide" refers to a drug which acts at the thiazide receptor. The thiazide receptor is a sodium-chloride transporter that pulls NaCl from the lumen in the distal convoluted tubule. Thiazide diuretics inhibit this receptor, causing the body to release NaCl and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |