|
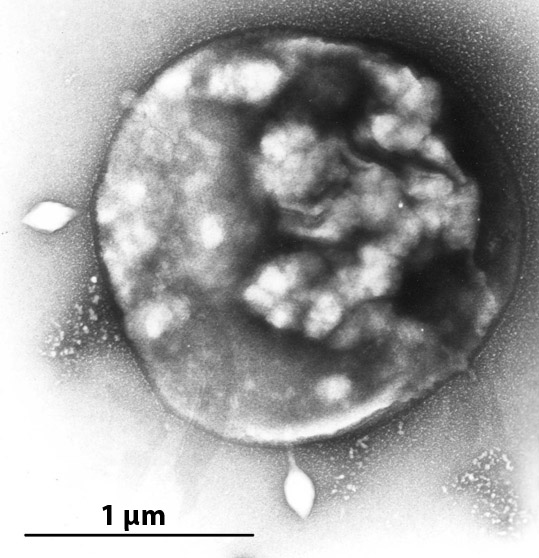
Sulfolobus Islandicus Filamentous Virus
''Sulfolobus islandicus filamentous virus'' (SIFV) is an archaeal virus, classified in the family ''Lipothrixviridae'' within the order ''Ligamenvirales''. The virus infects hypethermophilic and acidophilic archaeon ''Sulfolobus islandicus''. SIFV has a linear double-stranded DNA genome of 40,852 bp, which is the largest among characterized lipothrixviruses. The virions are enveloped filaments, nearly 2 micrometers in length. The nucleocapsid is formed from two paralogous major capsid proteins, which tightly wrap around the dsDNA genome; notably, dehydration of the genomic DNA by the major capsid proteins transforms the B-DNA, B-form DNA into A-DNA, A-form DNA. Life cycle SIFV virions assemble inside the cell. Binding of the major capsid protein dimers to the linear dsDNA genome lead to the assembly of nucleocapsids, which are subsequently enveloped intracellularly through an unknown mechanism. SIFV and probably other lipothrixviruses are lytic viruses. Virion release takes pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeal Virus
An archaeal virus is a virus that infects and replicates in archaea, a domain of unicellular, prokaryotic organisms. Archaeal viruses, like their hosts, are found worldwide, including in extreme environments inhospitable to most life such as acidic hot springs, highly saline bodies of water, and at the bottom of the ocean. They have been also found in the human body. The first known archaeal virus was described in 1974 and since then, a large diversity of archaeal viruses have been discovered, many possessing unique characteristics not found in other viruses. Little is known about their biological processes, such as how they replicate, but they are believed to have many independent origins, some of which likely predate the last archaeal common ancestor (LACA). Much of the diversity observed in archaeal viruses is their morphology. Their complete bodies, called virions, come in many different forms, including being shaped like spindles or lemons, rods, bottles, droplets, and coils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipothrixviridae
''Lipothrixviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order ''Ligamenvirales''. Thermophilic archaea in the phylum Thermoproteota serve as natural hosts. There are 11 species in this family, assigned to 4 genera. The genus Janekovic, D., Wunderl S, Holz I, Zillig W, Gierl A, Neumann H (1983) TTV1, TTV2 and TTV3, a family of viruses of the extremely thermophilic anaerobic, sulphur reducing, archaeabacterium Thermoproteus tenax. Mol. Gen. Genet. 19239–19245 Taxonomy The following genera and species are assigned to the family: * ''Alphalipothrixvirus'' ** '' Alphalipothrixvirus SBFV2'' ** '' Alphalipothrixvirus SFV1'' * '' Betalipothrixvirus'' ** '' Acidianus filamentous virus 3'' ** '' Acidianus filamentous virus 6'' ** '' Acidianus filamentous virus 7'' ** '' Acidianus filamentous virus 8'' ** '' Acidianus filamentous virus 9'' ** ''Sulfolobus islandicus filamentous virus'' * ''Deltalipothrixvirus'' ** ''Acidianus filamentous virus 2'' ** ''Deltalipothrixvirus SBFV3'' The family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligamenvirales
''Ligamenvirales'' is an order of linear viruses that infect archaea of the phylum Thermoproteota (formerly Crenarchaeota) and have double-stranded DNA genomes. The order was proposed by David Prangishvili and Mart Krupovic in 2012 and subsequently created by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). The name is derived from the Latin {{lang, la, ligamen, meaning ''string'' or ''thread''.{{cn, date=November 2022 Taxonomy There are three families in this order – ''Lipothrixviridae'', ''Rudiviridae'' and '' Ungulaviridae''.{{cn, date=November 2022 The virons are filamentous with a helical nucleocapsid. At either end are attached either fibers or more complex structures involved in host adhesion.{{cn, date=November 2022 The major coat proteins of both lipothrixviruses and rudiviruses have an unusual four-helix bundle topology.Goulet A, Blangy S, Redder P, Prangishvili D, Felisberto-Rodrigues C, Forterre P, Campanacci V, Cambillau C (2009) Acidianus filamentous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfolobus Islandicus
''Sulfolobus'' is a genus of microorganism in the family Sulfolobaceae. It belongs to the archaea domain. ''Sulfolobus'' species grow in volcanic springs with optimal growth occurring at pH 2-3 and temperatures of 75-80 °C, making them acidophiles and thermophiles respectively. ''Sulfolobus'' cells are irregularly shaped and flagellar. Species of ''Sulfolobus'' are generally named after the location from which they were first isolated, e.g. ''Sulfolobus solfataricus'' was first isolated in the Solfatara volcano. Other species can be found throughout the world in areas of volcanic or geothermal activity, such as geological formations called mud pots, which are also known as ''solfatare'' (plural of solfatara). ''Sulfolobus'' as a model to study the molecular mechanisms of DNA replication When the first Archaeal genome, '' Methanococcus jannaschii'', had been sequenced completely in 1996, it was found that the genes in the genome of ''Methanococcus jannaschii'' involv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-DNA
A-DNA is one of the possible double helical structures which DNA can adopt. A-DNA is thought to be one of three biologically active double helical structures along with B-DNA and Z-DNA. It is a right-handed double helix fairly similar to the more common B-DNA form, but with a shorter, more compact helical structure whose base pairs are not perpendicular to the helix-axis as in B-DNA. It was discovered by Rosalind Franklin, who also named the A and B forms. She showed that DNA is driven into the A form when under dehydrating conditions. Such conditions are commonly used to form crystals, and many DNA crystal structures are in the A form. The same helical conformation occurs in double-stranded RNAs, and in DNA-RNA hybrid double helices. Structure Like the more common B-DNA, A-DNA is a right-handed double helix with major and minor grooves. However, as shown in the comparison table below, there is a slight increase in the number of base pairs (bp) per turn. This results in a smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeal Viruses
An archaeal virus is a virus that infects and replicates in archaea, a domain of unicellular, prokaryotic organisms. Archaeal viruses, like their hosts, are found worldwide, including in extreme environments inhospitable to most life such as acidic hot springs, highly saline bodies of water, and at the bottom of the ocean. They have been also found in the human body. The first known archaeal virus was described in 1974 and since then, a large diversity of archaeal viruses have been discovered, many possessing unique characteristics not found in other viruses. Little is known about their biological processes, such as how they replicate, but they are believed to have many independent origins, some of which likely predate the last archaeal common ancestor (LACA). Much of the diversity observed in archaeal viruses is their morphology. Their complete bodies, called virions, come in many different forms, including being shaped like spindles or lemons, rods, bottles, droplets, and coils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |