|
Sukhothai Period
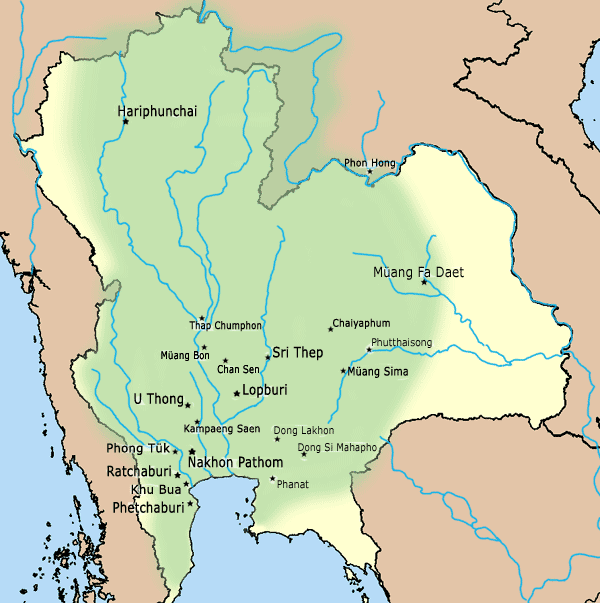
The Sukhothai Kingdom was a post-classical Siamese kingdom ( ''maṇḍala'') in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thailand. It evolved from a trading hub to a city-state in 1127 and emerged into the kingdom by Si Inthrathit in 1238. Sukhothai existed as an independent polity until 1438 when it fell under the influence of the neighboring Ayutthaya after the death of Borommapan (Maha Thammaracha IV). Sukhothai was originally a trade center in Lavo—itself under the suzerainty of the Khmer Empire from 946–1052—when Central Thai people led by Pho Khun Bang Klang Hao, a local leader, revolted and gained their independence. Bang Klang Hao took the regnal name of Si Inthrathit and became the first monarch of the Phra Ruang dynasty. The kingdom was centralized and expanded to its greatest extent during the reign of Ram Khamhaeng the Great (1279–1298), who some historians considered to have introduced T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maha Thammaracha (king Of Ayutthaya)
Maha Thammaracha (, , , ), Maha Thammarachathirat (, ), or Sanphet I (), formerly known as Khun Phirenthorathep (Old ; Modern ), was a king of Ayutthaya Kingdom from the Sukhothai dynasty, ruling from 1569 to 1590. As a powerful Sukhothai noble, Phirenthorathep gradually rose to power. After playing many political turns, he was eventually crowned as the King of Siam. A Sukhothai noble Before his ascension to the throne, Maha Thammaracha was known as Khun Phirenthorathep or "Okya Phitsanulok" (, ''okya'' being a high-ranking noble title conferred by the king). He descended from the Phra Ruang dynasty of the former Sukhothai Kingdom, which had been conquered by the Ayutthaya Kingdom in 1438. It was however not simply annexed, but its area—now known as the "northern cities" ''(Mueang Nuea)''—continued to be ruled by local aristocrats under Ayutthayan overlordship within the "mandala" model. During the reign of Borommatrailokkanat (1448–1488) however, the power of Sukhotha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spans . Thailand Template:Borders of Thailand, is bordered to the northwest by Myanmar, to the northeast and east by Laos, to the southeast by Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the southwest by the Andaman Sea; it also shares maritime borders with Vietnam to the southeast and Indonesia and India to the southwest. Bangkok is the state capital and List of municipalities in Thailand#Largest cities by urban population, largest city. Tai peoples, Thai peoples migrated from southwestern China to mainland Southeast Asia from the 6th to 11th centuries. Greater India, Indianised kingdoms such as the Mon kingdoms, Mon, Khmer Empire, and Monarchies of Malaysia, Malay states ruled the region, competing with Thai states s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan China
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai (Emperor Shizu or Setsen Khan), the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese history, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan's enthronement as Khagan in 1206 was described in Chinese as the Han-style title of Emperor and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in the Battle of Yamen. His realm was, by this point, isolated from the other Mongol-led khanates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
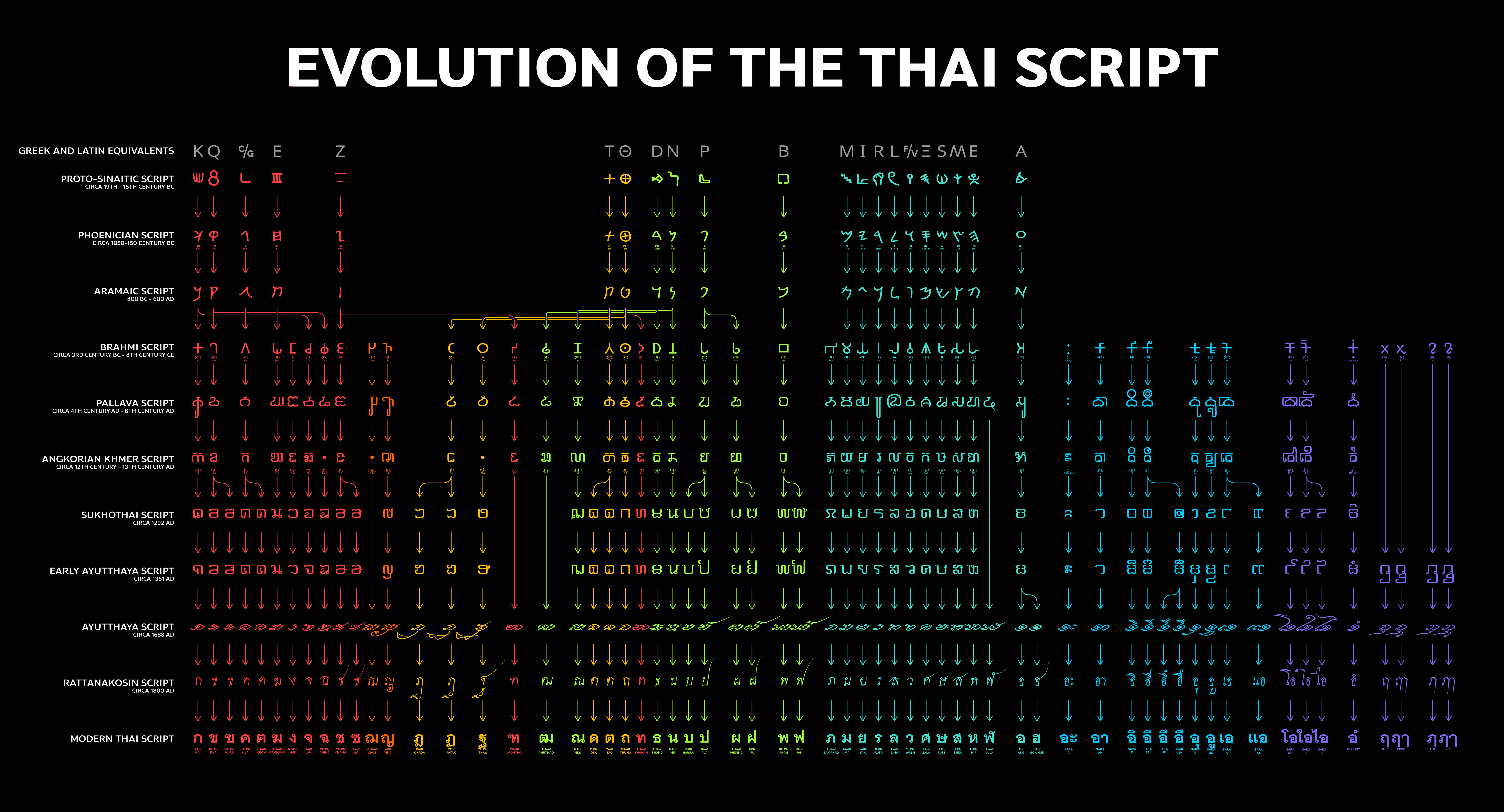
Sukhothai Script
The Sukhothai script, also known as the ''proto-Thai script'' and ''Ram Khamhaeng alphabet'', is a Brahmic script which originated in the Sukhothai Kingdom. The script is found on the Ram Khamhaeng Inscription and the ''Lö Thai inscription''. History Origin The Sukhothai script was based on a cursive form of Khmer script, which was formed by dissections, truncations and removal of flourishes from the original Khmer script. Scholar Michel Ferlus has demonstrated that certain peculiarities of ancient and modern Tai scripts can only be explained by inadequacies and gaps in the ancient Khmer script, in particular the pre-Angkorian Khmer script. The Sukhothai script is first attested on the Ram Khamhaeng stele, which is dated between 1283 and 1290, but it is the result of the modification of an unattested pre-existing script, based on the Khmer script. Ferlus theorizes that the pre-existing script may have developed during the pre-Angkorian period (7th–8th centuries), which would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theravada
''Theravāda'' (; 'School of the Elders'; ) is Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed ''Theravādins'' (anglicized from Pali ''theravādī''), have preserved their version of the Buddha's teaching or ''Dharma (Buddhism), Dhamma'' in the Pāli Canon for over two millennia. The Pāli Canon is the most complete Buddhist canon surviving in a Indo-Aryan languages, classical Indian language, Pāli, which serves as the school's sacred language and ''lingua franca''.Crosby, Kate (2013), ''Theravada Buddhism: Continuity, Diversity, and Identity'', p. 2. In contrast to Mahāyāna and Vajrayāna, Theravāda tends to be conservative in matters of doctrine (''pariyatti'') and monastic discipline (''vinaya''). One element of this Religious conservatism, conservatism is the fact that Theravāda rejects the authenticity of the Mahayana sutras (which appeared onwards). Consequently, Theravāda generally does not recognize the existence of many Buddhas and bodhisattva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Thai Monarchs
The succession of Monarchy of Thailand, Thai monarchs began with Si Inthrathit at the establishment of the Sukhothai Kingdom, first Thai kingdom in 1238. With brief interruptions, 55 monarchs have ruled over four successive kingdoms, the current monarch being Vajiralongkorn (Rama X) of the Chakri dynasty. Titles and naming conventions In the Sukhothai Kingdom, the monarch used the title ''Pho Khun'' (), and monarchs who reigned over the period of decline after Ram Khamhaeng the Great used the title ''Phraya'' (). In the Ayutthaya Kingdom and afterward, ''Thai royal ranks and titles, thanandon'', the system of Thai royal titles, determines the style of the monarch's full regnal name (which includes the title), consisting of two interconnected parts: * The first part is the title ''Phra Bat Somdet Phra Chao Yu Hua'' (, 'His Majesty the King'). The title is split by the regnal name, written between ''Phra'' and ''Chao''. If the monarch was not formally Coronation of the Thai monar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thai People
Thai people, historically known as Siamese people, are an ethnic group native to Thailand. In a narrower and ethnic sense, the Thais are also a Tai peoples, Tai ethnic group dominant in Central Thailand, Central and Southern Thailand (Siam proper). Part of the larger Tai ethno-linguistic group native to Southeast Asia as well as Southern China, Thais speak the Sukhothai languages (Thai language, Central Thai and Southern Thai language), which is classified as part of the Kra–Dai languages, Kra–Dai family of languages. The majority of Thais are followers of Theravada Buddhism. Thai cultural mandates, Government policies during the late 1930s and early 1940s resulted in the successful forced assimilation of various ethno-linguistic groups into the country's dominant Central Thai language and culture, leading to the term ''Thai people'' to come to refer to the Demographics of Thailand, population of Thailand overall. This includes other subgroups of the Tai ethno-linguistic grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khmer Empire
The Khmer Empire was an empire in Southeast Asia, centered on Hydraulic empire, hydraulic cities in what is now northern Cambodia. Known as Kambuja (; ) by its inhabitants, it grew out of the former civilization of Chenla and lasted from 802 to 1431. Historians call this period of History of Cambodia, Cambodian history the Angkor period, after the empire's most well-known capital, Angkor. The Khmer Empire ruled or vassalised most of Mainland Southeast Asia and stretched as far north as southern China. The beginning of the Khmer Empire is conventionally dated to 802, when Khmer people, Khmer prince Jayavarman II declared himself ''chakravartin'' (, a title equivalent to 'emperor') in the Phnom Kulen mountains. Although the end of the Khmer Empire has traditionally been marked with the fall of Angkor to the Siamese Ayutthaya Kingdom in 1431, the reasons for the empire's collapse are still debated amongst scholars. Researchers have determined that a period of strong monsoon rains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavo Kingdom
The Lavo Kingdom () was a political entity (Mandala (Southeast Asian political model), mandala) on the left bank of the Chao Phraya River in the Upper Chao Phraya valley from the end of Dvaravati civilization, in the 7th century, until 1388. The original center of Lavo was Lopburi, Lavapura and was shifted to Ayodhya (Xiān) in the 1080s. However, since both Ayodhya or Xiān and Lavo separately sent embassies to the Chinese court in the late 1200s, these two polities were potentially individual states. Before the 9th century, Lavo, together with other supra-regional settlements, such as Si Thep Historical Park, Si Thep, , Phimai Historical Park, Phimai, Nakhon Pathom, and others were the centers of the Mandala (political model), mandala-style polities of Dvaravati. Due to several circumstances, including climate changes and the invasions of the surrounding polities, several Dvaravati centers lost their prosperity, and the mandalas in the Chao Phraya River, Menam Valley was then s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainland Southeast Asia
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west and the Pacific Ocean to the east. It includes the countries of Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam as well as Peninsular Malaysia. The term ''Indochina'' (originally ''Indo-China'') was coined in the early nineteenth century, emphasizing the historical cultural influence of Indian and Chinese civilizations on the region. The term was later adopted as the name of the colony of French Indochina (present-day Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam). Today, the term "Mainland Southeast Asia" is more commonly used, in contrast to Maritime Southeast Asia for the island groups off the coast of the peninsula. Terminology In Indian sources, the earliest name connected with Southeast Asia is . Another possible early name of mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-classical
In Human history, world history, post-classical history refers to the period from about 500 CE to 1500 CE, roughly corresponding to the European Middle Ages. The period is characterized by the expansion of civilizations geographically and the development of trade networks between civilizations.The Post‐Classical Era by Joel Hermansen This period is also called the medieval era, post-antiquity era, post-ancient era, pre-modernity era, or pre-modern era. In Asia, the spread of Islam created a series of caliphates and inaugurated the Islamic Golden Age, leading to advances in science in the medieval Islamic world and trade among the Asian, African, and European continents. East Asia experienced the full establishment of the power of History of China#Imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAST
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Brahmic family, Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during the 19th century from suggestions by Sir Charles Trevelyan, 1st Baronet, Charles Trevelyan, William Jones (philologist), William Jones, Monier Monier-Williams and other scholars, and formalised by the Transliteration Committee of the Geneva International Congress of Orientalists, Oriental Congress, in September 1894. IAST makes it possible for the reader to read the Indic text unambiguously, exactly as if it were in the original Indic script. It is this faithfulness to the original scripts that accounts for its continuing popularity amongst scholars. Usage Scholars commonly use IAST in publications that cite textual material in Sanskrit, Pāḷi and other classical Indian languages. IAST is also used for major e-text repos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |