|
Subcostal Vein
The subcostal vein is a vein in the human body that runs along the bottom of the twelfth rib. It has the same essential qualities as the posterior intercostal veins, except that it cannot be considered ''intercostal'' because it is not between two ribs. Each subcostal vein gives off a posterior (dorsal) branch which has a similar distribution to the posterior ramus of an intercostal artery. See also * Subcostal nerve The subcostal nerve (anterior division of the twelfth thoracic nerve) is a mixed motor and sensory nerve contributing to the lumbar plexus. It runs along the lower border of the twelfth rib, often gives a communicating branch to the first lumbar ... * Subcostal artery References External links * http://www.instantanatomy.net/thorax/vessels/vinsuperiormediastinum.html Thoracic veins Veins of the torso {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascending Lumbar Vein
The ascending lumbar vein is a vein that runs up through the lumbar region on the side of the vertebral column. Structure The ascending lumbar vein is a paired structure (i.e. one each for the right and left sides of the body). It starts at the common iliac veins. It runs superiorly, intersecting with the lumbar veins as it crosses them. It passes behind the psoas major muscle, but in front of the lumbar vertebrae. When the ascending lumbar vein crosses the subcostal vein, it becomes one of the following: * the azygos vein (in the case of the ''right'' ascending lumbar vein). * the hemiazygos vein (in the case of the ''left'' ascending lumbar vein). The first and second lumbar veins ends in the ascending lumbar vein (the third and fourth lumbar veins open into the posterior aspect of the inferior vena cava) Clinical significance Contrast medium may be injected into the ascending lumbar vein via the femoral vein in order to visualise the spinal canal. The ascending lumbar vein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
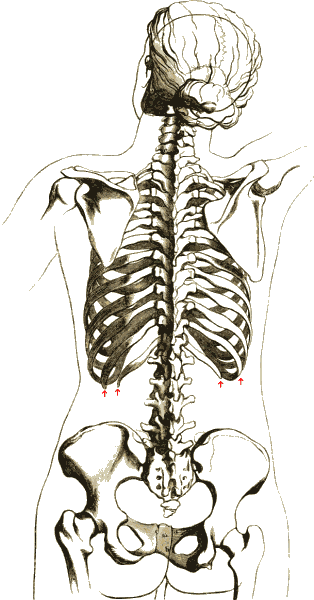
Subcostal Artery
The subcostal arteries, so named because they lie below the last ribs, constitute the lowest pair of branches derived from the thoracic aorta, and are in series with the intercostal arteries. Anatomy Course and relations Each intercostal artery is accompanied by the corresponding (i.e. ipsilateral) subcostal vein and nerve. Each passes along the lower border of the 12th rib. Before entering the anterior abdominal wall, each runs laterally upon the anterior surface of the lumbar fascia (and thus also anterior to the underlying quadratus lumborum muscle which the lumbar fascia envelops) posterior to the ipsilateral kidney. It then pierces the posterior aponeurosis of the transversus abdominis, thus entering the anterior abdominal wall to course in between the abdominal internal oblique muscle and transverse abdominal muscle (the neurovascular plane of the anterior abdominal wall). Branches Each subcostal artery gives off a posterior branch which has a similar distribution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins. There are three sizes of veins: large, medium, and small. Smaller veins are called venules, and the smallest the post-capillary venules are microscopic that make up the veins of the microcirculation. Veins are often closer to the skin than arteries. Veins have less smooth muscle and connective tissue and wider internal diameters than arteries. Because of their thinner walls and wider lumens they are able to expand and hold more blood. This greater capacity gives them the term of ''capacitance vessels''. At any time, nearly 70% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelfth Rib
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels and support the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the axial skeleton. A typical human thoracic cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs and the adjoining costal cartilages, the sternum (along with the manubrium and xiphoid process), and the 12 thoracic vertebrae articulating with the ribs. The thoracic cage also provides attachments for extrinsic skeletal muscles of the neck, upper limbs, upper abdomen and back, and together with the overlying skin and associated fascia and muscles, makes up the thoracic wall. In tetrapods, the rib cage intrinsically holds the muscles of respiration ( diaphragm, intercostal muscles, etc.) that are crucial for active inhalation and forced exhalation, and therefore has a major ventilatory function in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Intercostal Veins
The posterior intercostal veins are veins that drain the intercostal spaces posteriorly. They run with their corresponding posterior intercostal artery on the underside of the rib, the vein superior to the artery. Each vein also gives off a dorsal branch that drains blood from the muscles of the back. There are eleven posterior intercostal veins on each side. Their patterns are variable, but they are commonly arranged as: * The 1st posterior intercostal vein, supreme intercostal vein, drains into the brachiocephalic vein or the vertebral vein. * The 2nd and 3rd (and often 4th) posterior intercostal veins drain into the superior intercostal vein. * The remaining posterior intercostal veins drain into the azygos vein The azygos vein (from Ancient Greek ἄζυγος (ázugos), meaning 'unwedded' or 'unpaired') is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superio ... on the right, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcostal Nerve
The subcostal nerve (anterior division of the twelfth thoracic nerve) is a mixed motor and sensory nerve contributing to the lumbar plexus. It runs along the lower border of the twelfth rib, often gives a communicating branch to the first lumbar nerve, and passes under the lateral lumbocostal arch. It then runs in front of the quadratus lumborum, innervates the transversus, and passes forward between it and the abdominal internal oblique to be distributed in the same manner as the lower intercostal nerves. It communicates with the iliohypogastric nerve and the ilioinguinal nerve of the lumbar plexus, and gives a branch to the pyramidalis muscle The pyramidalis muscle is a small triangular muscle, anterior to the rectus abdominis muscle, and contained in the rectus sheath. Structure The pyramidalis muscle is part of the anterior abdominal wall. Inferiorly, the pyramidalis muscle attache ... and the quadratus lumborum muscle. It also gives off a lateral cutaneous branch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Veins
Thoracic vein may refer to: * Internal thoracic vein In human anatomy, the internal thoracic vein (previously known as the internal mammary vein) is the vein that drains the chest wall and breasts. Structure Bilaterally, the internal thoracic vein arises from the superior epigastric vein, and ... * Lateral thoracic vein {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |