|
Stonogobiops Nematodes
''Stonogobiops nematodes'', the Filament-finned prawn-goby, the Antenna goby, the high-fin goby, the red-banded goby, the high-fin red-banded goby, the striped goby, the barber-pole goby, or the black-ray Goby, is a species of marine goby native to the Indian Ocean and western Pacific Ocean from the Seychelles to the Philippines and Bali. Physical features Adult fish can grow up to in length, with the striking pointed dorsal fin becoming more raised and pronounced in adulthood. This elongated fin is the most obvious distinguishing feature between the black-ray goby and its close cousin, the yellow snout goby (''S. Xanthorhinica''). The fish are coloured with four diagonal brown stripes across a white body, and a distinctive yellow head. It is almost impossible for anybody less than a specialised expert in the specific field of these types of fish to discern differences between males and females of the species. Natural environment This goby inhabits sandy or sand-rubble botto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglass Fielding Hoese
Douglass may refer to: Surname * Douglass (surname) * Douglass family, family of Frederick Douglass ** Frederick Douglass (1818–1895), noted abolitionist Given name *Douglass Dumbrille (1889–1974), Canadian actor in early Hollywood *Douglass Houghton (1809–1845), American geologist and physician *Douglass Morse Howell (1906 – 1994), American papermaker and artist *Douglass Lubahn (1947–2019), rock bassist *Douglass Montgomery (1907–1966), American actor *Douglass North (1920–2015), American economist and Nobel Prize laureate *Douglass Wallop (1920–1985), American novelist and playwright *Douglass Watson (1921–1989), American actor Places In the United States: * Douglass, Kansas * Douglass (Memphis), a neighborhood in Memphis, Tennessee * Douglass, Texas * Douglass (Washington, D.C.), a neighborhood of Washington, D.C. * Douglass Township (other) Elsewhere: * Mount Douglass, Antarctica * Douglass (lunar crater), named after A. E. Douglass * Douglass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic. The organisms, each termed a symbiont, must be of different species. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined it as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term was subject to a century-long debate about whether it should specifically denote mutualism, as in lichens. Biologists have now abandoned that restriction. Symbiosis can be obligatory, which means that one or more of the symbionts depend on each other for survival, or facultative (optional), when they can generally live independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. When symbionts form a single body it is called conjunctive symbiosis, while all other arrangements are called disjunctive symbiosis."symbiosis." Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (marine Biology)
Stream substrate (sediment) is the material that rests at the bottom of a stream. There are several classification guides. One is: *Mud – silt and clay. *Sand – Particles between 0.06 and 2 mm in diameter. * Granule – Between 2 and 4 mm in diameter. *Pebble – Between 4 – 64 mm in diameter. *Cobble – between 6.4 and 25.6 cm in diameter *Boulder – more than 25.6 cm in diameter. Stream substrate can affect the life found within the stream habitat. Muddy streams generally have more sediment in the water, reducing clarity. Clarity is one guide to stream health. Marine substrate can be classified geologically as well. See Green et al., 1999 for a reference. Mollusks and clams that live in areas with substrate, and need them to survive, use their silky byssal threads to cling to it. See Cteniodes Ales for reference. See also * Grain size * Substrate (biology) In biology, a substrate is the surface on which an organism (such as a plant, fungus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellates, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirulina (dietary Supplement)
Spirulina is a biomass of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) that can be consumed by humans and animals. The three species are '' Arthrospira platensis'', ''A. fusiformis'', and ''A. maxima''. Cultivated worldwide, ''Arthrospira'' is used as a dietary supplement or whole food. It is also used as a feed supplement in the aquaculture, aquarium, and poultry industries.Vonshak, A. (ed.). ''Spirulina platensis (Arthrospira): Physiology, Cell-biology and Biotechnology.'' London: Taylor & Francis, 1997. Etymology and ecology The species ''A. maxima'' and ''A. platensis'' were once classified in the genus ''Spirulina''. The common name, spirulina, refers to the dried biomass of ''A. platensis'', which belongs to photosynthetic bacteria that cover the groups Cyanobacteria and Prochlorophyta. Scientifically, a distinction exists between spirulina and the genus ''Arthrospira''. Species of ''Arthrospira'' have been isolated from alkaline brackish and saline waters in tropical and subtro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
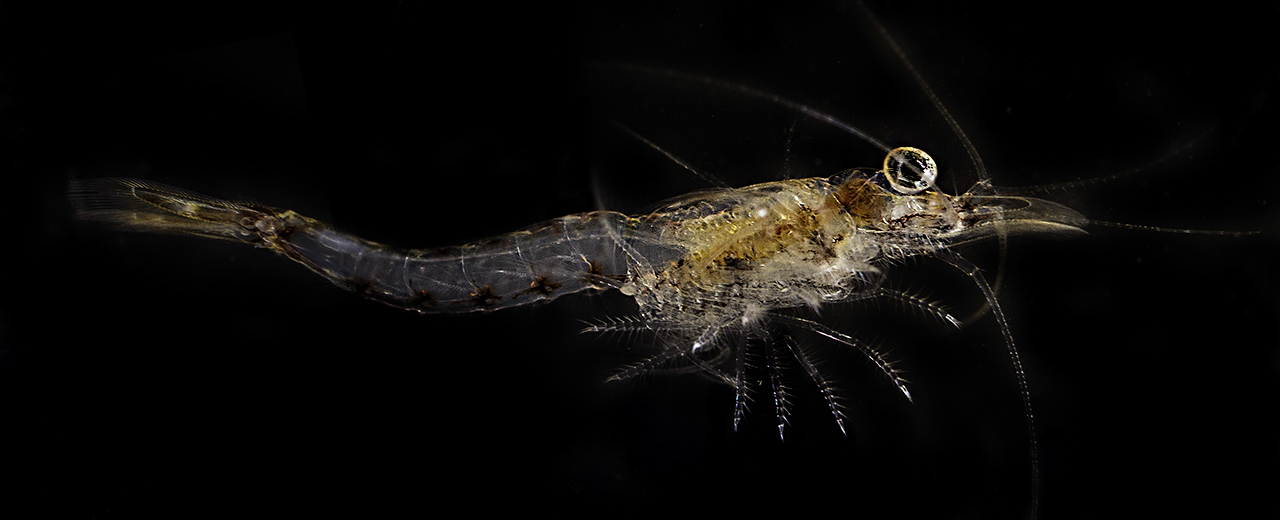
Brine Shrimp
''Artemia'' is a genus of aquatic crustaceans also known as brine shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Artemiidae. The first historical record of the existence of ''Artemia'' dates back to the first half of the 10th century AD from Urmia Lake, Iran, with an example called by an Iranian geographer an "aquatic dog," although the first unambiguous record is the report and drawings made by Schlösser in 1757 of animals from Lymington, England. ''Artemia'' populations are found worldwide in inland saltwater lakes, but not in oceans. ''Artemia'' are able to avoid cohabiting with most types of predators, such as fish, by their ability to live in waters of very high salinity (up to 25%). The ability of the ''Artemia'' to produce dormant eggs, known as cysts, has led to extensive use of ''Artemia'' in aquaculture. The cysts may be stored indefinitely and hatched on demand to provide a convenient form of live feed for larval fish and crustaceans. Nauplii of the brine shrimp ''Artemia' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysid
Mysida is an order of small, shrimp-like crustaceans in the malacostracan superorder Peracarida. Their common name opossum shrimps stems from the presence of a brood pouch or "marsupium" in females. The fact that the larvae are reared in this pouch and are not free-swimming characterises the order. The mysid's head bears a pair of stalked eyes and two pairs of antennae. The thorax consists of eight segments each bearing branching limbs, the whole concealed beneath a protective carapace and the abdomen has six segments and usually further small limbs. Mysids are found throughout the world in both shallow and deep marine waters where they can be benthic or pelagic, but they are also important in some fresh water and brackish ecosystems. Many benthic species make daily vertical migrations into higher parts of the water column. Mysids are filter feeders, omnivores that feed on algae, detritus and zooplankton. Some mysids are cultured in laboratories for experimental purposes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water (molecule), water at its densest (at ); for gases, the reference is air at room temperature (). The term "relative density" (often abbreviated r.d. or RD) is often preferred in scientific usage, whereas the term "specific gravity" is deprecation, deprecated. If a substance's relative density is less than 1 then it is less dense than the reference; if greater than 1 then it is denser than the reference. If the relative density is exactly 1 then the densities are equal; that is, equal volumes of the two substances have the same mass. If the reference material is water, then a substance with a relative density (or specific gravity) less than 1 will float in water. For example, an ice cube, with a relative density of about 0.91, will float. A substance wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
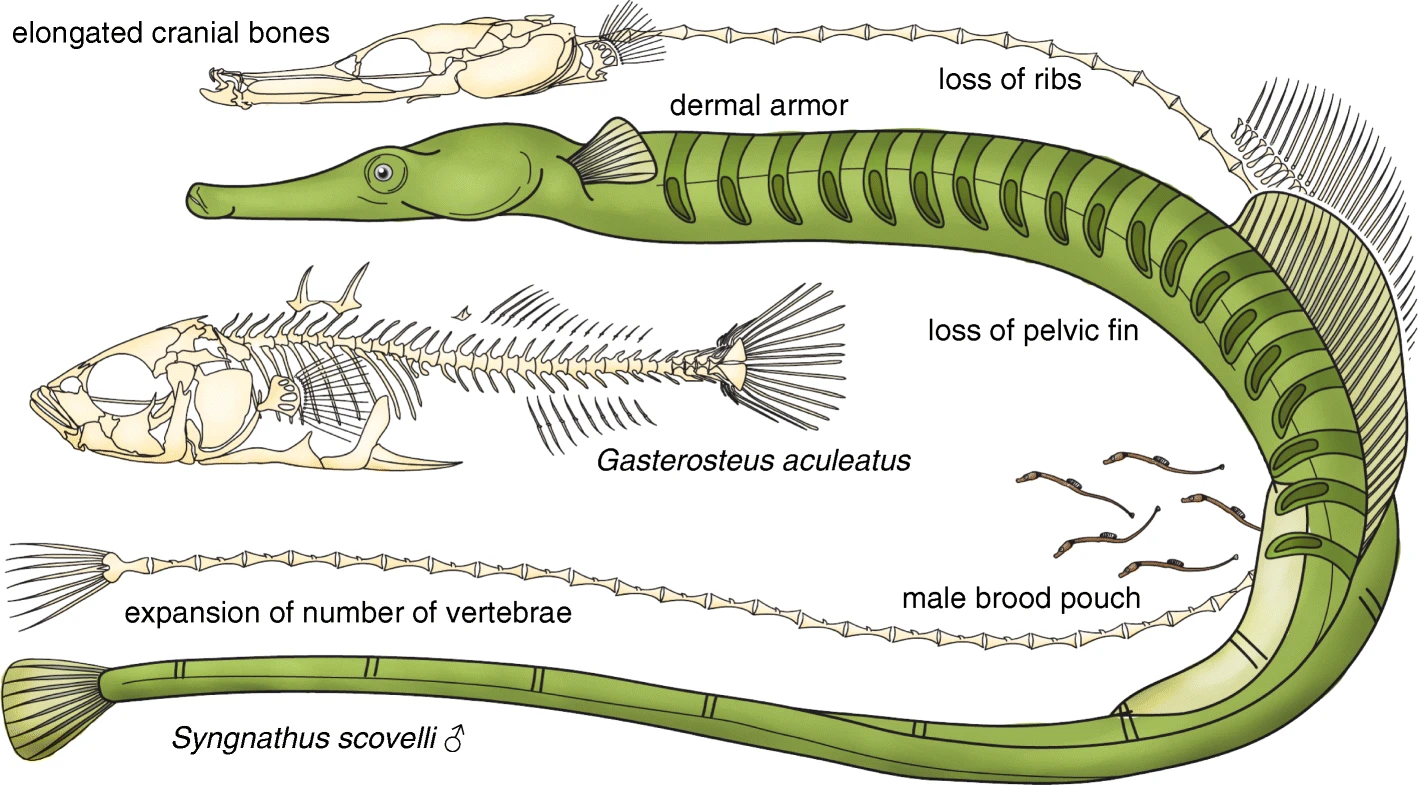
Pipefish
Pipefishes or pipe-fishes (Syngnathinae) are a subfamily of small fishes, which, together with the seahorses and seadragons (''Phycodurus'' and ''Phyllopteryx''), form the family Syngnathidae. Description Pipefish look like straight-bodied seahorses with tiny mouths. The name is derived from the peculiar form of the snout, which is like a long tube, ending in a narrow and small mouth which opens upwards and is toothless. The body and tail are long, thin, and snake-like. They each have a highly modified skeleton formed into armored plating. This dermal skeleton has several longitudinal ridges, so a vertical section through the body looks angular, not round or oval as in the majority of other fishes. A dorsal fin is always present, and is the principal (in some species, the only) organ of locomotion. The ventral fins are consistently absent, and the other fins may or may not be developed. The gill openings are extremely small and placed near the upper posterior angle of the gill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Horse
A seahorse (also written ''sea-horse'' and ''sea horse'') is any of 46 species of small marine fish in the genus ''Hippocampus''. "Hippocampus" comes from the Ancient Greek (), itself from () meaning "horse" and () meaning "sea monster" or "sea animal". Having a head and neck suggestive of a horse, seahorses also feature segmented bony armour, an upright posture and a curled prehensile tail. Along with the pipefishes and seadragons (''Phycodurus'' and ''Phyllopteryx'') they form the family Syngnathidae. Habitat Seahorses are mainly found in shallow tropical and temperate salt water throughout the world, from about 45°S to 45°N. They live in sheltered areas such as seagrass beds, estuaries, coral reefs, and mangroves. Four species are found in Pacific waters from North America to South America. In the Atlantic, ''Hippocampus erectus'' ranges from Nova Scotia to Uruguay. '' H. zosterae'', known as the dwarf seahorse, is found in the Bahamas. Colonies have been found in Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptereleotris
''Ptereleotris'' is a genus of dartfishes found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific oceans. Species There are currently 20 recognized species in this genus: * ''Ptereleotris arabica'' J. E. Randall & Hoese, 1985 * '' Ptereleotris brachyptera'' J. E. Randall & T. Suzuki, 2008 (Lowfin dartfish) * ''Ptereleotris caeruleomarginata'' G. R. Allen, Erdmann & Cahyani, 2012 (Bluemargin dartfish) * ''Ptereleotris calliura'' ( D. S. Jordan & C. H. Gilbert, 1882) (Blue goby) * ''Ptereleotris carinata'' W. A. Bussing, 2001 (Panamic dartfish) * ''Ptereleotris crossogenion'' J. E. Randall & T. Suzuki, 2008 (Fringechin dartfish) * ''Ptereleotris evides'' ( D. S. Jordan & C. L. Hubbs, 1925) (Blackfin dartfish) * ''Ptereleotris grammica'' J. E. Randall & Lubbock, 1982 (Lined dartfish) * ''Ptereleotris hanae'' ( D. S. Jordan & Snyder, 1901) (Blue hana goby) * ''Ptereleotris helenae'' ( J. E. Randall, 1968) (Hovering goby) * ''Ptereleotris heteroptera'' (Bleeker, 1855) (Blacktail goby) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartfish
Dartfishes are a group of fish, formerly considered to be a subfamily, Ptereleotrinae, of goby-like fishes in the family Microdesmidae of the order Gobiiformes, Authorities now consider the species in the family Microdesmidae are within the Gobiidae Gobiidae or gobies is a family of bony fish in the order Gobiiformes, one of the largest fish families comprising more than 2,000 species in more than 200 genera. Most of gobiid fish are relatively small, typically less than in length, and the ..., although the researchers do not define the taxonomic status of this grouping within that family. They are saltwater fish. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q16671538 Microdesmidae Gobiidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)