|
Stochastic Electrodynamics
Stochastic electrodynamics (SED) is a variant of classical electrodynamics (CED) of theoretical physics. SED consists of a set of controversial theories that posit the existence of a classical Lorentz invariant radiation field having statistical properties similar to that of the electromagnetic zero-point field (ZPF) of quantum electrodynamics (QED). Classical background field The background field is introduced as a Lorentz force in the (classical) Abraham–Lorentz–Dirac equation (see: Abraham–Lorentz–Dirac force), where the classical statistics of the electric and magnetic fields and quadratic combinations thereof are chosen to match the vacuum expectation values of the equivalent operators in QED. The field is generally represented as a discrete sum of Fourier components each with amplitude and phase that are independent classical random variables, distributed so that the statistics of the fields are isotropic and unchanged under boosts. This prescription is suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Electrodynamics
Classical electromagnetism or classical electrodynamics is a branch of theoretical physics that studies the interactions between electric charges and currents using an extension of the classical Newtonian model; It is, therefore, a classical field theory. The theory provides a description of electromagnetic phenomena whenever the relevant length scales and field strengths are large enough that quantum mechanical effects are negligible. For small distances and low field strengths, such interactions are better described by quantum electrodynamics, which is a quantum field theory. Fundamental physical aspects of classical electrodynamics are presented in many texts, such as those by Feynman, Leighton and Sands, Griffiths, Panofsky and Phillips, and Jackson. History The physical phenomena that electromagnetism describes have been studied as separate fields since antiquity. For example, there were many advances in the field of optics centuries before light was understood to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luis De La Peña
Luis Fernando de la Peña-Auerbach known as Luis de la Peña is a Mexican physicist, born in Mexico City in 1931. He is a researcher of the Institute of Physics and professor of the Faculty of Sciences of the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM) and is a member of the Science Advisory Council of the Presidency of Mexico. He graduated from ESIME of the National Polytechnic Institute with a degree in mechanical-electrical engineering and began his professional activity as a designer of audio systems. From 1954 was professor of the ESIME and from 1958 definitively joined UNAM. He completed his PhD in 1964 under the direction of Arseny Sokolov at the Moscow State University in the Soviet Union. He is known most for his contributions towards the field of stochastic electrodynamics (SED). In 2002 he was awarded the National Prize for Arts and Sciences The National Prize for Arts and Sciences ( es, Premio Nacional de Ciencias y Artes) is awarded annually by the Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Harmonic Oscillator
量子調和振動子 は、調和振動子, 古典調和振動子 の 量子力学, 量子力学 類似物です。任意の滑らかな ポテンシャル エネルギー, ポテンシャル は通常、安定した 平衡点 の近くで 調和振動子#単純調和振動子, 調和ポテンシャル として近似できるため、最も量子力学における重要なモデル系。さらに、これは正確な量子力学システムのリスト, 解析解法が知られている数少ない量子力学系の1つである。 author=Griffiths, David J. , title=量子力学入門 , エディション=2nd , 出版社=プレンティス・ホール , 年=2004 , isbn=978-0-13-805326-0 , author-link=David Griffiths (物理学者) , URL アクセス = 登録 , url=https://archive.org/details/introductiontoel00grif_0 One-dimensional harmonic oscillator Hamiltonian and energy eigenstates 粒子の ハミルトニアン (量子力学), ハミルトニアン は次の� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unruh Effect
The Unruh effect (also known as the Fulling–Davies–Unruh effect) is a kinematic prediction of quantum field theory that an accelerating observer will observe a thermal bath, like blackbody radiation, whereas an inertial observer would observe none. In other words, the background appears to be warm from an accelerating reference frame; in layman's terms, an accelerating thermometer (like one being waved around) in empty space, removing any other contribution to its temperature, will record a non-zero temperature, just from its acceleration. Heuristically, for a uniformly accelerating observer, the ground state of an inertial observer is seen as a mixed state in thermodynamic equilibrium with a non-zero temperature bath. The Unruh effect was first described by Stephen Fulling in 1973, Paul Davies in 1975 and W. G. Unruh in 1976. It is currently not clear whether the Unruh effect has actually been observed, since the claimed observations are disputed. There is also some do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
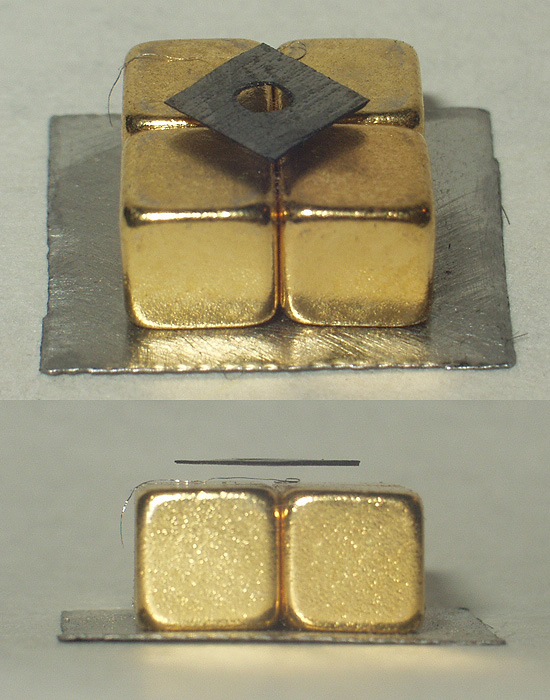
Diamagnetism
Diamagnetic materials are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials are attracted by a magnetic field. Diamagnetism is a quantum mechanical effect that occurs in all materials; when it is the only contribution to the magnetism, the material is called diamagnetic. In paramagnetic and ferromagnetic substances, the weak diamagnetic force is overcome by the attractive force of magnetic dipoles in the material. The magnetic permeability of diamagnetic materials is less than the permeability of vacuum, ''μ''0. In most materials, diamagnetism is a weak effect which can be detected only by sensitive laboratory instruments, but a superconductor acts as a strong diamagnet because it repels a magnetic field entirely from its interior. Diamagnetism was first discovered when Anton Brugmans observed in 1778 that bismuth w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Der Waals Force
In molecular physics, the van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and therefore more susceptible to disturbance. The van der Waals force quickly vanishes at longer distances between interacting molecules. Named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, the van der Waals force plays a fundamental role in fields as diverse as supramolecular chemistry, structural biology, polymer science, nanotechnology, surface science, and condensed matter physics. It also underlies many properties of organic compounds and molecular solids, including their solubility in polar and non-polar media. If no other force is present, the distance between atoms at which the force becomes repulsive rather than attractive as the atoms approach one another is called the van der Waals contact distance; this phenomen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casimir Effect
In quantum field theory, the Casimir effect is a physical force acting on the macroscopic boundaries of a confined space which arises from the quantum fluctuations of the field. It is named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik Casimir, who predicted the effect for electromagnetic systems in 1948. In the same year, Casimir together with Dirk Polder described a similar effect experienced by a neutral atom in the vicinity of a macroscopic interface which is referred to as the Casimir–Polder force. Their result is a generalization of the London– van der Waals force and includes retardation due to the finite speed of light. Since the fundamental principles leading to the London–van der Waals force, the Casimir and the Casimir–Polder force, respectively, can be formulated on the same footing, the distinction in nomenclature nowadays serves a historical purpose mostly and usually refers to the different physical setups. It was not until 1997 that a direct experiment by S. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirac Equation
In particle physics, the Dirac equation is a relativistic wave equation derived by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. In its free form, or including electromagnetic interactions, it describes all spin- massive particles, called "Dirac particles", such as electrons and quarks for which parity is a symmetry. It is consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and was the first theory to account fully for special relativity in the context of quantum mechanics. It was validated by accounting for the fine structure of the hydrogen spectrum in a completely rigorous way. The equation also implied the existence of a new form of matter, ''antimatter'', previously unsuspected and unobserved and which was experimentally confirmed several years later. It also provided a ''theoretical'' justification for the introduction of several component wave functions in Pauli's phenomenological theory of spin. The wave functions in the Dirac t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schrödinger Equation
The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a quantum-mechanical system. It is a key result in quantum mechanics, and its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of the subject. The equation is named after Erwin Schrödinger, who postulated the equation in 1925, and published it in 1926, forming the basis for the work that resulted in his Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933. Conceptually, the Schrödinger equation is the quantum counterpart of Newton's second law in classical mechanics. Given a set of known initial conditions, Newton's second law makes a mathematical prediction as to what path a given physical system will take over time. The Schrödinger equation gives the evolution over time of a wave function, the quantum-mechanical characterization of an isolated physical system. The equation can be derived from the fact that the time-evolution operator must be unitary, and must therefore be generated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherence Theory (optics)
In physics, coherence theory is the study of optical effects arising from partially coherent light and radio sources. Partially coherent sources are sources where the coherence time or coherence length are limited by bandwidth, by thermal noise, or by other effect. Many aspects of modern coherence theory are studied in quantum optics. The theory of partial coherence was awoken in the 1930s due to work by Pieter Hendrik van Cittert and Frits Zernike. Topics in coherence theory * Visibility * Mutual coherence function * Degree of coherence * Self coherence function * Coherence function * Low frequency fluctuations * General interference law * Van Cittert–Zernike theorem * Michelson stellar interferometer * Correlation interferometry * Hanbury–Brown and Twiss effect * Phase-contrast microscope * Pseudothermal light * Englert–Greenberger duality relation * Coherence Collapse See also * Nonclassical light * Optical coherence tomography References * Eugene Hech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-slit
In modern physics, the double-slit experiment is a demonstration that light and matter can display characteristics of both classically defined waves and particles; moreover, it displays the fundamentally probabilistic nature of quantum mechanical phenomena. This type of experiment was first performed by Thomas Young in 1801, as a demonstration of the wave behavior of visible light. At that time it was thought that light consisted of ''either'' waves ''or'' particles. With the beginning of modern physics, about a hundred years later, it was realized that light could in fact show behavior characteristic of ''both'' waves ''and'' particles. In 1927, Davisson and Germer demonstrated that electrons show the same behavior, which was later extended to atoms and molecules. Thomas Young's experiment with light was part of classical physics long before the development of quantum mechanics and the concept of wave–particle duality. He believed it demonstrated that the wave theory of lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Rays
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk is deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have been interpreted as evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
