|
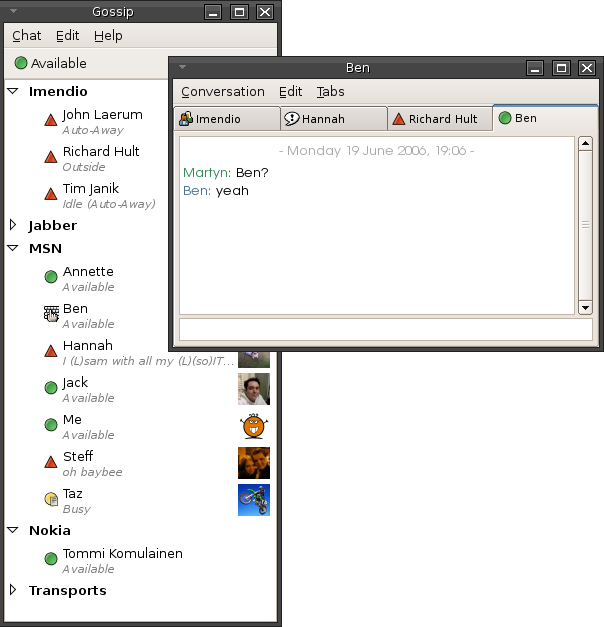
Status Message (instant Messaging)
A status message is a function of some instant messaging applications whereby a user may post a message that appears automatically to other users if they attempt to make contact. A status message can tell other contacts the user's current status, such as being busy or what the user is currently doing. It is analogous to the voice message in an answering machine or voice mail system. However, status messages may be displayed even if the person is present. They are often updated much more frequently than messages in answering machines, and thus may serve as a means of instant, limited "publication" or indirect communication. Generally, the available status is denoted by a green dot, while the busy status is denoted by a red dot on most of the instant messengers. Whereas answering machine or voice mail messages often have a generic greeting to leave a message, status messages more often contain a description of where the person is at the moment or what they are doing. Because mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saved Statuses
Save, SAVE, or Saved may refer to: Places *Save (Garonne), a river in southern France * Save River (Africa), a river in Zimbabwe and Mozambique *Sava, a river in Eastern Europe also known as Save * Savè, Benin, a commune and city * Save, Rwanda, a settlement * Säve, a locality in Göteborg Municipality, Västra Götaland County, Sweden ** Säve Airport * Esquel Airport (ICAO airport code: SAVE; IATA airport code: EQS), Esquel, Chubut Province, Argentina Organizations, groups, companies *Spirit Airlines (NASDAQ stockticker: SAVE), a U.S. airline Charities * Society Against Violence in Education, a non-profit organization working against ragging in India * Save Britain's Heritage (''SAVE''), a historic building conservation group in the United Kingdom In technology *Saved game, saved progress of a player in a video game *Computer files are "saved" to achieve persistence In media and entertainment Music * ''Saved'' (Bob Dylan album), 1980, or the song * ''Saved'' (Now, Now alb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instant Messaging
Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of synchronous computer-mediated communication involving the immediate ( real-time) transmission of messages between two or more parties over the Internet or another computer network. Originally involving simple text message exchanges, modern IM applications and services (also called "social messengers", "messaging apps", "chat apps" or "chat clients") tend to also feature the exchange of multimedia, emojis, file transfer, VoIP (voice calling), and video chat capabilities. Instant messaging systems facilitate connections between specified known users (often using a contact list also known as a "buddy list" or "friend list") or in chat rooms, and can be standalone apps or integrated into a wider social media platform, or in a website where it can, for instance, be used for conversational commerce. Originally the term "instant messaging" was distinguished from " text messaging" by being run on a computer network instead of a cellula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Answering Machine
An answering machine, answerphone, or message machine, also known as telephone messaging machine (or TAM) in the United Kingdom, UK and some Commonwealth countries, ansaphone or ansafone (from a trade name), or telephone answering device (TAD), is used for answering telephone calls and recording callers' messages. When a telephone rings a set number of times predetermined by the call's recipient the answering machine will activate and play either a generic announcement or a customized greeting created by the recipient. Unlike voicemail, an answering machine is placed at the user's premises alongside—or incorporated within—the user's landline telephone, and unlike operator messaging, the caller does not talk to a human. As landlines become less important due to the shift to cell phone technology, and as unified communications evolve, the installed base of TADs is shrinking. History Most 20th-century answering machines used magnetic recording, which Valdemar Poulsen invent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Mail
A voicemail system (also known as voice message or voice bank) is a computer-based system that allows callers to leave a Voice recording, recorded message when the recipient has been unable (or unwilling) to answer the Telephone, phone. Calls may be directed to voicemail manually or automatically. The caller is prompted to leave a message that the recipient can retrieve at a later time. Voicemail can be used for personal calls, but more complex systems exist for companies and services to handle the volume of customer requests. The term is also used more broadly to denote ''any'' system of conveying stored telecommunications voice messages, including using older technology like answering machine, answering machines. Features Voicemail systems are designed to convey a caller's recorded audio message to a recipient. To do so they contain a user interface to select, play, and manage messages; a delivery method to either play or otherwise deliver the message; and a notification abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Client (computing)
is a computer that gets information from another computer called server in the context of client–server model of computer networks. The server is often (but not always) on another computer system, in which case the client accesses the service by way of a network. A client is a program that, as part of its operation, relies on sending a request to another program or a computer hardware or software that accesses a service made available by a server (which may or may not be located on another computer). For example, web browsers are clients that connect to web servers and retrieve web pages for display. Email clients retrieve email from mail servers. Online chat uses a variety of clients, which vary on the chat protocol being used. Multiplayer video games or online video games may run as a client on each computer. The term "client" may also be applied to computers or devices that run the client software or users that use the client software. A client is part of a cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensible Messaging And Presence Protocol
Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (abbreviation XMPP, originally named Jabber) is an open communication protocol designed for instant messaging (IM), presence information, and contact list maintenance. Based on XML (Extensible Markup Language), it enables the near-real-time exchange of structured data between two or more network entities. Designed to be extensible, the protocol offers a multitude of applications beyond traditional IM in the broader realm of message-oriented middleware, including signalling for VoIP, video, file transfer, gaming and other uses. Unlike most commercial instant messaging protocols, XMPP is defined in an open standard in the application layer. The architecture of the XMPP network is similar to email; anyone can run their own XMPP server and there is no central master server. This federated open system approach allows users to interoperate with others on any server using a 'JID' user account, similar to an email address. XMPP implemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finger Protocol
In computer networking, the Name/Finger protocol and the Finger user information protocol are simple network protocols for the exchange of human-oriented status and user information. Name/Finger protocol The Name/Finger protocol is based on Request for Comments document RFC 742 (December 1977) as an interface to the name and finger programs that provide status reports on a particular computer system or a particular person at network sites. The finger program was written in 1971 by Les Earnest who created the program to solve the need of users who wanted information on other users of the network. Information on who is logged in was useful to check the availability of a person to meet. This was probably the earliest form of presence information for remote network users. Prior to the finger program, the only way to get this information on WAITS was with a WHO program that showed IDs and terminal line numbers (the server's internal number of the communication line over which the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Culture
Internet culture refers to culture developed and maintained among frequent and active users of the Internet (also known as netizens) who primarily communicate with one another as members of online communities; that is, a culture whose influence is "mediated by computer screens" and information communication technology, specifically the Internet. Internet culture arises from the frequent interactions between members within various online communities and the use of these communities for communication, entertainment, business, and recreation. Studied aspects of Internet culture include anonymity/pseudonymity, social media, gaming and specific communities, such as fandoms. History The Internet developed in parallel with rapid and sustained technological advances in computing and data communication. Widespread access to the Internet emerged as the cost of infrastructure dropped by several orders of magnitude with consecutive technological improvements. Though Internet cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |