|
Starlight (SP Train)
Starlight is the light emitted by stars. It typically refers to visible electromagnetic radiation from stars other than the Sun, observable from Earth at night, although a component of starlight is observable from Earth during daytime. Sunlight is the term used for the Sun's starlight observed during daytime. During nighttime, albedo describes solar reflections from other Solar System objects, including moonlight, planetshine, and zodiacal light. Observation Observation and measurement of starlight through telescopes is the basis for many fields of astronomy, including photometry and stellar spectroscopy. Hipparchus did not have a telescope or any instrument that could measure apparent brightness accurately, so he simply made estimates with his eyes. He sorted the stars into six brightness categories, which he called magnitudes.''Astronomy''. https://d3bxy9euw4e147.cloudfront.net/oscms-prodcms/media/documents/Astronomy-Draft-20160817.pdf: Rice University. 2016. p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseid Meteor
The Perseids are a prolific meteor shower associated with the comet Swift–Tuttle. The meteoroid, meteors are called the Perseids because the point from which they appear to hail (called the radiant (meteor shower), radiant) lies in the constellation Perseus (constellation), Perseus. Etymology The name is derived from the word Perseidai ( el, Περσείδαι), the sons of Perseus in Greek mythology. Characteristics The stream of debris is called the Perseid cloud and stretches along the orbit of the comet Swift–Tuttle. The cloud consists of particles ejected by the comet as it travels on its 133-year orbit. Most of the particles have been part of the cloud for around a thousand years. However, there is also a relatively young filament of dust in the stream that was pulled off the comet in 1865, which can give an early mini-peak the day before the maximum shower. The dimensions of the cloud in the vicinity of the Earth are estimated to be approximately 0.1 astronomical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
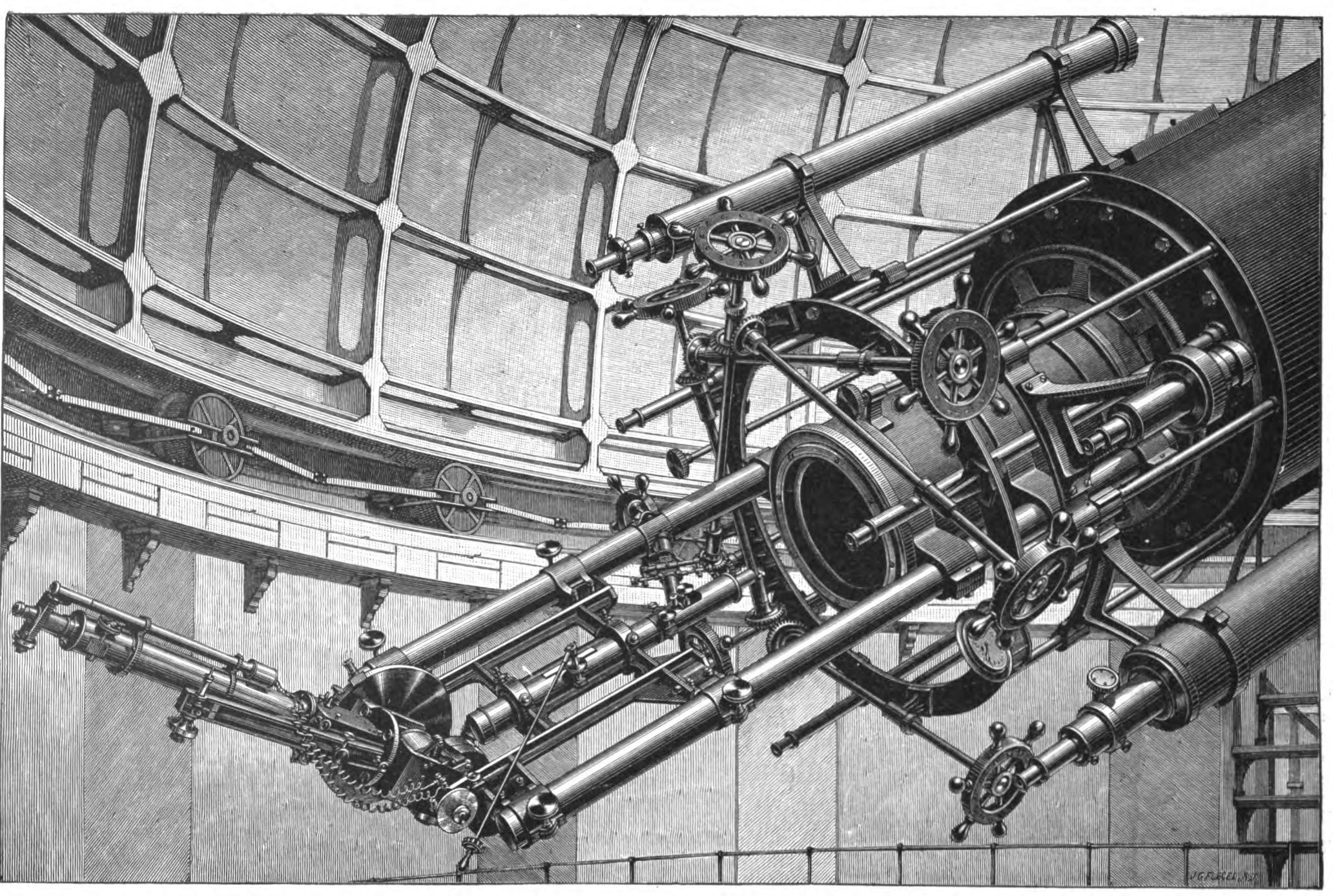
Astronomical Spectroscopy
Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, ultraviolet, X-ray, infrared and radio waves that radiate from stars and other celestial objects. A stellar spectrum can reveal many properties of stars, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance and luminosity. Spectroscopy can show the velocity of motion towards or away from the observer by measuring the Doppler shift. Spectroscopy is also used to study the physical properties of many other types of celestial objects such as planets, nebulae, galaxies, and active galactic nuclei. Background Astronomical spectroscopy is used to measure three major bands of radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum: visible light, radio waves, and X-rays. While all spectroscopy looks at specific bands of the spectrum, different methods are required to acquire the signal depending on the frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as spacetime. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. Debates concerning the nature, essence and the mode of existence of space date back to antiquity; namely, to treatises like the ''Timaeus'' of Plato, or Socrates in his reflections on what the Greeks called ''khôra'' (i.e. "space"), or in the ''Physics'' of Aristotle (Book IV, Delta) in the definition of ''topos'' (i.e. place), or in the later "geometrical conception of place" as "spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of The Universe
In physical cosmology, the age of the universe is the time elapsed since the Big Bang. Astronomers have derived two different measurements of the age of the universe: a measurement based on direct observations of an early state of the universe, which indicate an age of billion years as interpreted with the Lambda-CDM concordance model as of 2018; and a measurement based on the observations of the local, modern universe, which suggest a younger age. The uncertainty of the first kind of measurement has been narrowed down to 20 million years, based on a number of studies which all show similar figures for the age and which include studies of the microwave background radiation by the ''Planck'' spacecraft, the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe and other space probes. Measurements of the cosmic background radiation give the cooling time of the universe since the Big Bang, and measurements of the expansion rate of the universe can be used to calculate its approxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMSS J031300 Sky Survey''
{{disambig ...
SMSS may refer to: *Session Manager Subsystem (smss.exe), a component of the Microsoft Windows NT operating system * Switching and Management Subsystem, in wireless communication technology * Squad Mission Support System, military robotic system developed by Western company Lockheed Martin * St. Margaret's Secondary School, a government-aided autonomous girls' secondary school in Bukit Timah, Singapore *''Sailor Moon SuperS'', the fourth season of the anime series ''Sailor Moon'' * ''SkyMapper SkyMapper is a fully automated 1.35 m (4.4 ft) wide-angle optical telescope at Siding Spring Observatory in northern New South Wales, Australia. It is one of the telescopes of the Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Fraunhofer
Joseph Ritter von Fraunhofer (; ; 6 March 1787 – 7 June 1826) was a German physicist and optical lens manufacturer. He made optical glass, an achromatic telescope, and objective lenses. He also invented the spectroscope and developed diffraction grating. In 1814, he discovered and studied the dark absorption lines in the spectrum of the sun now known as Fraunhofer lines. The German research organization Fraunhofer Society, which is Europe's biggest Society for the advancement of applied research, is named after him. Biography Joseph Fraunhofer was the 11th child, born into a Roman Catholic family in Straubing, in the Electorate of Bavaria, to Franz Xaver Fraunhofer and Maria Anna Fröhlich. He was orphaned at the age of 11 and started working as an apprentice to a harsh glassmaker named Philipp Anton Weichelsberger. In 1801, the workshop in which he was working collapsed, and he was buried in the rubble. The rescue operation was led by Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria, Prince-El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observable Universe
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these objects has had time to reach the Solar System and Earth since the beginning of the cosmological expansion. There may be 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe, although that number was reduced in 2021 to only several hundred billion based on data from '' New Horizons''. Assuming the universe is isotropic, the distance to the edge of the observable universe is roughly the same in every direction. That is, the observable universe is a spherical region centered on the observer and is unique for every unique observational position. The word ''observable'' in this sense does not refer to the capability of modern technology to detect light or other information from an object, or whether there is anything to be detected. It refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characteristics. It is broader than the term ''flora'' which refers to species composition. Perhaps the closest synonym is plant community, but ''vegetation'' can, and often does, refer to a wider range of spatial scales than that term does, including scales as large as the global. Primeval redwood forests, coastal mangrove stands, sphagnum bogs, desert soil crusts, roadside weed patches, wheat fields, cultivated gardens and lawns; all are encompassed by the term ''vegetation''. The vegetation type is defined by characteristic dominant species, or a common aspect of the assemblage, such as an elevation range or environmental commonality. The contemporary use of ''vegetation'' approximates that of ecologist Frederic Clements' term earth cover, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation. A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the visible region; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct color that can only be seen when the substance has been exposed to UV light. Fluorescent materials cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops, unlike phosphorescent materials, which continue to emit light for some time after. Fluorescence has many practical applications, including mineralogy, gemology, medicine, chemical sensors (fluorescence spectroscopy), fluorescent labelling, dyes, biological detectors, cosmic-ray detection, vacu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
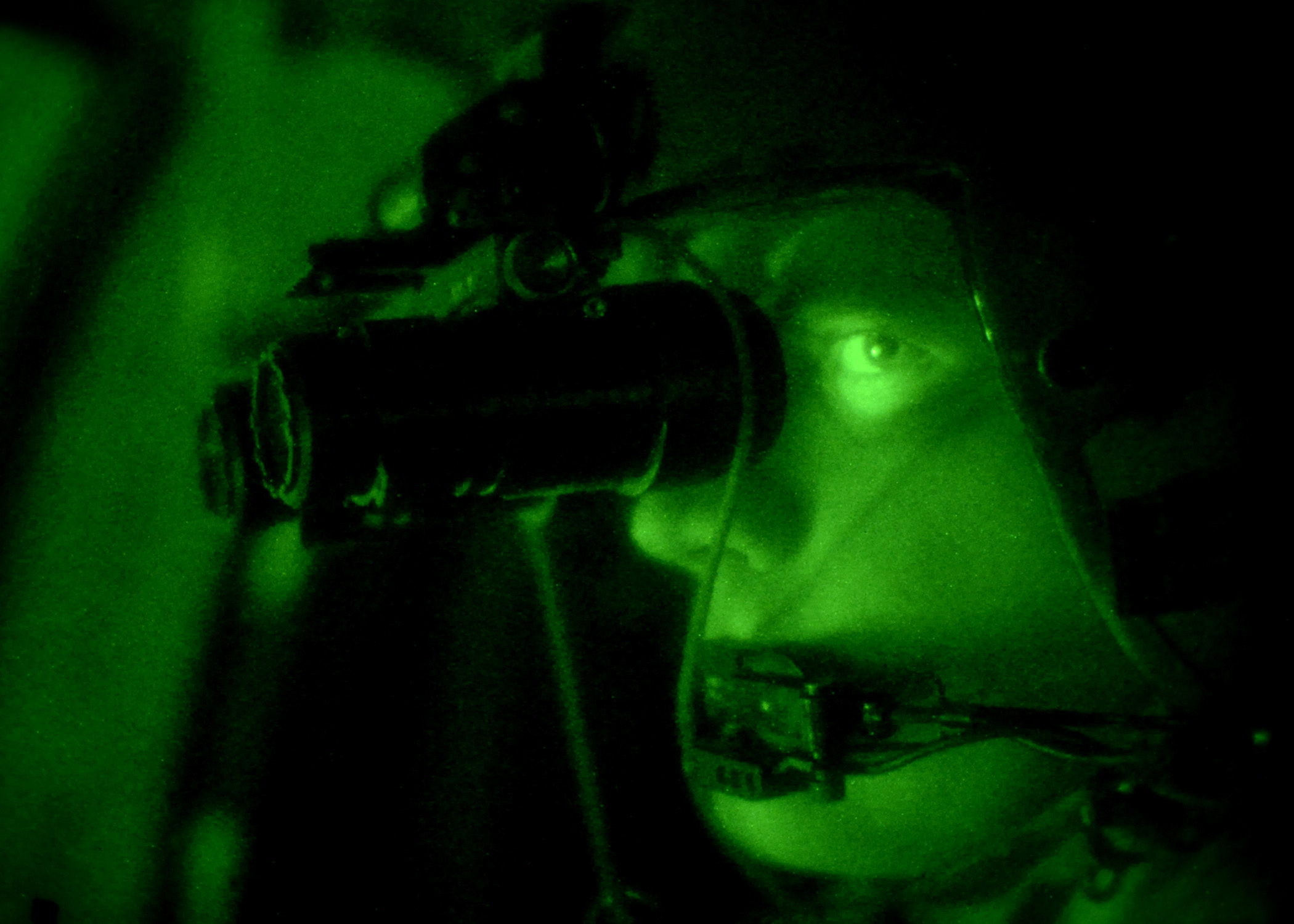
Starlight Scope
A night-vision device (NVD), also known as a night optical/observation device (NOD), night-vision goggle (NVG), is an optoelectronic device that allows visualization of images in low levels of light, improving the user's night vision. The device enhances ambient visible light and converts near-infrared light into visible light which can be seen by the user; this is known as I2 (image intensification). By comparison, viewing of infrared thermal radiation is referred to as thermal imaging and operates in a different section of the infrared spectrum. A night vision device usually consists of an image intensifier tube, a protective housing, and may have some type of mounting system. Many NVDs also include a protective sacrificial lens, mounted over the front lens (ie. objective lens) on NVDs to protect the latter from damage by environmental hazards and some can incorporate [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United States Constitution (1789). See alsTitle 10, Subtitle B, Chapter 301, Section 3001 The oldest and most senior branch of the U.S. military in order of precedence, the modern U.S. Army has its roots in the Continental Army, which was formed 14 June 1775 to fight the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)—before the United States was established as a country. After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army.Library of CongressJournals of the Continental Congress, Volume 27/ref> The United States Army considers itself to be a continuation of the Continental Army, and thus considers its institutional inception to be th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |