|
St Wilfrid's Church, Low Marnham
St Wilfrid's Church is a redundant Anglican church in the village of Low Marnham, to the east of Edwinstowe, Nottinghamshire, England. It is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade I listed building, and is under the care of the Churches Conservation Trust. History The church dates from the 13th century, with additions or alterations in the 14th, 15th and 19th centuries, and a restoration in 1846. Architecture Exterior St Wilfrid's is constructed in stone with slate roofs. Its plan consists of a nave with a clerestory, north and south aisles, a south porch, a north chapel, a chancel and a west tower. From the exterior, the style of the church is Perpendicular. The tower is in two stages, with diagonal buttresses. In the lower stage is a three-light west window, and there are clock faces on the north, west and south sides. The upper stage contains two-light bell openings on each side. At the top of the tower is an embattle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Marnham
Low Marnham is a small village 12 miles east of Edwinstowe, in the civil parish of Marnham, in the Bassetlaw district, in the county of Nottinghamshire Nottinghamshire (; abbreviated Notts.) is a landlocked county in the East Midlands region of England, bordering South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west. The trad ..., England. Located in the village is St Wilfrid's Church, a grade I listed building. See also * Listed buildings in Marnham, Nottinghamshire References External links Villages in Nottinghamshire Bassetlaw District {{Nottinghamshire-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse. Overview The chancel is generally the area used by the clergy and choir during worship, while the congregation is in the nave. Direct access may be provided by a priest's door, usually on the south side of the church. This is one definition, sometimes called the "strict" one; in practice in churches where the eastern end contains other elements such as an ambulatory and side chapels, these are also often counted as part of the chancel, especially when discussing architecture. In smaller churches, where the altar is backed by the outside east wall and there is no distinct choir, the chancel and sanctuary may be the same area. In churches with a retroquire area behind the altar, this may only be included in the broader definition of chancel. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade I Listed Buildings In Nottinghamshire
There are over 9,000 Grade I listed buildings in England. This page is a list of these buildings in the county of Nottinghamshire, by district. Ashfield Bassetlaw Broxtowe City of Nottingham Gedling Mansfield Newark and Sherwood Rushcliffe See also * :Grade I listed buildings in Nottinghamshire *Grade II* listed buildings in Nottinghamshire Notes References National Heritage List for England External links {{GradeIListedbuilding[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funerary Hatchment
A funerary hatchment is a depiction within a black lozenge-shaped frame, generally on a black (''sable'') background, of a deceased's heraldic achievement, that is to say the escutcheon showing the arms, together with the crest and supporters of his family or person. Regimental Colours and other military or naval emblems are sometimes placed behind the arms of military or naval officers. Such funerary hatchments, generally therefore restricted in use to members of the nobility or armigerous gentry, used to be hung on the wall of a deceased person's house, and were later transferred to the parish church, often within the family chapel therein which appertained to the manor house, the family occupying which, generally being lord of the manor, generally held the advowson of the church. In Germany, the approximate equivalent is a ''Totenschild'', literally "shield of the dead". Etymology The ancient term used in place of "achievement" was "hatchment", being a corruption (through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aumbry
An ambry (or ''almery'', ''aumbry''; from the medieval form ''almarium'', cf. Lat. ''armārium'', "a place for keeping tools"; cf. O. Fr. ''aumoire'' and mod. armoire) is a recessed cabinet in the wall of a Christian church for storing sacred vessels and vestments. They are sometimes near the piscina, but more often on the opposite side. The word also seems in medieval times to be used commonly for any closed cupboard and even bookcase. Items kept in an ambry include chalices and other vessels, as well as items for the reserved sacrament, the consecrated elements from the Eucharist. This latter use was infrequent in pre-Reformation churches, although it was known in Scotland, Sweden, Germany and Italy. More usually the sacrament was reserved in a pyx, usually hanging in front of and above the altar or later in a "sacrament house". After the Reformation and the Tridentine reforms, in the Roman Catholic Church the sacrament was no longer reserved in ambries; some ambries were used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piscina
A piscina is a shallow basin placed near the altar of a church, or else in the vestry or sacristy, used for washing the communion vessels. The sacrarium is the drain itself. Anglicans usually refer to the basin, calling it a piscina. For Roman Catholics, a sacrarium is “special sink used for the reverent disposal of sacred substances. This sink has a cover, a basin, and a special pipe and drain that empty directly into the earth, rather than into the sewer system” (USCCB, Built of Living Stones, 236). Precious or sacred items are disposed of, when possible, by returning them to the ground. They are in some cases used to dispose of materials used in the sacraments and water from liturgical ablutions. They are found in Roman Catholic, Anglican, and Lutheran churches, and a similar vessel is used in Eastern Orthodox churches. History The ''piscina'' is a Latin word originally applied to a fish pond, and later used for natural or artificial pools for bathing, and also for a wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital (architecture)
In architecture the capital (from the Latin ''caput'', or "head") or chapiter forms the topmost member of a column (or a pilaster). It mediates between the column and the load thrusting down upon it, broadening the area of the column's supporting surface. The capital, projecting on each side as it rises to support the abacus, joins the usually square abacus and the usually circular shaft of the column. The capital may be convex, as in the Doric order; concave, as in the inverted bell of the Corinthian order; or scrolling out, as in the Ionic order. These form the three principal types on which all capitals in the classical tradition are based. The Composite order established in the 16th century on a hint from the Arch of Titus, adds Ionic volutes to Corinthian acanthus leaves. From the highly visible position it occupies in all colonnaded monumental buildings, the capital is often selected for ornamentation; and is often the clearest indicator of the architectural orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcade (architecture)
An arcade is a succession of contiguous arches, with each arch supported by a colonnade of columns or piers. Exterior arcades are designed to provide a sheltered walkway for pedestrians. The walkway may be lined with retail stores. An arcade may feature arches on both sides of the walkway. Alternatively, a blind arcade superimposes arcading against a solid wall. Blind arcades are a feature of Romanesque architecture that influenced Gothic architecture. In the Gothic architectural tradition, the arcade can be located in the interior, in the lowest part of the wall of the nave, supporting the triforium and the clerestory in a cathedral, or on the exterior, in which they are usually part of the walkways that surround the courtyard and cloisters. Many medieval arcades housed shops or stalls, either in the arcaded space itself, or set into the main wall behind. From this, "arcade" has become a general word for a group of shops in a single building, regardless of the architectural f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molding (decorative)
Moulding (spelled molding in the United States), or coving (in United Kingdom, Australia), is a strip of material with various profiles used to cover transitions between surfaces or for decoration. It is traditionally made from solid milled wood or plaster, but may be of plastic or reformed wood. In classical architecture and sculpture, the moulding is often carved in marble or other stones. A "plain" moulding has right-angled upper and lower edges. A "sprung" moulding has upper and lower edges that bevel towards its rear, allowing mounting between two non-parallel planes (such as a wall and a ceiling), with an open space behind. Mouldings may be decorated with paterae as long, uninterrupted elements may be boring for eyes. Types Decorative mouldings have been made of wood, stone and cement. Recently mouldings have been made of extruded PVC and Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) as a core with a cement-based protective coating. Synthetic mouldings are a cost-effective alternative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
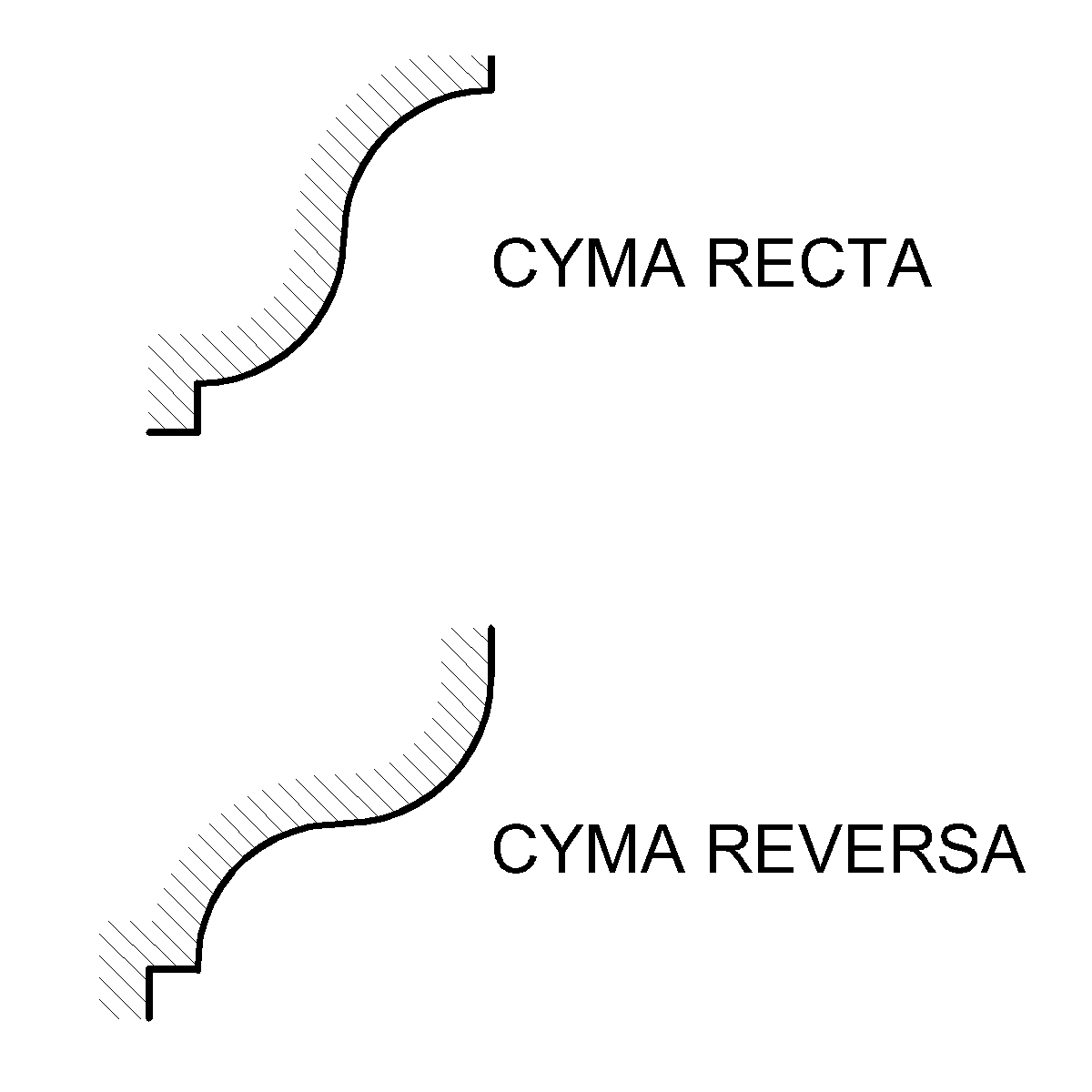
Ogee
An ogee ( ) is the name given to objects, elements, and curves—often seen in architecture and building trades—that have been variously described as serpentine-, extended S-, or sigmoid-shaped. Ogees consist of a "double curve", the combination of two semicircular curves or arcs that, as a result of a point of inflection from concave to convex or ''vice versa'', have ends of the overall curve that point in opposite directions (and have tangents that are approximately parallel). First seen in textiles in the 12th century, the use of ogee elements—in particular, in the design of arches—has been said to characterise various Gothic and Gothic Revival architectural styles. The shape has many such uses in architecture from those periods to the present day, including in the ogee arch in these architectural styles, where two ogees oriented as mirror images compose the sides of the arch, and in decorative molding designs, where single ogees are common profiles (see opening image) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gargoyle
In architecture, and specifically Gothic architecture, a gargoyle () is a carved or formed grotesque with a spout designed to convey water from a roof and away from the side of a building, thereby preventing it from running down masonry walls and eroding the mortar between. Architects often used multiple gargoyles on a building to divide the flow of rainwater off the roof to minimize potential damage from rainstorms. A trough is cut in the back of the gargoyle and rainwater typically exits through the open mouth. Gargoyles are usually elongated fantastical animals because their length determines how far water is directed from the wall. When Gothic flying buttresses were used, aqueducts were sometimes cut into the buttress to divert water over the aisle walls. Etymology The term originates from the French ''gargouille,'' which in English is likely to mean "throat" or is otherwise known as the "gullet"; cf. Latin ''gurgulio, gula, gargula'' ("gullet" or "throat") and similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinnacle
A pinnacle is an architectural element originally forming the cap or crown of a buttress or small turret, but afterwards used on parapets at the corners of towers and in many other situations. The pinnacle looks like a small spire. It was mainly used in Gothic architecture. The pinnacle had two purposes: # Ornamental – adding to the loftiness and verticity of the structure. They sometimes ended with statues, such as in Milan Cathedral. # Structural – the pinnacles were very heavy and often rectified with lead, in order to enable the flying buttresses to contain the stress of the structure vaults and roof. This was done by adding compressive stress (a result of the pinnacle weight) to the thrust vector and thus shifting it downwards rather than sideways. History The accounts of Jesus' temptations in Matthew's and Luke's gospels both suggest that the Second Temple in Jerusalem had one or more pinnacles ( gr, το πτερυγιον του ιερου): :Then he (Satan) br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |