|
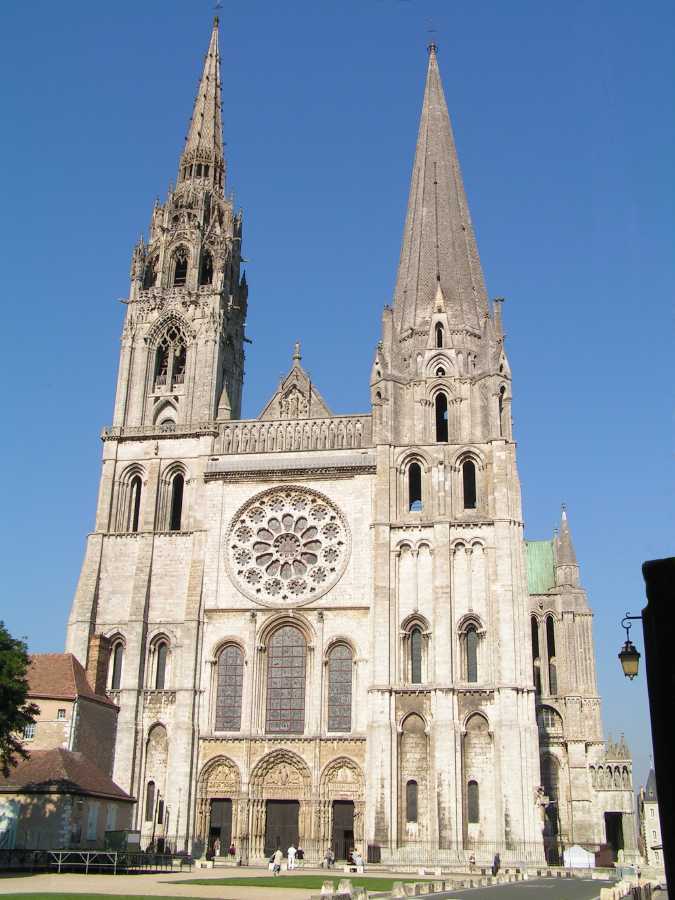
St John The Baptist's Church, Hove
St John the Baptist's Church is an Anglican church in Hove, part of the English city of Brighton and Hove. It was built between 1852 and 1854 to serve the community of the Brunswick area of Hove, which had originally been established in the 1830s. History The land on which the Brunswick estate was built was originally a farming estate known as Wick Farm. It was sold to Thomas Read Kemp, who had been responsible for the Kemp Town residential development in neighbouring Brighton, in 1825. Some houses had been built the previous year, and Read Kemp is believed to have planned to create a similar exclusive development on this land; but little happened until after it had been sold to the Jewish baronet Sir Isaac Lyon Goldsmid in 1830. Even then, it took another 20 years for the scheme to be altered and started properly. Brunswick Town eventually consisted of 150 houses, many of which were exclusive and expensive, but there was no suitable church nearby. Hove's original parish ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
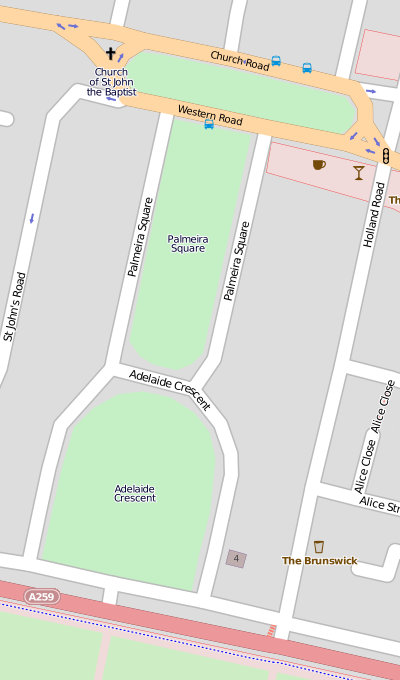
Palmeira Square
Palmeira Square () is a mid-19th-century residential development in Hove, part of the English city and seaside resort of Brighton and Hove. At the southern end it adjoins Adelaide Crescent, another architectural set-piece which leads down to the seafront; large terraced houses occupy its west and east sides, separated by a public garden; and at the north end is one of Hove's main road junctions. This is also called Palmeira Square, and its north side is lined with late 19th-century terraced mansions. Commercial buildings and a church also stand on the main road, which is served by many buses (some of which terminate there). The land was originally occupied by "the world's largest conservatory", the Anthaeum, Hove, Anthaeum—a visitor attraction planned by botanist, author and building promoter Henry Phillips (horticulturist), Henry Phillips. The giant dome's collapse and total destruction on the day it was due to open in 1833 made Phillips go blind from shock, and the debris o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kemp Town
Kemp Town Estate, also known as Kemp Town, is a 19th-century Regency architecture residential estate in the east of Brighton in East Sussex, England, UK. It consists of Arundel Terrace, Lewes Crescent, Sussex Square, Chichester Terrace, and the Kemp Town Enclosures (the gardens). The estate was conceived and financed by Thomas Read Kemp, designed by Charles Busby and Amon Henry Wilds, and constructed by Thomas Cubitt. Work began in 1823 and it was completed in 1855. It has given its name to the larger Kemptown region of Brighton. History Kemp Town Estate was designed by Charles Busby and Amon Henry Wilds and constructed by Thomas Cubitt. Building work started in 1823 on Arundel Terrace, Chichester Terrace, Lewes Crescent and Sussex Square. Chichester Terrace incorporated the earlier Chichester House. In 1837 Thomas Kemp fled the country to escape his creditors. The project continued under Cubitt with the support of the Fifth Earl of Bristol. It was completed in 1855, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the name given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The original book, published in 1549 in the reign of King Edward VI of England, was a product of the English Reformation following the break with Rome. The work of 1549 was the first prayer book to include the complete forms of service for daily and Sunday worship in English. It contained Morning Prayer, Evening Prayer, the Litany, and Holy Communion and also the occasional services in full: the orders for Baptism, Confirmation, Marriage, " prayers to be said with the sick", and a funeral service. It also set out in full the "propers" (that is the parts of the service which varied week by week or, at times, daily throughout the Church's Year): the introits, collects, and epistle and gospel readings for the Sunday service of Holy Communion. Old Testament and New Testament readings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instituted by Jesus Christ during the Last Supper; giving his disciples bread and wine during a Passover meal, he commanded them to "do this in memory of me" while referring to the bread as "my body" and the cup of wine as "the blood of my covenant, which is poured out for many". The elements of the Eucharist, sacramental bread ( leavened or unleavened) and wine (or non-alcoholic grape juice), are consecrated on an altar or a communion table and consumed thereafter, usually on Sundays. Communicants, those who consume the elements, may speak of "receiving the Eucharist" as well as "celebrating the Eucharist". Christians generally recognize a special presence of Christ in this rite, though they differ about exactly how, where, and when Chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, medieval castles, Roman forts and country houses. The charity states that it uses these properties to "bring the story of England to life for over 10 million people each year". Within its portfolio are Stonehenge, Dover Castle, Tintagel Castle and the best preserved parts of Hadrian's Wall. English Heritage also manages the London Blue Plaque scheme, which links influential historical figures to particular buildings. When originally formed in 1983, English Heritage was the operating name of an executive non-departmental public body of the British Government, officially titled the Historic Buildings and Monuments Commission for England, that ran the national system of heritage protection and managed a range of historic properties. It was created to combine the roles of existing bodies that had emerged from a long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Images Of England
Images of England is an online photographic record of all the listed buildings in England at the date of February 2002. The archive gives access to over 323,000 colour images, each of which is matched with the item's listed designation architectural description. It is a snapshot rather than an up-to-date record: it does not include all listed buildings, only those listed at February 2001, and is not updated as listing details change. the Images of England content moved to the main Historic England website alongside the list entry. Purpose Images of England was a stand-alone project funded jointly by English Heritage and the Heritage Lottery Fund. The aim of the project was to photograph every listed building and object (some 370,000) in England and to make the images available online to create, what was at the time, one of the largest free-to-view picture libraries of buildings in the world. It is part of the Historic England Archive of England's historic environment. The projec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracery
Tracery is an architecture, architectural device by which windows (or screens, panels, and vaults) are divided into sections of various proportions by stone ''bars'' or ''ribs'' of Molding (decorative), moulding. Most commonly, it refers to the stonework elements that support the glass in a window. The term probably derives from the tracing floors on which the complex patterns of windows were laid out in late Gothic architecture. Tracery can also be found on the interior of buildings and the exterior. There are two main types: plate tracery and the later bar tracery.Hugh Honour, Honour, H. and J. Fleming, (2009) ''A World History of Art''. 7th edn. London: Laurence King Publishing, p. 948. The evolving style from Romanesque architecture, Romanesque to Gothic architecture and changing features, such as the thinning of lateral walls and enlarging of windows, led to the innovation of tracery. The earliest form of tracery, called plate tracery, began as openings that were pierced fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancet Window
A lancet window is a tall, narrow window with a pointed arch at its top. It acquired the "lancet" name from its resemblance to a lance. Instances of this architectural element are typical of Gothic church edifices of the earliest period. Lancet windows may occur singly, or paired under a single moulding, or grouped in an odd number with the tallest window at the centre. The lancet window first appeared in the early French Gothic period (c. 1140–1200), and later in the English period of Gothic architecture (1200–1275). So common was the lancet window feature that this era is sometimes known as the "Lancet Period". Retrieved 24 October 2006 The term ''lancet window'' is properly applied to windows of austere form, without |
Spire
A spire is a tall, slender, pointed structure on top of a roof of a building or tower, especially at the summit of church steeples. A spire may have a square, circular, or polygonal plan, with a roughly conical or pyramidal shape. Spires are typically made of stonework or brickwork, or else of timber structures with Cladding (construction), metal cladding, ceramic tile, ceramic tiling, roof shingles, or Slate roof, slates on the exterior. Since towers supporting spires are usually square, square-plan spires emerge directly from the tower's walls, but octagonal spires are either built for a pyramidal transition section called a ''Broach spire, broach'' at the spire's base, or else freed spaces around the tower's summit for decorative elements like pinnacles. The former solution is known as a ''broach spire''. Small or short spires are known as ''spikes'', ''spirelets'', or ''flèche (architecture), flèches''. Etymology This sense of the word spire is attested in English since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruciform
Cruciform is a term for physical manifestations resembling a common cross or Christian cross. The label can be extended to architectural shapes, biology, art, and design. Cruciform architectural plan Christian churches are commonly described as having a cruciform architecture. In Early Christian, Byzantine and other Eastern Orthodox forms of church architecture this is likely to mean a tetraconch plan, a Greek cross, with arms of equal length or, later, a cross-in-square plan. In the Western churches, a cruciform architecture usually, though not exclusively, means a church built with the layout developed in Gothic architecture. This layout comprises the following: *An east end, containing an altar and often with an elaborate, decorated window, through which light will shine in the early part of the day. *A west end, which sometimes contains a baptismal font, being a large decorated bowl, in which water can be firstly, blessed (dedicated to the use and purposes of God) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Chichester
The Bishop of Chichester is the ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Chichester in the Province of Canterbury. The diocese covers the counties of East and West Sussex. The see is based in the City of Chichester where the bishop's seat is located at the Cathedral Church of the Holy Trinity. On 3 May 2012 the appointment was announced of Martin Warner, Bishop of Whitby, as the next Bishop of Chichester. His enthronement took place on 25 November 2012 in Chichester Cathedral. The bishop's residence is The Palace, Chichester. Since 2015, Warner has also fulfilled the diocesan-wide role of alternative episcopal oversight, following the decision by Mark Sowerby, then Bishop of Horsham, to recognise the orders of priests and bishops who are women. Between 1984 and 2013, the Bishop of Chichester, in addition to being the diocesan bishop, also had specific oversight of the Chichester Episcopal Area (the then Archdeaconry of Chichester), which covered the coastal region of We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashurst Gilbert
Ashurst Turner Gilbert (14 May 1786 – 21 February 1870) was an English churchman and academic, Principal of Brasenose College, Oxford, from 1822 and bishop of Chichester. Life The son of Thomas Gilbert of Ratcliffe, Buckinghamshire, a captain in the Royal Marines, by Elizabeth, daughter of William Long Nathaniel Hutton, rector of Maids Moreton, Buckinghamshire, was born near Burnham Beeches, Buckinghamshire, 14 May 1786, and educated at Manchester Grammar School from 1800. He was nominated to a school exhibition, and matriculated at Brasenose College, Oxford, on 30 May 1805. At the Michaelmas examination of 1808 he was placed in the first class in '' literis humanioribus'', one of his four companions being Robert Peel. He graduated B.A. 16 January 1809, and succeeded to one of Hulme's exhibitions on 8 March following. Having been elected to a fellowship, he proceeded M. A. 1811, and B.D. 1819. He was actively engaged for many years as a college tutor, and in 1816–18 w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


