|
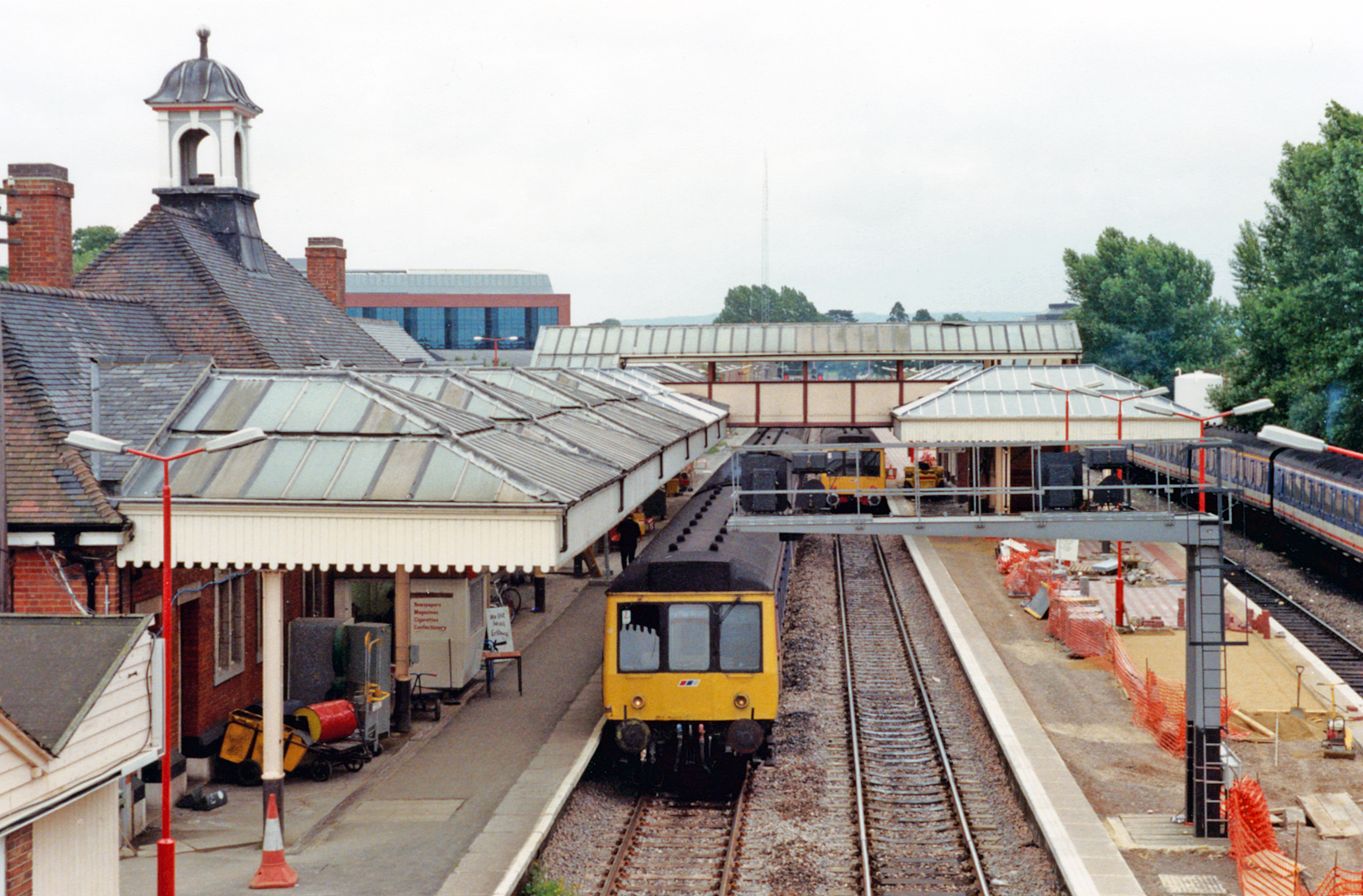
St Albans Abbey Station
St Albans Abbey railway station in St Albans, Hertfordshire, England is about south of the city centre in the St Stephen's area. It is the terminus of the Abbey Line from Watford Junction, operated by London Northwestern Railway. It is one of two stations in St Albans, the other being the much larger and busier St Albans City. The unstaffed station consists of a single open-air platform and a car park. Improvement works were carried out in 2008. It was the second UK railway station to receive a Harrington Hump to improve accessibility. History St Albans Abbey was the first railway station in St Albans, built by the London and North Western Railway in 1858. It was, as it is now, a terminus; the company's plans to extend northwards to Luton and Dunstable never materialised. Although the Midland Railway opened their station (St Albans City) in 1868, it was not until 1924 that "Abbey" was added to the station's title to avoid confusion – by this stage, both stations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Albans
St Albans () is a cathedral city in Hertfordshire, England, east of Hemel Hempstead and west of Hatfield, Hertfordshire, Hatfield, north-west of London, south-west of Welwyn Garden City and south-east of Luton. St Albans was the first major town on the old Roman Britain, Roman road of Watling Street for travellers heading north and became the city of Verulamium. It is within the London commuter belt and the Greater London Built-up Area. Name St Albans takes its name from the first British saint, Saint Alban, Alban. The most elaborate version of his story, Bede's ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'', relates that he lived in Verulamium, sometime during the 3rd or 4th century, when Christians were suffering persecution. Alban met a Christian priest fleeing from his persecutors and sheltered him in his house, where he became so impressed with the priest's piety that he converted to Christianity. When the authorities searched Alban's house, he put on the priest's cloa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
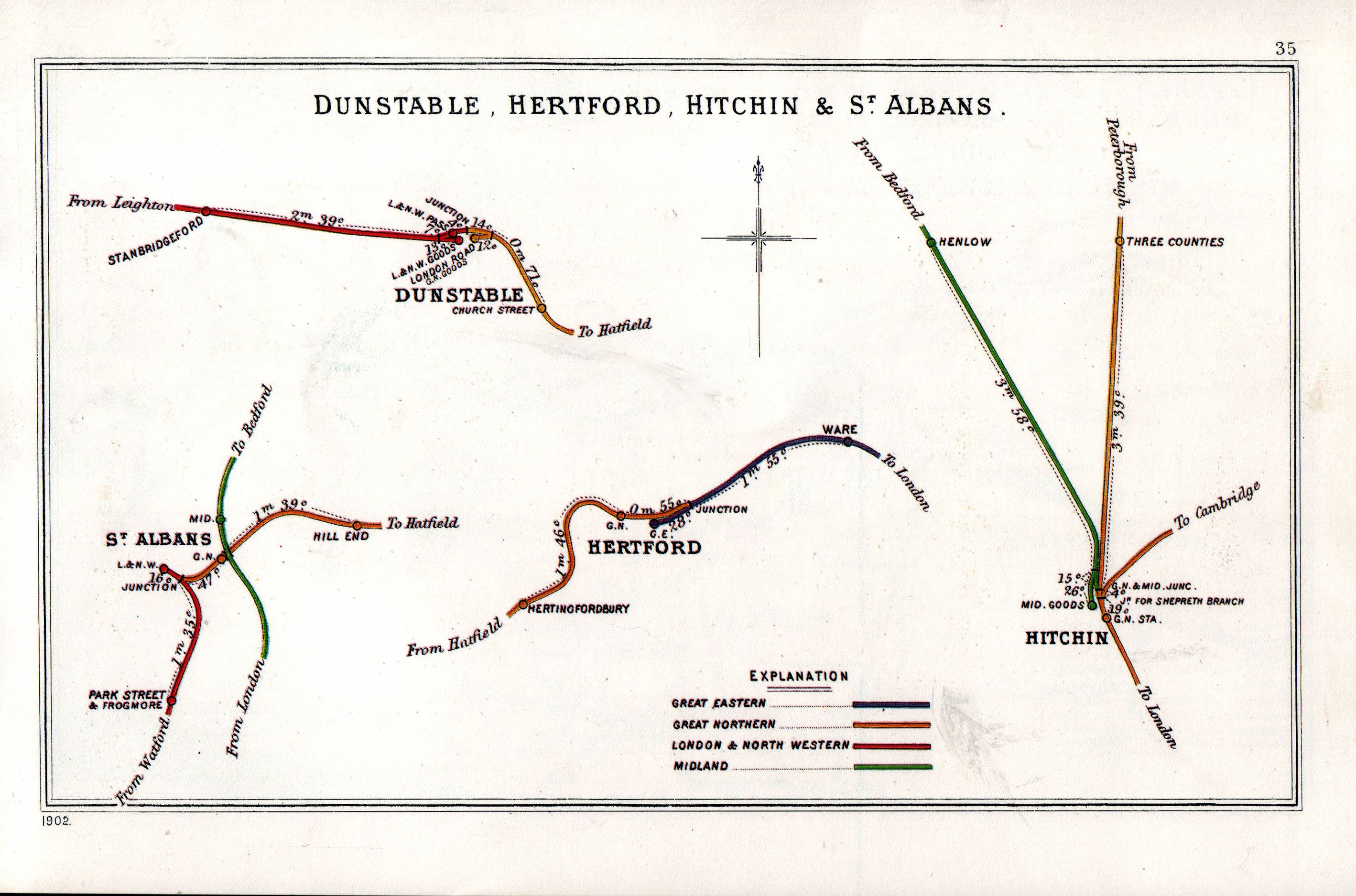
Dunstable
Dunstable ( ) is a market town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in Bedfordshire, England, east of the Chiltern Hills, north of London. There are several steep chalk escarpments, most noticeable when approaching Dunstable from the north. Dunstable is the fourth largest town in Bedfordshire and along with Houghton Regis forms the westernmost part of the Luton/Dunstable Urban Area. Etymology In Ancient Rome, Roman times there was a minor settlement called Durocobrivis in the area now occupied by modern-day Dunstable. There was a general assumption that the nominative form of the name had been Durocobrivae, so that is what appears on the map of 1944 illustrated Dunstable#History, below. But current thinking is that the form ''Durocobrivis'', which occurs in the Antonine Itinerary, is a fossilised locative that was used all the time and Ordnance Survey now uses this form. There are several theories concerning its modern name: *Legend tells that the lawlessness of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Multiple Unit
A diesel multiple unit or DMU is a multiple-unit train powered by on-board diesel engines. A DMU requires no separate locomotive, as the engines are incorporated into one or more of the carriages. Diesel-powered single-unit railcars are also generally classed as DMUs. Diesel-powered units may be further classified by their transmission type: diesel–mechanical DMMU, diesel–hydraulic DHMU, or diesel–electric DEMU. Design The diesel engine may be located above the frame in an engine bay or under the floor. Driving controls can be at both ends, on one end, or in a separate car. Types by transmission DMUs are usually classified by the method of transmitting motive power to their wheels. Diesel–mechanical In a diesel–mechanical multiple unit (DMMU), the rotating energy of the engine is transmitted via a gearbox and driveshaft directly to the wheels of the train, like a car. The transmissions can be shifted manually by the driver, as in the great majority of first-gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanmore Village Railway Station
Stanmore Village railway station was a station in Stanmore, Middlesex in the south of England (now in Greater London). Originally called simply ''Stanmore'', it was opened on 18 December 1890 by the Harrow and Stanmore Railway, a company owned by the hotel millionaire Frederick Gordon, as the terminus of the Stanmore branch line, a short branch line running north from Harrow & Wealdstone. Trains were operated by the London & North Western Railway (LNWR). The station was located on the south side of the junction of Gordon Avenue and Old Church Lane (the section north of the junction was originally named Station Road), and was noted for its architectural style, designed to resemble a village church, including a short spire. It closed to passenger traffic in 1952. History In 1882 the entrepreneur and hotelier Frederick Gordon purchased Bentley Priory, a large country house near Stanmore. He planned to open it up as a country retreat for wealthy guests. Known as "The Napoleon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherstone Railway Station
Atherstone is a railway station serving the town of Atherstone in Warwickshire, England. It is on the Trent Valley section of the West Coast Main Line, exactly from London Euston station. History The station was designed by John William Livock and opened by the London and North Western Railway in 1847. It was absorbed by the London Midland and Scottish Railway in the Grouping of 1923. The station passed to the London Midland Region of British Railways on nationalisation in 1948. When British Rail introduced sectorisation in the 1980s, the station was served by the Regional Railways Sector until the Privatisation of British Railways. In 1860 there was a train crash at Atherstone that killed 10 people. The Tudor style station building has been grade II listed since 1980. All of the stations on the Trent Valley Line originally had similar station buildings in the same style, designed by John William Livock, however the one at Atherstone is the only remaining example on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aylesbury Railway Station
Aylesbury railway station is a railway station in Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire, England, on the London–Aylesbury line from via Amersham. It is from Aylesbury to Marylebone. A branch line from on the Chiltern Main Line terminates at the station. It was the terminus for London Underground's Metropolitan line until the service was cut back to Amersham in 1961. The station was also known as Aylesbury Town under the management of British Railways from until the 1960s. History The first station on the site was opened in 1863 by the Wycombe Railway, which in 1867 was taken over by the Great Western Railway. In 1868 the Aylesbury & Buckingham Railway (later part of the Metropolitan Railway) reached Aylesbury. When opened, the line to Aylesbury from Princes Risborough was broad gauge. To avoid mixed gauge track when the standard gauge Aylesbury and Buckingham arrived at the station in 1868, the section to Princes Risborough was converted to standard gauge, and therefore until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Langley Railway Station
Kings Langley railway station is almost under the M25 motorway near Junction 20. It serves the village of Kings Langley, and the nearby villages of Abbots Langley and Hunton Bridge. The station is north west of London Euston on the West Coast Main Line. The station and all services calling at the station are operated by London Northwestern Railway. The station was opened in 1839. Services Monday to Saturday a half-hourly service to London Euston southbound and (Saturdays ) northbound. On evenings and Sundays there is an hourly train in each direction. A number of night and rush hour services are extended to and from Milton Keynes Central, Northampton and Birmingham New Street. Off peak weekday service in trains per hour: * 1 to London Euston. * 1 to London Euston via Wembley Central. * 2 to Tring. History In July 1837 the London and Birmingham Railway (L&BR) opened the first part of its new railway line between London Euston Station and (now Hemel Hempstead). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watford Junction
Watford Junction is a railway station that serves Watford, Hertfordshire. The station is on the West Coast Main Line (WCML), 17 miles 34 chains from London Euston and the Abbey Line, a branch line to St Albans. Journeys to London take between 16 and 52 minutes depending on the service used: shorter times on fast non-stop trains and slower on the stopping Watford DC line services. Trains also run to and East Croydon via the West London Line. The station is a major hub for local bus services and the connecting station for buses to Warner Bros. Studio Tour London – The Making of Harry Potter. The station is located north of a viaduct over the Colne valley and immediately south of Watford Tunnel. History The first railway station to open in Watford was situated on the north side of St Albans Road, approximately further up the line from the present-day station. This small, single-storey red-brick building was built 1836-7 when the first section of the London and Birmingham Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alban Way
The Alban Way is a traffic free multi-user route along a former railway line in Hertfordshire, England, that has been constructed along the route of the former Hatfield and St Albans Railway, Hatfield to St Albans railway line. It runs from St Albans, close to St Albans Abbey railway station and the site of Roman Verulamium, through Fleetville and Smallford to Hatfield, ending close to Hatfield railway station. It is long. Part of National Cycle Network Route 61, which runs from the River Thames at Maidenhead to the River Lea in Ware, Hertfordshire, Ware, the Alban Way is fully tarmacked throughout making it usable all year round. It can be linked to a separate section of Route 61, also along a disused railway route, runs from Welwyn Garden City to Hertford and is called the Cole Green Way. The remains of most of the station platforms still exist along the route, with many as of 2017 having recently been refurbished along with signage and street names painted into the tarmac. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Albans (London Road) Railway Station
St Albans London Road was one of three railway stations in St Albans, Hertfordshire. History The station was opened by the Hatfield and St Albans Railway on 16 October 1865,Butt (1995), page 202 and passenger services ceased on 1 October 1951. The station building has been restored, and the trackbed now forms part of the Alban Way, a six and a half-mile-long cycle track from St Albans to Hatfield. The old station building has been listed Grade II on the National Heritage List for England since June 1994. Station masters *James Barnes 1865 – 1883 *J. D. Rhodes 1884 – 1888 (formerly station master at Essendine) *Mr Perkins 1888 – 1890 (formerly station master at Meldreth and Melbourn) *Jonas Ellingham 1899 – 1918 (murdered by his wife) *Ernest Wallis 1919 – 1920 (afterwards station master at Palmers Green) *C. John Whitehead 1920 – 1926 *Campbell George Correll 1926- 1934 *George Howlett 1935 – 1941 (also station master of St Albans City railway station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatfield And St Albans Railway
The Hatfield & St Albans Railway was a branch of the Great Northern Railway which connected St Albans to Hatfield in Hertfordshire, England. It opened in 1865 with the principal aim of allowing St Albans traffic to access the Great Northern's main line to London at , but soon came into difficulties when the Midland Railway inaugurated a direct route to London through St Albans. Passenger receipts declined in the 1930s, resulting in the temporary withdrawal of services in 1939. Passenger services were permanently withdrawn in 1951, leaving goods traffic to linger on until December 1968. Much of the route of the line is now incorporated into the Alban Way, a footpath and cycleway. History Authorisation and opening The Hatfield and St Albans Railway Company was incorporated by Act of Parliament on 30 June 1862. It had been promoted by various landowners in Hatfield and St Albans in Hertfordshire and supported by the Great Northern Railway, which saw the line as a mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern Railway (Great Britain)
The Great Northern Railway (GNR) was a British railway company incorporated in 1846 with the object of building a line from London to York. It quickly saw that seizing control of territory was key to development, and it acquired, or took leases of, many local railways, whether actually built or not. In so doing, it overextended itself financially. Nevertheless, it succeeded in reaching into the coalfields of Nottinghamshire, Derbyshire and Yorkshire, as well as establishing dominance in Lincolnshire and north London. Bringing coal south to London was dominant, but general agricultural business, and short- and long-distance passenger traffic, were important activities too. Its fast passenger express trains captured the public imagination, and its Chief Mechanical Engineer Nigel Gresley became a celebrity. Anglo-Scottish travel on the East Coast Main Line became commercially important; the GNR controlled the line from London to Doncaster and allied itself with the North Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |