|
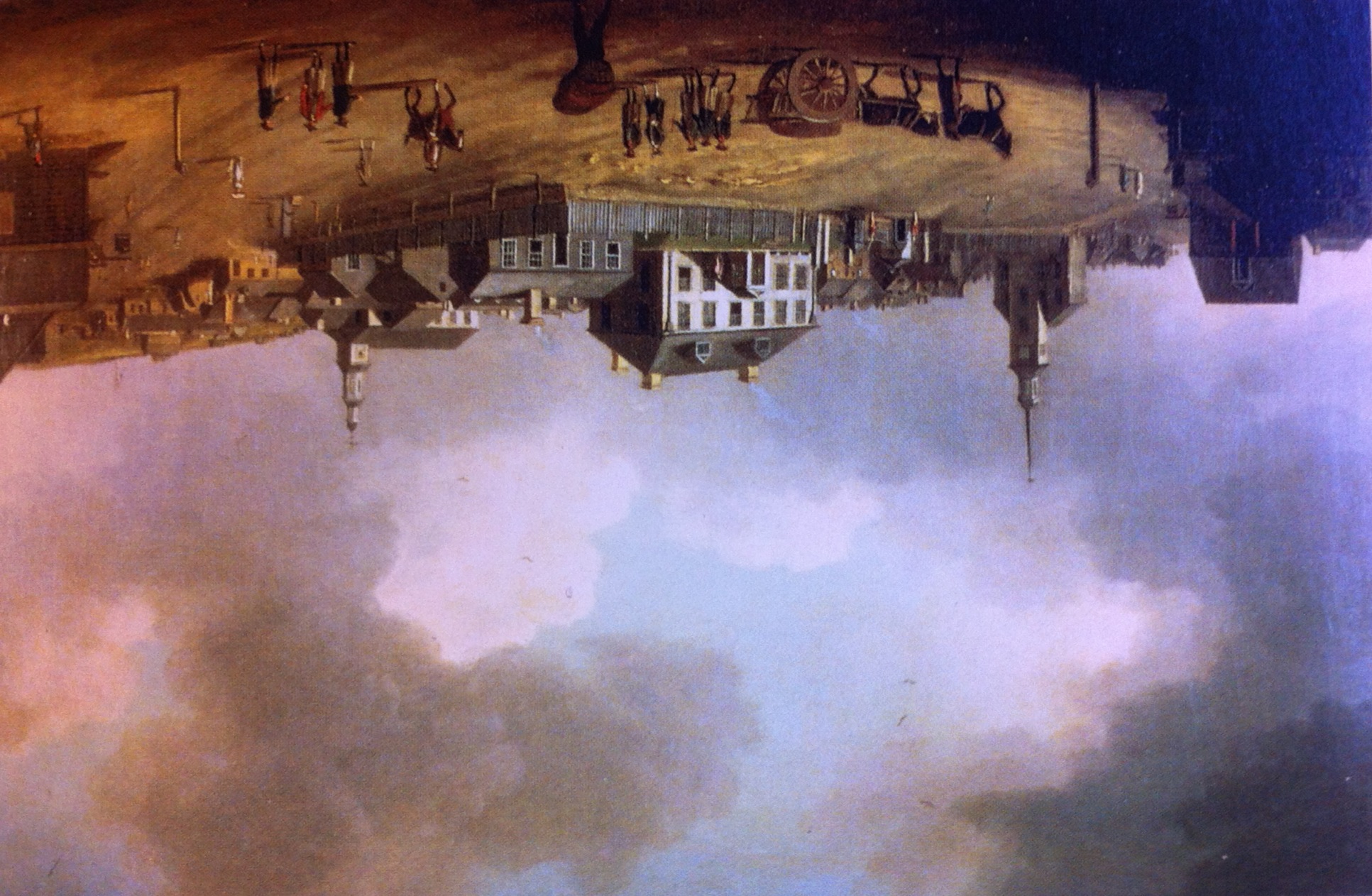
St. Matthew's United Church, Halifax
St. Matthew's United Church is a United Church of Canada church in downtown Halifax, Nova Scotia. The church was founded at the same time as the original colony in 1749 as a home for the various groups of dissenting Protestants who were from New England and who did not follow the Church of England. It originally met Sunday afternoons in St. Paul's Church, the Church of England building completed in 1750. The church got its own home in 1754 when a church was constructed at Hollis and Prince streets. This building was destroyed by fire in 1857, and a new church was built at the current location at 1479 Barrington Street, land parcelled off of the Black-Binney House estate by Bishop Hibbert Binney. The church used the Old Burying Ground (Halifax, Nova Scotia). The church was originally an amalgam of various dissenting Protestant groups with it mostly being a mix of Scottish Presbyterians and Puritan Congregationalists from the American colonies. Over the course of the 19th century t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Matthews, Halifax
ST, St, or St. may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Stanza, in poetry * Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band * Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise * Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy and theology by St. Thomas Aquinas * St or St., abbreviation of "State", especially in the name of a college or university Businesses and organizations Transportation * Germania (airline) (IATA airline designator ST) * Maharashtra State Road Transport Corporation, abbreviated as State Transport * Sound Transit, Central Puget Sound Regional Transit Authority, Washington state, US * Springfield Terminal Railway (Vermont) (railroad reporting mark ST) * Suffolk County Transit, or Suffolk Transit, the bus system serving Suffolk County, New York Other businesses and organizations * Statstjänstemannaförbundet, or Swedish Union of Civil Servants, a trade union * The Secret Team#Secret Team, The Secret Team, an alleged covert alliance between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Monro Grant
George Monro Grant (December 22, 1835 – May 10, 1902) was a Canadian church minister, writer, and political activist. He served as principal of Queen's College, Kingston, Ontario, for 25 years, from 1877 until 1902. Early life, education Grant was born in Stellarton, Pictou County, Nova Scotia. He was educated at the Pictou Academy and the anti-burgher seminary in West River in Nova Scotia, and, from 1853 to 1860, in Scotland at the University of Glasgow, where he had a brilliant academic career. Having entered the ministry of the Church of Scotland in 1861, he returned to serve in Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island, before being called to the St Matthew's congregation in Halifax, Nova Scotia, where he was minister from 1863 to 1877. Support of Confederation, railway development He quickly gained a high reputation as a preacher and as an eloquent speaker on political subjects. In 1867, Nova Scotia was the province most strongly opposed to federal union. Grant threw the wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua Mauger
Joshua Mauger (1725– 18 October 1788) was a prominent merchant and slave trader in Halifax, Nova Scotia (1749–60) and then went to England and became Nova Scotia's colonial agent (1762). He has been referred to as "the first great merchant and shipowner" in Halifax. He was a member of St. Matthew's United Church (Halifax). Along with prominent merchant Captain Ephraim Cook (mariner), Mauger pushed Governor Lawrence for an elected assembly (1757). He was born in Jersey the son of José Mauger and Sarah Le Couteur and went to sea with his uncle Matthew Mauger. He eventually became master of his own ship and settled in Halifax as an agent victualler to the British navy and a merchant. He later returned to England and became a Member of Parliament for Poole from 1768 to 1780. He died in 1788, having married his Uncle Matthew's daughter, with whom he had a daughter. Legacy Maugerville, New Brunswick (q.v.) is named for him. He is the namesake of Mauger Beach (later known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Scott (minister)
John Scott may refer to: Academics * John Scott (1639–1695), English clergyman and devotional writer * John Witherspoon Scott (1800–1892), American minister, college president, and father of First Lady Caroline Harrison * John Work Scott (1807–1879), American president of Washington College * John Scott (medical school dean) (1851–1914), New Zealand professor, artist, and medical school dean * John Scott (sociologist) (born 1949), British sociologist * John R. Scott Sr. (1840/41–1929), president of Edward Waters College, minister of the African Methodist Episcopal Church * John Paul Scott (geneticist) (1909–2000), American behavior geneticist and comparative psychologist Arts and entertainment * John Scott (engraver) (1774–1827), English engraver * John Scott (1849–1919), English artist * John Beldon Scott, American art historian * John T. Scott (1940–2007), African-American sculptor, painter, printmaker, and collagist * John Scott of Amwell (1730–1783), Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archibald Gray
Reverend Archibald Gray (died 1831) was an influential Presbyterian minister in Halifax, Nova Scotia. He served in the St. Matthew's United Church (Halifax) for 30 years (1795–1826). Gray was a native of Morayshire and a graduate of King's College, Aberdeen. While he baptized his son at St Matthew's, his mother belonged to the Church of England, and after Gray's death his son entered the Anglican ministry. He was a strong advocate for public education. Gray is buried in the Old Burying Ground. He was a member of the North British Society The North British Society (also known as "The Scots" and "Scots Club") was founded in Halifax Regional Municipality, Halifax, Nova Scotia in 1768, the oldest Scottish heritage society outside Great Britain. North British is an adjective used as a .... References Canadian Presbyterian ministers History of Nova Scotia 1831 deaths Year of birth missing {{Canada-reli-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 1582 and officially opened in 1583, it is one of Scotland's four ancient universities and the sixth-oldest university in continuous operation in the English-speaking world. The university played an important role in Edinburgh becoming a chief intellectual centre during the Scottish Enlightenment and contributed to the city being nicknamed the " Athens of the North." Edinburgh is ranked among the top universities in the United Kingdom and the world. Edinburgh is a member of several associations of research-intensive universities, including the Coimbra Group, League of European Research Universities, Russell Group, Una Europa, and Universitas 21. In the fiscal year ending 31 July 2021, it had a total income of £1.176 billion, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Brown (minister)
Andrew Brown (22 August 1763 – 19 February 1834) was Professor of Rhetoric at Edinburgh University and Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland in 1813. He was also a historian and author, closely connected to the history of Nova Scotia, having served as a minister at St. Matthew's United Church (Halifax). Life Early years Brown was born on 22 August 1763 in Biggar, South Lanarkshire, the son of Richard Brown, a weaver, and Isabella Forrest. He studied theology at the University of Glasgow and became a licensed minister of the Church of Scotland in 1786, being licensed by the Presbytery of Biggar, South Lanarkshire, Biggar but not receiving a post there. In North America In 1787 Brown crossed the Atlantic to serve as a minister in St Matthews Church in Halifax, Nova Scotia and also served as chaplin to the North British Society and British naval and army forces in the area. In 1788, during his time in Halifax, he received an honorary doctorate (Doctor of D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Seccombe
Rev. John Seccombe (25 April 1708 – 27 October 1792) was an author, a founder of Chester, Nova Scotia and was “the best-known and most highly respected clergyman in Nova Scotia.” He was also the author of ''Father Abbey's Will'', which was printed as a poem and a broadsheet over 30 times throughout the 18th century in England and America. According to the ''Manual of American Literature'', the poem "was one of the best comic poems of that day." As a result of the poem, the ''History of American Literature'' indicated that Seccombe "had an extraordinary notoriety" in America's early literary history. Harvard, Massachusetts Seccombe graduated Harvard College (1728) and then became the first congregational minister of the town of Harvard, Massachusetts, where he stayed for 25 years (1733 -1757). While at Harvard, he built the "grandest house" in Harvard at the centre of town and a cottage on one of the two largest islands in Bare Hill Pond (now named Ministers Island). (He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading intellectuals of his time, Franklin was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States, a drafter and signer of the United States Declaration of Independence, and the first United States Postmaster General. As a scientist, he was a major figure in the American Enlightenment and the history of physics for his studies of electricity, and for charting and naming the current still known as the Gulf Stream. As an inventor, he is known for the lightning rod, bifocals, and the Franklin stove, among others. He founded many civic organizations, including the Library Company, Philadelphia's first fire department, and the University of Pennsylvania. Isaacson, 2004, p. Franklin earned the title of "The First American" for his early and indefa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aaron Cleveland
Aaron Cleveland (29 October 171511 August 1757 Philadelphia) was a clergyman. He established the first Presbyterian church in Canada. He was a great-great-grandfather of United States President Grover Cleveland. Biography His father was also named Aaron Cleveland. At the time of the Aaron's birth his father was making a modest living as a publican in Cambridge, Massachusetts, where Aaron was born, and also working in construction. His father would later become a militia captain and a man of some wealth. The son graduated from Harvard in 1735. He was a man of great physical strength and activity, and the best skater, swimmer, and wrestler in the college in his day. In 1739, he was made pastor of the church in Haddam, Connecticut, where his father possessed landed property. In this year, he also married Susannah, the daughter of Aaron Porter of Medford, Massachusetts. The preaching of George Whitefield produced a great impression on his mind, and led to subsequent changes in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandford Fleming
Sir Sandford Fleming (January 7, 1827 – July 22, 1915) was a Scottish Canadian engineer and inventor. Born and raised in Scotland, he emigrated to colonial Canada at the age of 18. He promoted worldwide standard time zones, a prime meridian, and use of the 24-hour clock as key elements to communicating the accurate time, all of which influenced the creation of Coordinated Universal Time. He designed Canada's first postage stamp, produced a great deal of work in the fields of surveying, land surveying and cartography, map making, engineered much of the Intercolonial Railway and the first several hundred kilometers of the Canadian Pacific Railway, and was a founding member of the Royal Society of Canada and founder of the Royal Canadian Institute, Canadian Institute (a science organization in Toronto). Early life In 1827, Fleming was born in Kirkcaldy, Fife, Scotland to Andrew and Elizabeth Fleming. At the age of 14 he was apprenticed as a surveyor and in 1845, at the age of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen's University At Kingston
Queen's University at Kingston, commonly known as Queen's University or simply Queen's, is a public research university in Kingston, Ontario, Canada. Queen's holds more than of land throughout Ontario and owns Herstmonceux Castle in East Sussex, England. Queen's is organized into eight faculties and schools. The Church of Scotland established Queen's College in October 1841 via a royal charter from Queen Victoria. The first classes, intended to prepare students for the ministry, were held 7 March 1842 with 13 students and two professors. In 1869, Queen's was the first Canadian university west of the Maritime provinces to admit women. In 1883, a women's college for medical education affiliated with Queen's University was established after male staff and students reacted with hostility to the admission of women to the university's medical classes. In 1912, Queen's ended its affiliation with the Presbyterian Church, and adopted its present name. During the mid-20th century, the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |