|
Spin–lattice Relaxation
During nuclear magnetic resonance observations, spin–lattice relaxation is the mechanism by which the longitudinal component of the total nuclear magnetic moment vector (parallel to the constant magnetic field) exponentially relaxes from a higher energy, non-equilibrium state to thermodynamic equilibrium with its surroundings (the "lattice"). It is characterized by the spin–lattice relaxation time, a time constant known as ''T1''. There is a different parameter, ''T2'', the spin-spin relaxation time, which concerns the exponential relaxation of the transverse component of the nuclear magnetization vector ( to the external magnetic field). Measuring the variation of ''T1'' and ''T2'' in different materials is the basis for some magnetic resonance imaging techniques. Nuclear physics ''T1'' relaxation or longitudinal relaxation curve ''T1'' characterizes the rate at which the longitudinal ''Mz'' component of the magnetization vector recovers exponentially towards its thermodyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are perturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a frequency characteristic of the magnetic field at the nucleus. This process occurs near resonance, when the oscillation frequency matches the intrinsic frequency of the nuclei, which depends on the strength of the static magnetic field, the chemical environment, and the magnetic properties of the isotope involved; in practical applications with static magnetic fields up to ca. 20 tesla, the frequency is similar to VHF and UHF television broadcasts (60–1000 MHz). NMR results from specific magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is widely used to determine the structure of organic molecules in solution and study molecular physics and crystals as well as non-crystalline materials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larmor Frequency
In physics, Larmor precession (named after Joseph Larmor) is the precession of the magnetic moment of an object about an external magnetic field. The phenomenon is conceptually similar to the precession of a tilted classical gyroscope in an external torque-exerting gravitational field. Objects with a magnetic moment also have angular momentum and effective internal electric current proportional to their angular momentum; these include electrons, protons, other fermions, many atomic and nuclear systems, as well as classical macroscopic systems. The external magnetic field exerts a torque on the magnetic moment, :\vec = \vec\times\vec = \gamma\vec\times\vec, where \vec is the torque, \vec is the magnetic dipole moment, \vec is the angular momentum vector, \vec is the external magnetic field, \times symbolizes the cross product, and \gamma is the gyromagnetic ratio which gives the proportionality constant between the magnetic moment and the angular momentum. The angular momentum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMR In Biomedicine
''NMR in Biomedicine'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published since 1988 by John Wiley & Sons. It publishes original full-length papers, rapid communications, and review articles in which magnetic resonance spectroscopy or imaging methods are used to investigate physiological, biochemical, biophysical, or medical problems. The current editor-in-chief is John R. Griffiths (Cancer Research UK). Highest cited articles The following articles have been cited most frequently: # "The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system - a technical review", 15 (7-8) Nov-Dec 2002: 435–455, Beaulieu C. # "A review of chemical issues in H-1-NMR spectroscopy - n-acetyl-l-aspartate, creatine and choline", 4 (2) Apr 1991: 47–52, Miller BL. # "Fiber tracking: principles and strategies - a technical review", 15 (7-8) Nov-Dec 2002: 468–480, DMori S, van Zijl PCM. # "Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
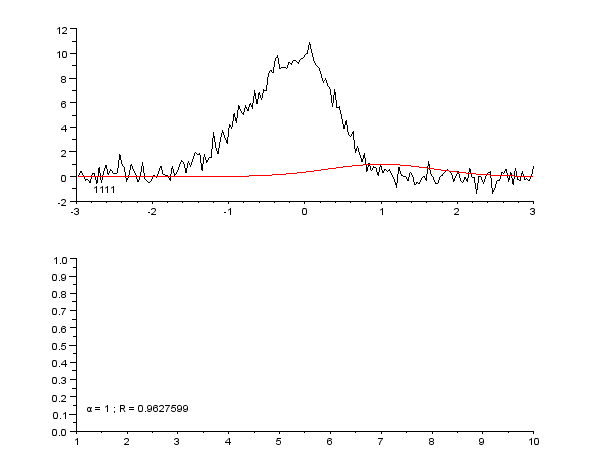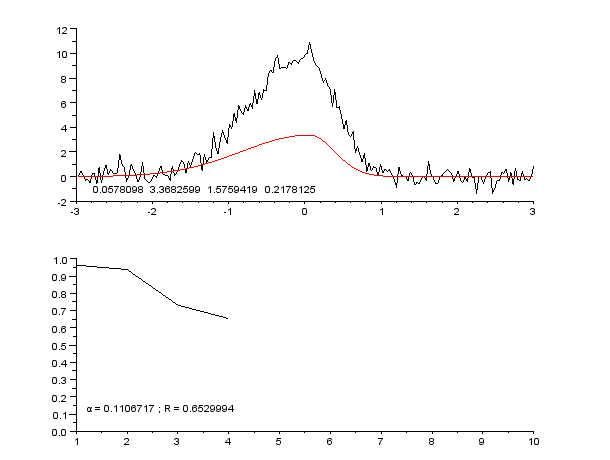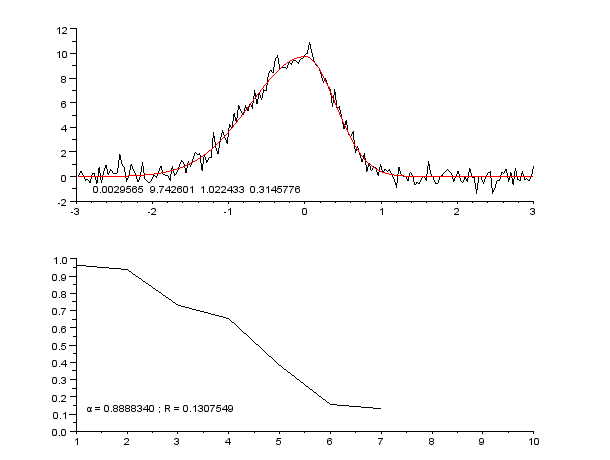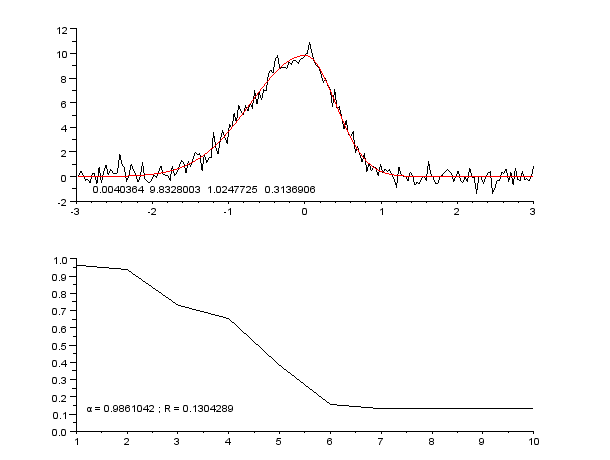
Curve Fitting
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function is constructed that approximately fits the data. A related topic is regression analysis, which focuses more on questions of statistical inference such as how much uncertainty is present in a curve that is fit to data observed with random errors. Fitted curves can be used as an aid for data visualization, to infer values of a function where no data are available, and to summarize the relationships among two or more variables. Extrapolation refers to the use of a fitted curve beyond the range of the observed data, and is subject to a degree of uncertainty since it may reflect the method used to construct the curve as much as it reflects the observed data. For linear-algebraic analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upper limit of audio frequencies and the lower limit of infrared frequencies; these are the frequencies at which energy from an oscillating current can radiate off a conductor into space as radio waves. Different sources specify different upper and lower bounds for the frequency range. Electric current Electric currents that oscillate at radio frequencies (RF currents) have special properties not shared by direct current or lower audio frequency alternating current, such as the 50 or 60 Hz current used in electrical power distribution. * Energy from RF currents in conductors can radiate into space as electromagnetic waves ( radio waves). This is the basis of radio technology. * RF current does not penetrate deeply into electrica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution of action potentials, acting as a relay and coordinating communication between different brain regions. White matter is named for its relatively light appearance resulting from the lipid content of myelin. However, the tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish-white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Its white color in prepared specimens is due to its usual preservation in formaldehyde. Structure White matter White matter is composed of bundles, which connect various grey matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other, and carry nerve impulses between neurons. Myelin acts as an insulator, which allows electrical signals to jump, rather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey Matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal Soma (biology), cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and unmyelinated axons), Glia, glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and Capillary, capillaries. Grey matter is distinguished from white matter in that it contains numerous cell bodies and relatively few myelinated axons, while white matter contains relatively few cell bodies and is composed chiefly of long-range myelinated axons. The colour difference arises mainly from the whiteness of myelin. In living tissue, grey matter actually has a very light grey colour with yellowish or pinkish hues, which come from capillary blood vessels and neuronal cell bodies. Structure Grey matter refers to unmyelinated neurons and other cells of the central nervous system The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
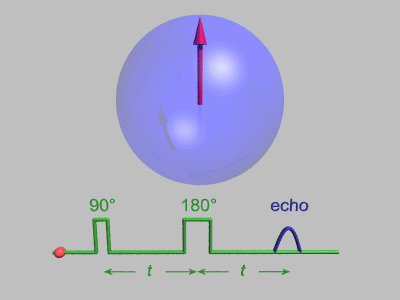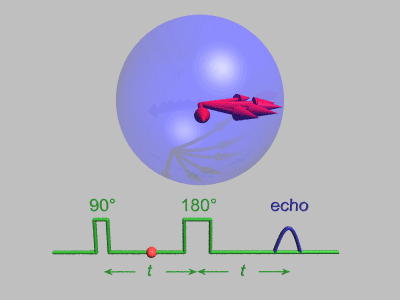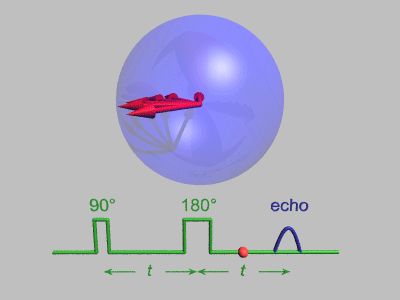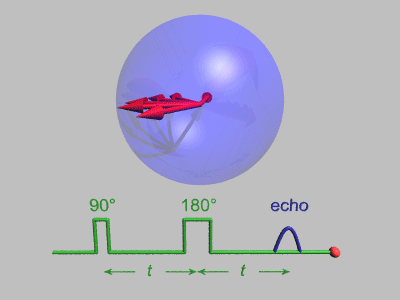
Spin Echo
In magnetic resonance, a spin echo or Hahn echo is the refocusing of spin magnetisation by a pulse of resonant electromagnetic radiation. Modern nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) make use of this effect. The NMR signal observed following an initial excitation pulse decays with time due to both spin relaxation and any ''inhomogeneous'' effects which cause spins in the sample to precess at different rates. The first of these, relaxation, leads to an irreversible loss of magnetisation. But the inhomogeneous dephasing can be removed by applying a 180° ''inversion'' pulse that inverts the magnetisation vectors. Examples of inhomogeneous effects include a magnetic field gradient and a distribution of chemical shifts. If the inversion pulse is applied after a period ''t'' of dephasing, the inhomogeneous evolution will rephase to form an echo at time 2''t''. In simple cases, the intensity of the echo relative to the initial signal is given by ''e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repetition Time
The physics of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) concerns fundamental physical considerations of MRI techniques and technological aspects of MRI devices. MRI is a medical imaging technique mostly used in radiology and nuclear medicine in order to investigate the anatomy and physiology of the body, and to detect pathologies including tumors, inflammation, neurological conditions such as stroke, disorders of muscles and joints, and abnormalities in the heart and blood vessels among others. Contrast agents may be injected intravenously or into a joint to enhance the image and facilitate diagnosis. Unlike CT and X-ray, MRI uses no ionizing radiation and is, therefore, a safe procedure suitable for diagnosis in children and repeated runs. Patients with specific non-ferromagnetic metal implants, cochlear implants, and cardiac pacemakers nowadays may also have an MRI in spite of effects of the strong magnetic fields. This does not apply on older devices, and details for medical prof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |