|
Spinoloricus Nov. Sp.
''Spinoloricus cinziae'' is an animal species described in 2014 in the phylum Loricifera. It was the first described animal species that does not require oxygen at any point during its life.Jackson P. (8 April 2010). http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/8609246.stm "First oxygen-free animals found". ''BBC News''. accessed 16 April 2010.New species 'live without oxygen' The Telegraph, April 9, 2010 The species, along with two other newly discovered species, '' nov. sp.'' and '' |
Species Description
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been described previously or are related. In order for species to be validly described, they need to follow guidelines established over time. Zoological naming requires adherence to the ICZN code, plants, the ICN, viruses ICTV, and so on. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of type material along with a note on where they are deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct throughout the existence of life on Earth. Naming process A name of a new species becomes valid (available in zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loricifera
Loricifera (from Latin, '' lorica'', corselet (armour) + ''ferre'', to bear) is a phylum of very small to microscopic marine cycloneuralian sediment-dwelling animals that had been determined to be 37 described species, in 9 genera, but in 2021 has increased to 43 species. Aside from these described species, there are approximately 100 more that have been collected and not yet described. Their sizes range from 100 μm to ca. 1 mm. They are characterised by a protective outer case called a lorica and their habitat is in the spaces between marine gravel to which they attach themselves. The phylum was discovered in 1983 by R.M. Kristensen, near Roscoff, France. They are among the most recently discovered groups of animals. They attach themselves quite firmly to the substrate, and hence remained undiscovered for so long. The first specimen was collected in the 1970s, and later described in 1983. They are found at all depths, in different sediment types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMC Biology
''BMC Biology'' is an online open access scientific journal that publishes original, peer-reviewed research in all fields of biology, together with opinion and comment articles. The publication was established in 2003. The journal is part of a series of BMC journals published by the UK-based publisher BioMed Central, owned by Springer Nature. The journal has an international editorial board of researchers and editorial offices in London and New York. Since 2010 it has incorporated what was previously the separate '' Journal of Biology''. Video abstracts associated with the BMC Biology articles are collected on the BMC YouTube Channel. Abstracting and Indexing BMC Biology is indexed in PubMed, MEDLINE (added in 2005), BIOSIS Previews, Chemical Abstracts Service, EMBASE, Scopus, Zoological Record, CAB International, Institute for Scientific Information and Google Scholar. The journal has a (2019) impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an acad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugiloricus
''Rugiloricus'' is a genus of marine organisms of the phylum Loricifera and the family Pliciloricidae, described by Higgins & Kristensen in 1986. Species References External links Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS): ''Rugiloricus'' Higgins and Kristensen, 1986 Taxonomic Serial No.: 722180uBio: ''Rugiloricus'' Higgins & Kristensen 1986 NamebankID:4581983 {{Taxonbar, from=Q3452949 Loricifera Protostome genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliciloricus
''Pliciloricus'' is a genus of marine organisms Pliciloricidae family, the phylum Loricifera described by Higgins & Kristensen, 1986.Higgins, Robert P.; Kristensen, Reinhardt M 1986: New Loricifera from southeastern United States coastal waters Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology, 438 Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington D.C.. III, 70 pp. ISSN 0081-0282 Species * '' Pliciloricus cavernicola'' Heiner, Boesgaard & Kristensen, 2009 * '' Pliciloricus corvus'' Gad, 2005 * '' Pliciloricus diva'' Gad, 2009 * '' Pliciloricus dubius'' Higgins & Kristensen, 1986 * ''Pliciloricus enigmaticus '' Pliciloricus enigmaticus'' is a marine Loriciferan species of genus ''Pliciloricus'' first described by Higgins & Kristensen 1986. Description ''Pliciloricus enigmaticus'' is a marine species in which adults measure between 160–268&nbs ...'' Higgins & Kristensen, 1986 * '' Pliciloricus gracilis'' Higgins & Kristensen, 1986 * '' Pliciloricus hadalis'' Kristensen & Shirayama, 1988 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anoxic Waters
Anoxic waters are areas of sea water, fresh water, or groundwater that are depleted of dissolved oxygen. The US Geological Survey defines anoxic groundwater as those with dissolved oxygen concentration of less than 0.5 milligrams per litre. Anoxic waters can be contrasted with hypoxic waters, which are low (but not lacking) in dissolved oxygen. This condition is generally found in areas that have restricted water exchange. In most cases, oxygen is prevented from reaching the deeper levels by a physical barrier, as well as by a pronounced density stratification, in which, for instance, heavier hypersaline waters rest at the bottom of a basin. Anoxic conditions will occur if the rate of oxidation of organic matter by bacteria is greater than the supply of dissolved oxygen. Anoxic waters are a natural phenomenon, and have occurred throughout geological history. The Permian–Triassic extinction event, a mass extinction of species from the world's oceans, may have resulted from w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'Atalante Basin
L'Atalante basin is a hypersaline brine lake at the bottom of the Mediterranean Sea about west of the island of Crete. It is named for the French ''L'Atalante'', one of the oceanographic research vessels involved in its discovery in 1993. L'Atalante and its neighbors the Urania and Discovery deep hyper saline anoxic basins (DHABs) are at most 35,000 years old. They were formed by Messinian evaporite salt deposits dissolving out of the Mediterranean Ridge and collecting in abyssal depressions about deep. L'Atalante is the smallest of the three; its surface begins at about below sea level. Description and biology The L'Atalante basin's salinity is near saturation at 365 (about 8 times that of ordinary seawater), which prevents it from mixing with the oxygenated waters above; therefore, it is completely anoxic. The approximately halocline between the seawater above and brine below teems with bacterial and archaeal cells: they are chemoautotrophs, which feed on ammonia from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. The Mediterranean Sea e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a higher resolving power than light microscopes and can reveal the structure of smaller objects. A scanning transmission electron microscope has achieved better than 50 pm resolution in annular dark-field imaging mode and magnifications of up to about 10,000,000× whereas most light microscopes are limited by diffraction to about 200 nm resolution and useful magnifications below 2000×. Electron microscopes use shaped magnetic fields to form electron optical lens systems that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope. Electron microscopes are used to investigate the ultrastructure of a wide range of biological and inorganic specimens including microorganisms, cells, large molecules, biopsy samples, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
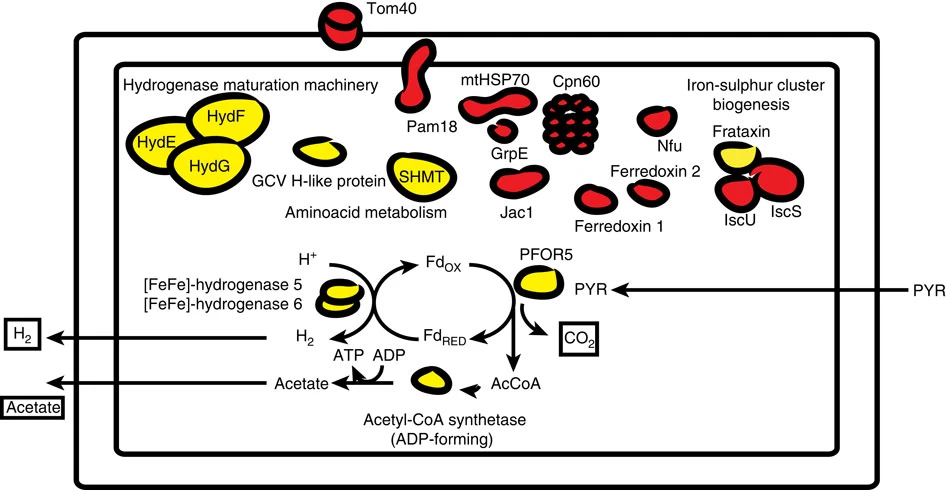
Hydrogenosome
A hydrogenosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in some anaerobic ciliates, flagellates, and fungi. Hydrogenosomes are highly variable organelles that have presumably evolved from protomitochondria to produce molecular hydrogen and ATP in anaerobic conditions. Hydrogenosomes were discovered in 1973 by D. G. Lindmark and M. Müller. Because hydrogenosomes hold evolutionary lineage significance for organisms living in anaerobic or oxygen-stressed environments, many research institutions have since documented their findings on how the organelle differs in various sources. History Hydrogenosomes were isolated, purified, biochemically characterized and named in the early 1970s by Lindmark and Müller at Rockefeller University. In addition to this seminal study on hydrogenosomes, they also demonstrated for the first time the presence of pyruvate:ferredoxin oxido-reductase and hydrogenase in eukaryotes. Further studies were subsequently conducted on the biochemical cytology a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment. Anaerobes may be unicellular (e.g. protozoans, bacteria) or multicellular. Most fungi are obligate aerobes, requiring oxygen to survive. However, some species, such as the Chytridiomycota that reside in the rumen of cattle, are obligate anaerobes; for these species, anaerobic respiration is used because oxygen will disrupt their metabolism or kill them. Deep waters of the ocean are a common anoxic environment. First observation In his letter of 14 June 1680 to The Royal Society, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described an experiment he carried out by filling two identical glass tubes about halfway with crushed pepper powder, to which some clean rain water was added. Van Leeuwenhoek sealed one of the glass tubes using a flame an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biota Of The Mediterranean Sea
Biota may refer to: * Biota (ecology), the plant and animal life of a region * Biota (plant), common name for a coniferous tree, ''Platycladus orientalis'' * Biota, Cinco Villas, a municipality in Aragon, Spain * Biota (band), a band from Colorado, USA * Biota! Biota! was a proposed aquarium in the Silvertown Quays redevelopment, on the site of Millennium Mills adjacent to the Royal Victoria Dock, part of the wider Thames Gateway regeneration project for East London. The £80 million building by Ter ..., a proposed aquarium in London * ''Biota'' (album), a 1982 album by Mnemonist Orchestra See also * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |