|
Spinal Portion
The spinal root of accessory nerve (or part) is firm in texture, and its fibers arise from the motor cells in the lateral part of the anterior column of the gray substance of the medulla spinalis as low as the fifth cervical nerve. Passing through the lateral funiculus of the medulla spinalis, they emerge on its surface and unite to form a single trunk, which ascends between the ligamentum denticulatum and the posterior roots of the spinal nerves; enters the skull through the foramen magnum, and is then directed to the jugular foramen, through which it passes, lying in the same sheath of dura mater as the vagus, but separated from it by a fold of the arachnoid. In the jugular foramen, it receives one or two filaments from the cranial part of the nerve, or else joins it for a short distance and then separates from it again. As it exits from the jugular foramen, it runs backward in front of the internal jugular vein in 66.6% of cases, and behind it in 33% of cases. The nerve then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Spinalis
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from in the cervical and lumbar regions to in the thoracic area. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex to the body, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Funiculus
The most lateral of the bundles of the anterior nerve roots is generally taken as a dividing line that separates the anterolateral system into two parts. These are the anterior funiculus, between the anterior median fissure and the most lateral of the anterior nerve roots, and the lateral funiculus (or lateral column) between the exit of these roots and the posterolateral sulcus. The lateral funiculus transmits the contralateral corticospinal and spinothalamic tracts. A lateral cutting of the spinal cord results in the transection of both ipsilateral posterior column and lateral funiculus and this produces Brown-Séquard syndrome Brown-Séquard syndrome (also known as Brown-Séquard's hemiplegia, Brown-Séquard's paralysis, hemiparaplegic syndrome, hemiplegia et hemiparaplegia spinalis, or spinal hemiparaplegia) is caused by damage to one half of the spinal cord, i.e. hem ....Kaplan Qbook - USMLE Step 1 - 5th edition - page References Central nervous system {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligamentum Denticulatum
Denticulate ligaments (also known as dentate ligaments) are lateral projections of the spinal pia mater forming triangular-shaped ligaments that anchor the spinal cord along its length to the dura mater on each side. There are usually 21 denticulate ligaments on each side, with the uppermost pair occurring just below the foramen magnum, and the lowest pair occurring between spinal nerve roots of T12 and L1. The denticulate ligaments are traditionally believed to provide stability for the spinal cord against motion within the vertebral column. Their tooth-like appearance originates the word which derives from Latin ''denticulatus'', from ''denticulus'' (meaning ‘small tooth’). Anatomy The bases of denticulate ligaments arise in the pia mater and are firmly attached to the arachnoid mater and dura mater at the apex. The denticulate ligaments extend across the subarachnoid space between anterior nerve roots and posterior nerve roots, piercing the intervening spinal arachnoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugular Foramen
A jugular foramen is one of the two (left and right) large foramina (openings) in the base of the skull, located behind the carotid canal. It is formed by the temporal bone and the occipital bone. It allows many structures to pass, including the inferior petrosal sinus, three cranial nerves, the sigmoid sinus, and meningeal arteries. Structure The jugular foramen is formed in front by the petrous portion of the temporal bone, and behind by the occipital bone. It is generally slightly larger on the right side than on the left side. Contents The jugular foramen may be subdivided into three compartments, each with their own contents. * The ''anterior'' compartment transmits the inferior petrosal sinus. * The ''intermediate'' compartment transmits the glossopharyngeal nerve, the vagus nerve, and the accessory nerve. * The ''posterior'' compartment transmits the sigmoid sinus (becoming the internal jugular vein), and some meningeal branches from the occipital artery and ascending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dura Mater
In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. The other two meningeal layers are the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. It envelops the arachnoid mater, which is responsible for keeping in the cerebrospinal fluid. It is derived primarily from the neural crest cell population, with postnatal contributions of the paraxial mesoderm. Structure The dura mater has several functions and layers. The dura mater is a membrane that envelops the arachnoid mater. It surrounds and supports the dural sinuses (also called dural venous sinuses, cerebral sinuses, or cranial sinuses) and carries blood from the brain toward the heart. Cranial dura mater has two layers called ''lamellae'', a superficial layer (also called the periosteal layer), which serves as the skull's inner periosteum, called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right vagus nerves—but they are typically referred to collectively as a single subsystem. The vagus is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body and comprises both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers originate from neurons of the nodose ganglion, whereas the motor fibers come from neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus. The vagus was also historically called the pneumogastric nerve. Structure Upon leaving the medulla oblongata between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle, the vagus nerve extends through the jugular foramen, then passes into the carotid sheath between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein down to the neck, chest, and abdomen, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnoid Mater
The arachnoid mater (or simply arachnoid) is one of the three meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is so named because of its resemblance to a spider web. The arachnoid mater is a derivative of the neural crest mesoectoderm in the embryo. Structure It is interposed between the two other meninges, the more superficial and much thicker dura mater and the deeper pia mater, from which it is separated by the subarachnoid space. The delicate arachnoid layer is not attached to the inside of the dura but against it and surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It does not line the brain down into its sulci (folds), as does the pia mater, with the exception of the longitudinal fissure, which divides the left and right cerebral hemispheres. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows under the arachnoid in the subarachnoid space, within a meshwork of trabeculae which span between the arachnoid and the pia. The arachnoid mater makes arachnoid villi, small protrusions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Jugular Vein
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve. It begins in the posterior compartment of the jugular foramen, at the base of the skull. It is somewhat dilated at its origin, which is called the ''superior bulb''. This vein also has a common trunk into which drains the anterior branch of the retromandibular vein, the facial vein, and the lingual vein. It runs down the side of the neck in a vertical direction, being at one end lateral to the internal carotid artery, and then lateral to the common carotid artery, and at the root of the neck, it unites with the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein (innominate vein); a little above its termination is a second dilation, the ''inferior bulb''. Above, it lies upon the rectus capitis lateralis, behind the internal carotid artery and the nerves passing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digastricus
The digastric muscle (also digastricus) (named ''digastric'' as it has two 'bellies') is a small muscle located under the jaw. The term "digastric muscle" refers to this specific muscle. However, other muscles that have two separate muscle bellies include the suspensory muscle of duodenum, omohyoid, occipitofrontalis. It lies below the body of the mandible, and extends, in a curved form, from the mastoid notch to the mandibular symphysis. It belongs to the suprahyoid muscles group. A broad aponeurotic layer is given off from the tendon of the digastric muscle on either side, to be attached to the body and greater cornu of the hyoid bone; this is termed the suprahyoid aponeurosis. Structure The digastricus (digastric muscle) consists of two muscular bellies united by an intermediate rounded tendon. The two bellies of the digastric muscle have different embryological origins, and are supplied by different cranial nerves. Each person has a right and left digastric muscle. In mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylohyoideus
The stylohyoid muscle is a Gracility, slender muscle, lying anterior and Anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, superior of the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. It is one of the suprahyoid muscles. It shares this muscle's innervation by the facial nerve, and functions to draw the lingual bone, hyoid bone backwards and elevate the tongue. Its origin is the styloid process of the temporal bone. It inserts on the body of the hyoid. Structure The stylohyoid muscle originates from the posterior and lateral surface of the styloid process (temporal), styloid process of the temporal bone, near the base. Passing inferior and anterior, it inserts into the body of the hyoid bone, at its junction with the greater cornu, and just superior to the omohyoid muscle. It belongs to the group of suprahyoid muscles. It is perforated, near its insertion, by the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle. The stylohyoid muscle has vascular supply from the lingual artery, a branch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternocleidomastoideus
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve. Etymology and location It is given the name ''sternocleidomastoid'' because it originates at the manubrium of the sternum (''sterno-'') and the clavicle (''cleido-'') and has an insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull. Structure The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations: the manubrium of the sternum and the clavicle. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull by a thin aponeurosis. The sternocleidomastoid is thick and narrow at its centre, and broader and thinner at either end. The sternal head is a round fasciculus, tendinous in front, fleshy behind, arising from the upper part of the front of the manubri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
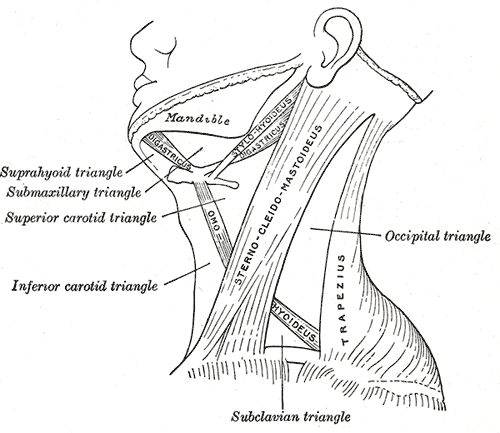
Posterior Triangle
Posterior may refer to: * Posterior (anatomy), the end of an organism opposite to its head ** Buttocks, as a euphemism * Posterior horn (other) * Posterior probability The posterior probability is a type of conditional probability that results from updating the prior probability with information summarized by the likelihood via an application of Bayes' rule. From an epistemological perspective, the posterior ..., the conditional probability that is assigned when the relevant evidence is taken into account * Posterior tense, a relative future tense {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |