|
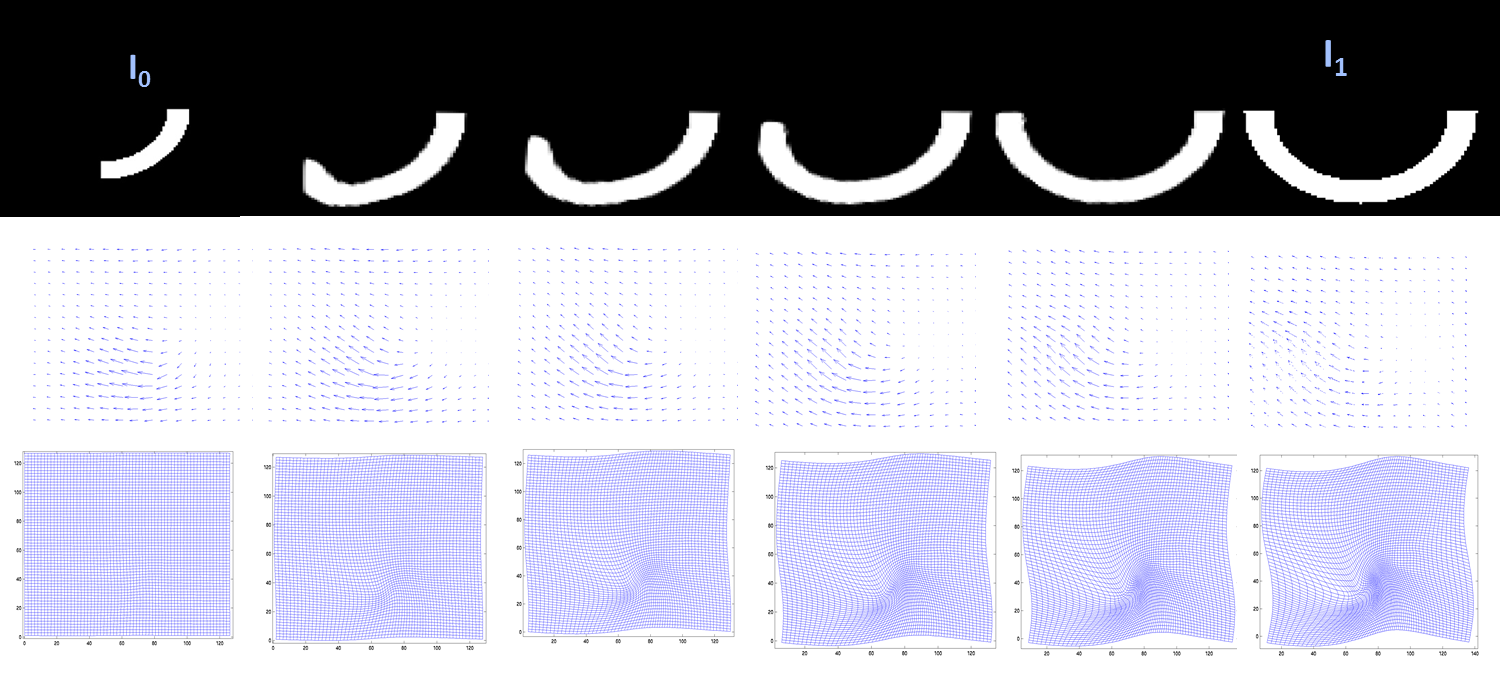
Spatial Normalization
In neuroimaging, spatial normalization is an image processing step, more specifically an image registration method. Human brains differ in size and shape, and one goal of spatial normalization is to deform human brain scans so one location in one subject's brain scan corresponds to the same location in another subject's brain scan. It is often performed in research-based functional neuroimaging where one wants to find common brain activation across multiple human subjects. The brain scan can be obtained from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or positron emission tomography (PET) scanners. There are two steps in the spatial normalization process: * Specification/estimation of warp-field * Application of warp-field with resampling The estimation of the warp-field can be performed in one modality, e.g., MRI, and be applied in another modality, e.g., PET, if MRI and PET scans exist for the same subject and they are coregistered. Spatial normalization typically employs a 3-dimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Increasingly it is also being used for quantitative studies of brain disease and psychiatric illness. Neuroimaging is a highly multidisciplinary research field and is not a medical specialty. Neuroimaging differs from neuroradiology which is a medical specialty and uses brain imaging in a clinical setting. Neuroradiology is practiced by radiologists who are medical practitioners. Neuroradiology primarily focuses on identifying brain lesions, such as vascular disease, strokes, tumors and inflammatory disease. In contrast to neuroimaging, neuroradiology is qualitative (based on subjective impressions and extensive clinical training) but sometimes uses basic quantitative methods. Functional brain imaging techniques, such as functional magn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse are differentiable. Definition Given two manifolds M and N, a differentiable map f \colon M \rightarrow N is called a diffeomorphism if it is a bijection and its inverse f^ \colon N \rightarrow M is differentiable as well. If these functions are r times continuously differentiable, f is called a C^r-diffeomorphism. Two manifolds M and N are diffeomorphic (usually denoted M \simeq N) if there is a diffeomorphism f from M to N. They are C^r-diffeomorphic if there is an r times continuously differentiable bijective map between them whose inverse is also r times continuously differentiable. Diffeomorphisms of subsets of manifolds Given a subset X of a manifold M and a subset Y of a manifold N, a function f:X\to Y is said to be smooth if for all p in X there is a neighb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Anatomy
Computational anatomy is an interdisciplinary field of biology focused on quantitative investigation and modelling of anatomical shapes variability. It involves the development and application of mathematical, statistical and data-analytical methods for modelling and simulation of biological structures. The field is broadly defined and includes foundations in anatomy, applied mathematics and pure mathematics, machine learning, computational mechanics, computational science, biological imaging, neuroscience, physics, probability, and statistics; it also has strong connections with fluid mechanics and geometric mechanics. Additionally, it complements newer, interdisciplinary fields like bioinformatics and neuroinformatics in the sense that its interpretation uses metadata derived from the original sensor imaging modalities (of which magnetic resonance imaging is one example). It focuses on the anatomical structures being imaged, rather than the medical imaging devices. It is simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voxel-based Morphometry
Voxel-based morphometry is a computational approach to neuroanatomy that measures differences in local concentrations of brain tissue, through a voxel-wise comparison of multiple brain images. In traditional morphometry, volume of the whole brain or its subparts is measured by drawing regions of interest (ROIs) on images from brain scanning and calculating the volume enclosed. However, this is time consuming and can only provide measures of rather large areas. Smaller differences in volume may be overlooked. The value of VBM is that it allows for comprehensive measurement of differences, not just in specific structures, but throughout the entire brain. VBM registers every brain to a template, which gets rid of most of the large differences in brain anatomy among people. Then the brain images are smoothed so that each voxel represents the average of itself and its neighbors. Finally, the image volume is compared across brains at every voxel. However, VBM can be sensitive to va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIR (program)
The AIR (''Automated Image Registration'') is a program suite for volume-based image registration constructed by Roger P. Woods from UCLA School of Medicine. It reads and writes Analyze volume files and can work with 4x4 transformation matrices stored in its own file format with the filename extension .air. It is especially designed for neuroimaging applications and has primarily been used in research-oriented functional neuroimaging with brain scans from positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance scanners. The suite provides a number of programs for image registration with different transformation models, such as rigid-body, affine and nonlinear warping Warp, warped or warping may refer to: Arts and entertainment Books and comics * WaRP Graphics, an alternative comics publisher * ''Warp'' (First Comics), comic book series published by First Comics based on the play ''Warp!'' * Warp (comics), a .... For example, for affine transformation the registration from one bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Parametric Mapping
Statistical parametric mapping (SPM) is a statistical technique for examining differences in brain activity recorded during functional neuroimaging experiments. It was created by Karl Friston. It may alternatively refer to software created by the Wellcome Department of Imaging Neuroscience at University College London to carry out such analyses. Approach Unit of measurement Functional neuroimaging is one type of 'brain scanning'. It involves the measurement of brain activity. The measurement technique depends on the imaging technology (e.g., fMRI and PET). The scanner produces a 'map' of the area that is represented as voxels. Each voxel represents the activity of a specific volume in three-dimensional space. The exact size of a voxel varies depending on the technology. fMRI voxels typically represent a volume of 27 mm3 in an equilateral cuboid. Experimental design Researchers examine brain activity linked to a specific mental process or processes. One approach involves as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Deformation Diffeomorphic Metric Mapping
Large deformation diffeomorphic metric mapping (LDDMM) is a specific suite of algorithms used for diffeomorphic mapping and manipulating dense imagery based on diffeomorphic metric mapping within the academic discipline of computational anatomy, to be distinguished from its precursor based on diffeomorphic mapping. The distinction between the two is that diffeomorphic metric maps satisfy the property that the length associated to their flow away from the identity induces a metric on the group of diffeomorphisms, which in turn induces a metric on the orbit of shapes and forms within the field of Computational Anatomy. The study of shapes and forms with the metric of diffeomorphic metric mapping is called diffeomorphometry. A diffeomorphic mapping system is a system designed to map, manipulate, and transfer information which is stored in many types of spatially distributed medical imagery. Diffeomorphic mapping is the underlying technology for mapping and analyzing information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Actions In Computational Anatomy
Group actions are central to Riemannian geometry and defining orbits (control theory). The orbits of computational anatomy consist of anatomical shapes and medical images; the anatomical shapes are submanifolds of differential geometry consisting of points, curves, surfaces and subvolumes,. This generalized the ideas of the more familiar orbits of linear algebra which are linear vector spaces. Medical images are scalar and tensor images from medical imaging. The group actions are used to define models of human shape which accommodate variation. These orbits are deformable templates as originally formulated more abstractly in pattern theory. The orbit model of computational anatomy The central model of human anatomy in computational anatomy is a Groups and group action, a classic formulation from differential geometry. The orbit is called the space of shapes and forms. The space of shapes are denoted m \in \mathcal , with the group (\mathcal, \circ ) with law of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffeomorphic Mapping In Computational Anatomy
Large deformation diffeomorphic metric mapping (LDDMM) is a specific suite of algorithms used for diffeomorphic mapping and manipulating dense imagery based on diffeomorphic metric mapping within the academic discipline of computational anatomy, to be distinguished from its precursor based on diffeomorphic mapping. The distinction between the two is that diffeomorphic metric maps satisfy the property that the length associated to their flow away from the identity induces a metric on the group of diffeomorphisms, which in turn induces a metric on the orbit of shapes and forms within the field of Computational Anatomy. The study of shapes and forms with the metric of diffeomorphic metric mapping is called diffeomorphometry. A diffeomorphic mapping system is a system designed to map, manipulate, and transfer information which is stored in many types of spatially distributed medical imagery. Diffeomorphic mapping is the underlying technology for mapping and analyzing information m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Anatomy
Computational anatomy is an interdisciplinary field of biology focused on quantitative investigation and modelling of anatomical shapes variability. It involves the development and application of mathematical, statistical and data-analytical methods for modelling and simulation of biological structures. The field is broadly defined and includes foundations in anatomy, applied mathematics and pure mathematics, machine learning, computational mechanics, computational science, biological imaging, neuroscience, physics, probability, and statistics; it also has strong connections with fluid mechanics and geometric mechanics. Additionally, it complements newer, interdisciplinary fields like bioinformatics and neuroinformatics in the sense that its interpretation uses metadata derived from the original sensor imaging modalities (of which magnetic resonance imaging is one example). It focuses on the anatomical structures being imaged, rather than the medical imaging devices. It is simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeomorphism
In the mathematical field of topology, a homeomorphism, topological isomorphism, or bicontinuous function is a bijective and continuous function between topological spaces that has a continuous inverse function. Homeomorphisms are the isomorphisms in the category of topological spaces—that is, they are the mappings that preserve all the topological properties of a given space. Two spaces with a homeomorphism between them are called homeomorphic, and from a topological viewpoint they are the same. The word ''homeomorphism'' comes from the Greek words '' ὅμοιος'' (''homoios'') = similar or same and '' μορφή'' (''morphē'') = shape or form, introduced to mathematics by Henri Poincaré in 1895. Very roughly speaking, a topological space is a geometric object, and the homeomorphism is a continuous stretching and bending of the object into a new shape. Thus, a square and a circle are homeomorphic to each other, but a sphere and a torus are not. However, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Processing
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensional picture, that resembles a subject. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term “image” may refer specifically to a 2D image. An image does not have to use the entire visual system to be a visual representation. A popular example of this is of a greyscale image, which uses the visual system's sensitivity to brightness across all wavelengths, without taking into account different colors. A black and white visual representation of something is still an image, even though it does not make full use of the visual system's capabilities. Images are typically still, but in some cases can be moving or animated. Characteristics Images may be two or three- dimensional, such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |