|
Spanish Aircraft Carrier Dédalo
''Dédalo'' (Spanish for ''Daedalus'') was the first Spanish aircraft carrier and the second aviation ship in the Spanish Navy (after the seaplane tender and balloon ship Spanish seaplane carrier Dédalo, ''Dédalo'' that took part in the Alhucemas landing, landings at Al Hoceima in 1925). She remained the fleet's flagship until Spanish aircraft carrier Príncipe de Asturias, ''Príncipe de Asturias'' replaced her. ''Dédalo'' was formerly the World War II-era light aircraft carrier USS Cabot (CVL-28), USS ''Cabot'', which was acquired from the United States in the 1960s. History In 1953 the Spanish government Pact of Madrid, signed military agreements with the United States, which would be endorsed in the following years. The Spanish Navy studied several options to incorporate a helicopter carrier/aircraft carrier of North American design; specifically studied requesting the delivery of a Casablanca-class escort carrier, Casablanca-class escort carrier (USS Thetis Bay, U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energy, digital industry, additive manufacturing and venture capital and finance, but has since divested from several areas, now primarily consisting of the first four segments. In 2020, GE ranked among the Fortune 500 as the 33rd largest firm in the United States by gross revenue. In 2011, GE ranked among the Fortune 20 as the 14th most profitable company, but later very severely underperformed the market (by about 75%) as its profitability collapsed. Two employees of GE – Irving Langmuir (1932) and Ivar Giaever (1973) – have been awarded the Nobel Prize. On November 9, 2021, the company announced it would divide itself into three investment-grade public companies. On July 18, 2022, GE unveiled the brand names of the companies it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antisubmarine Warfare Carrier
An anti-submarine warfare carrier (ASW carrier) (US hull classification symbol CVS) is a type of small aircraft carrier whose primary role is as the nucleus of an anti-submarine warfare hunter-killer group. This type of ship came into existence during the Cold War as a development of the escort carriers used in the ASW role in the North Atlantic during World War II. Role After World War II, the main naval threat to most Western nations was confrontation with the Soviet Union. The Soviets ended the war with a small navy and took the route of asymmetric confrontation against Western surface ship superiority by investing heavily in submarines both for attack and later fielding submarine-launched missiles. Several nations who purchased British and US surplus light carriers were most easily able to accommodate slow-moving, less expensive, and easy-to-land anti-submarine aircraft from the 1960s forward, such as the S-2 Tracker, which flew from the decks of US, Canadian, Australian, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserve Fleet
A reserve fleet is a collection of naval vessels of all types that are fully equipped for service but are not currently needed; they are partially or fully decommissioned. A reserve fleet is informally said to be "in mothballs" or "mothballed"; an equivalent expression in unofficial modern US naval usage is "ghost fleet". In earlier times, especially in British usage, the ships were said to be "laid up in ordinary". Overview Such ships are held in reserve against a time when it may be necessary to call them back into service. They are usually tied up in backwater areas near naval bases or shipyards in order to speed the reactivation process. They may be modified for storage during such a period, for instance by having rust-prone areas sealed off or wrapped in plastic or, in the case of sailing warships, the masts removed. While being held in the reserve fleet, ships typically have a minimal crew (known informally as a skeleton crew) to ensure that they stay in somewhat usable co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS San Jacinto (CVL-30)
USS ''San Jacinto'' (CVL-30) of the United States Navy was an light aircraft carrier that served during World War II. She was named for the Battle of San Jacinto during the Texas Revolution. Former U.S. President George H. W. Bush served aboard the ship during World War II. Operational history Originally laid down as the light cruiser ''Newark'' (CL-100), on 26 October 1942 by the New York Shipbuilding Co., Camden, New Jersey; redesignated CV-30 and renamed ''Reprisal'' on 2 June 1942; renamed ''San Jacinto'' on 30 January 1943, converted, while building, to a light aircraft carrier and reclassified as CVL-30; launched on 26 September 1943; sponsored by Mary Gibbs Jones (wife of U.S. Commerce Secretary Jesse H. Jones); and commissioned on 15 November 1943, Capt. Harold M. Martin, in command. After shakedown in the Caribbean, ''San Jacinto'' sailed, via the Panama Canal, San Diego, and Pearl Harbor, for the Pacific war zone. Arriving at Majuro, Marshall Islands, sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
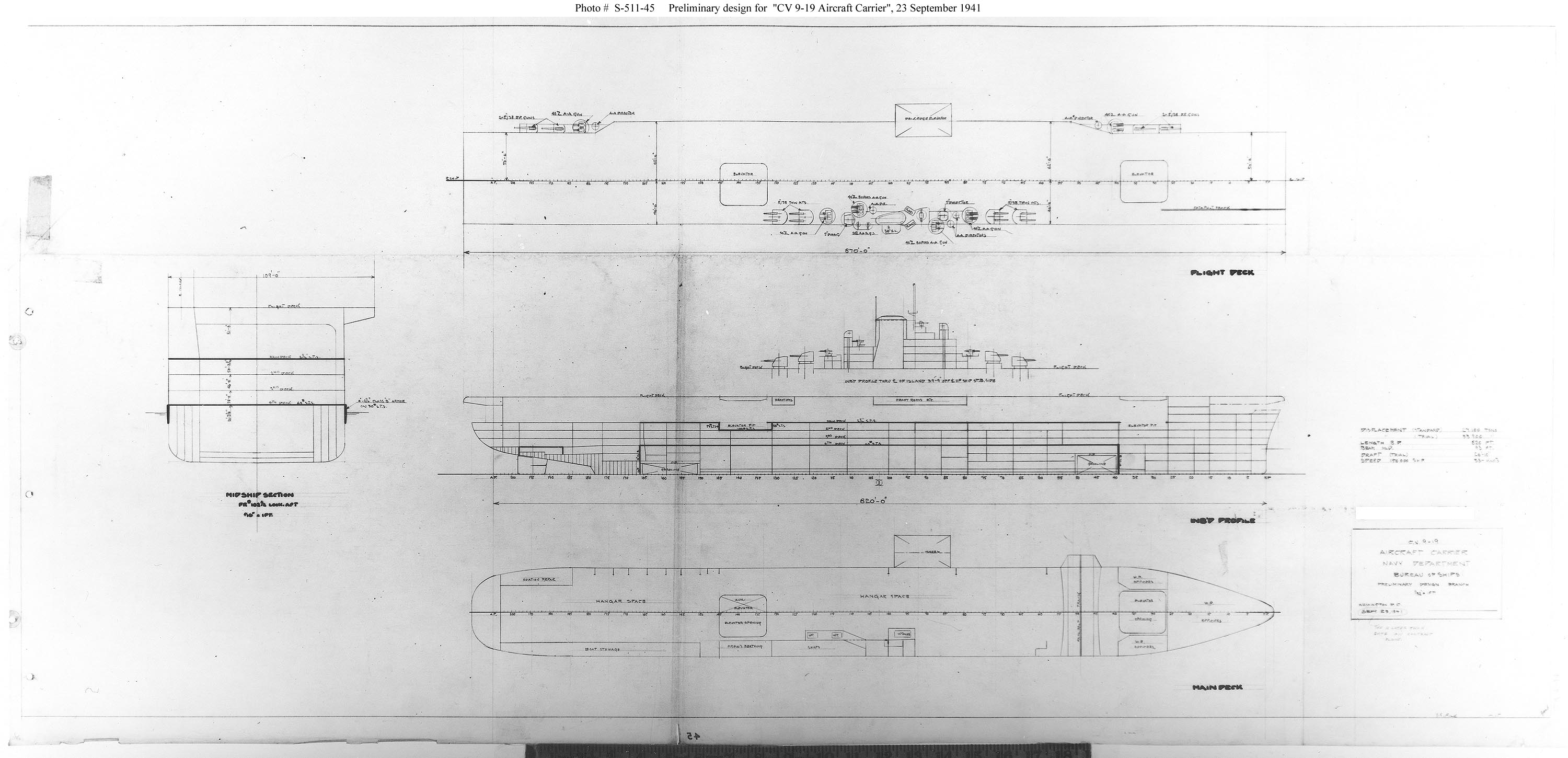
Independence-class Aircraft Carrier
The ''Independence''-class aircraft carriers were a class of light carriers built for the United States Navy that served during World War II. Development Adapted from the design for the light cruisers, this class of ship resulted from the interest of President Franklin D. Roosevelt in naval air power. With war looming, Roosevelt, a former Assistant Secretary of the Navy, noted no new fleet aircraft carriers were expected to be completed before 1944. He proposed to convert some of the many cruisers then under construction to carriers. Studies of cruiser-size aircraft carriers had shown the type had serious limitations, and on 13 October 1941, the General Board of the United States Navy replied that such a conversion showed too many compromises to be effective. Undeterred, President Roosevelt ordered another study. On 25 October 1941, the Navy's Bureau of Ships reported that aircraft carriers converted from cruiser hulls would be of lesser capability, but available much sooner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Lake Champlain (CV-39)
USS ''Lake Champlain'' (CV/CVA/CVS-39) was one of 24 s completed during or shortly after World War II for the United States Navy. She was the second US Navy ship to bear the name, and was named for the Battle of Lake Champlain in the War of 1812. Commissioned on 3 June 1945, ''Lake Champlain'' did not participate in World War II, but did serve as a transport, bringing troops home from Europe as part of Operation Magic Carpet. Like many of her sister ships, she was decommissioned shortly after the end of the war, but was modernized and recommissioned in the early 1950s, and redesignated as an attack carrier (CVA). She participated in the Korean War but spent the rest of her career in the Atlantic, Caribbean, and Mediterranean. In the late 1950s, she was redesignated as an antisubmarine carrier (CVS). She was the prime recovery ship for the first manned Project Mercury mission (''Freedom 7''), the second unmanned Gemini mission (Gemini 2), and for the third manned Gemini (Gemini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essex-class
The ''Essex'' class was a class of aircraft carriers of the United States Navy. The 20th century's most numerous class of capital ship, the class consisted of 24 vessels, which came in "short-hull" and "long-hull" versions. Thirty-two ships were ordered, but as World War II wound down, six were canceled before construction, and two were canceled after construction had begun. Fourteen saw combat during World War II. None were lost to enemy action, though several sustained crippling damage. ''Essex''-class carriers were the backbone of the U.S. Navy from mid-1943 and, with the three carriers added just after the war, continued to be the heart of U.S. naval strength until supercarriers joined the fleet in the 1960s and 1970s. Several of the carriers were rebuilt to handle heavier and faster aircraft of the early jet age, and some served until well after the Vietnam War. Overview The preceding s and the designers' list of trade-offs and limitations forced by arms control treaty ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Thetis Bay
USS ''Thetis Bay'' (CVE-90) was the thirty-sixth of fifty s built for the United States Navy during World War II. She was launched in March 1944, commissioned in April, and served as a transport carrier in the Pacific, as well as a replenishment carrier supporting the Allied bombardment of Tokyo and the Main Islands. Postwar, she participated in Operation Magic Carpet, before being decommissioned in August 1946, being mothballed in the Pacific Reserve Fleet. She was reactivated in July 1956, and converted to a helicopter transport carrier, serving in relief operations in Taiwan and Haiti. Ultimately, she was broken up in 1966, the last ''Casablanca''-class hull to be scrapped. Design and description ''Thetis Bay'' was a ''Casablanca''-class escort carrier, the most numerous type of aircraft carrier ever built, and was designed specifically to be rapidly mass-produced using prefabricated sections, in order to replace heavy early-war losses. By the end of their production ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casablanca-class Escort Carrier
The ''Casablanca''-class escort carrier were a series of escort carriers constructed for the United States Navy during World War II. They are the most numerous class of aircraft carriers ever built. Fifty were laid down, launched and commissioned within the space of less than two years – 3 November 1942 through to 8 July 1944. These were nearly one third of the 143 aircraft carriers built in the United States during the war. Despite their numbers, and the preservation of more famous and larger carriers as museums, none of these modest ships survive today. Five were lost to enemy action during World War II and the remainder were scrapped. ''Casablanca'' was the first class to be designed from keel up as an escort carrier. It had a larger and more useful hangar deck than previous conversions. It also had a larger flight deck than the . Unlike larger carriers which had extensive armor, protection was limited to splinter plating. Their small size made them useful for transport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pact Of Madrid
The Pact of Madrid, signed on 23 September 1953 by Francoist Spain and the United States, was a significant effort to break the international isolation of Spain after World War II, together with the Concordat of 1953. This development came at a time when other victorious Allies of World War II and much of the rest of the world remained hostile (for the 1946 United Nations condemnation of the Francoist regime, see Spanish Question) to a fascist regime sympathetic to the cause of the Axis powers and established with the Axis assistance. The 1953 accord took the form of three separate executive agreements that pledged the United States to furnish economic and military aid to Spain. The United States, in turn, was to be permitted to construct and to utilize air and naval bases on Spanish territory (Naval Station Rota, Morón Air Base, Torrejón Air Base and Zaragoza Air Base). Although not a full-fledged military alliance, the pact did result in a substantial United States contribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_at_sea_off_Hawaii%2C_circa_in_1962_(NH_97458-KN).jpg)
_underway_c1947.jpg)
_insignia%2C_1957_(NH_71880-KN).png)