|
SpaceX Rocket Engines
Since the founding of SpaceX in 2002, the company has developed four families of rocket engines — Merlin (rocket engine family), Merlin, Kestrel (rocket engine), Kestrel, Draco (rocket engine family), Draco and SuperDraco — and since 2016 New product development, developed the Raptor (rocket engine family), Raptor methane rocket engine and after 2020, a line of Methane-oxygen gaseous thruster, methalox thrusters. History In the first ten years of SpaceX, led by engineer Tom Mueller, the company developed a variety of Liquid-propellant rocket, liquid-propellant rocket engines, with at least one more of that type under development. , each of the engines developed to date—Kestrel (rocket engine), Kestrel, Merlin 1C, Merlin 1, Draco (rocket engine family), Draco and Super Draco—had been developed for initial use in the SpaceX launch vehicles—Falcon 1, Falcon 9, and Falcon Heavy—or for the SpaceX Dragon, Dragon space capsule, capsule. Each main engine developed by 2012 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Making A SpaceX Engine
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX Dragon
Dragon is a family of spacecraft developed and produced by American private space transportation company SpaceX. The first variant, later named SpaceX Dragon 1, Dragon 1, flew 23 cargo missions to the International Space Station (ISS) between 2010 and 2020 before retiring. Design of this version, not designed to carry astronauts, was funded by NASA with $396 million awarded through the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services program and contracted to ferry cargo under the Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) program. An improved version, the SpaceX Dragon 2, Dragon 2, was introduced in 2019 and has both crewed and cargo versions. The first un-crewed flight test (Crew Dragon Demo-1, Demo-1) took place in March 2019, followed by a crewed flight test (Crew Dragon Demo-2, Demo-2) in May 2020. Since those flight tests, the Crew Dragon has become one of the primary spacecraft ferrying crew to and from the ISS. While the Cargo Dragon continues to carry cargo under the CRS program. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merlin 1A
Merlin is a family of rocket engines developed by SpaceX. They are currently a part of the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles, and were formerly used on the Falcon 1. Merlin engines use RP-1 and liquid oxygen as rocket propellants in a gas-generator power cycle. The Merlin engine was originally designed for sea recovery and reuse, but since 2016 the entire Falcon 9 booster is recovered for reuse by landing vertically on a landing pad using one of its nine Merlin engines. The injector at the heart of Merlin is of the pintle type that was first used in the Apollo Lunar Module landing engine ( LMDE). Propellants are fed by a single-shaft, dual-impeller turbopump. The turbopump also provides high-pressure fluid for the hydraulic actuators, which then recycles into the low-pressure inlet. This eliminates the need for a separate hydraulic drive system and means that thrust vectoring control failure by running out of hydraulic fluid is not possible. Revisions Merlin 1A The ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
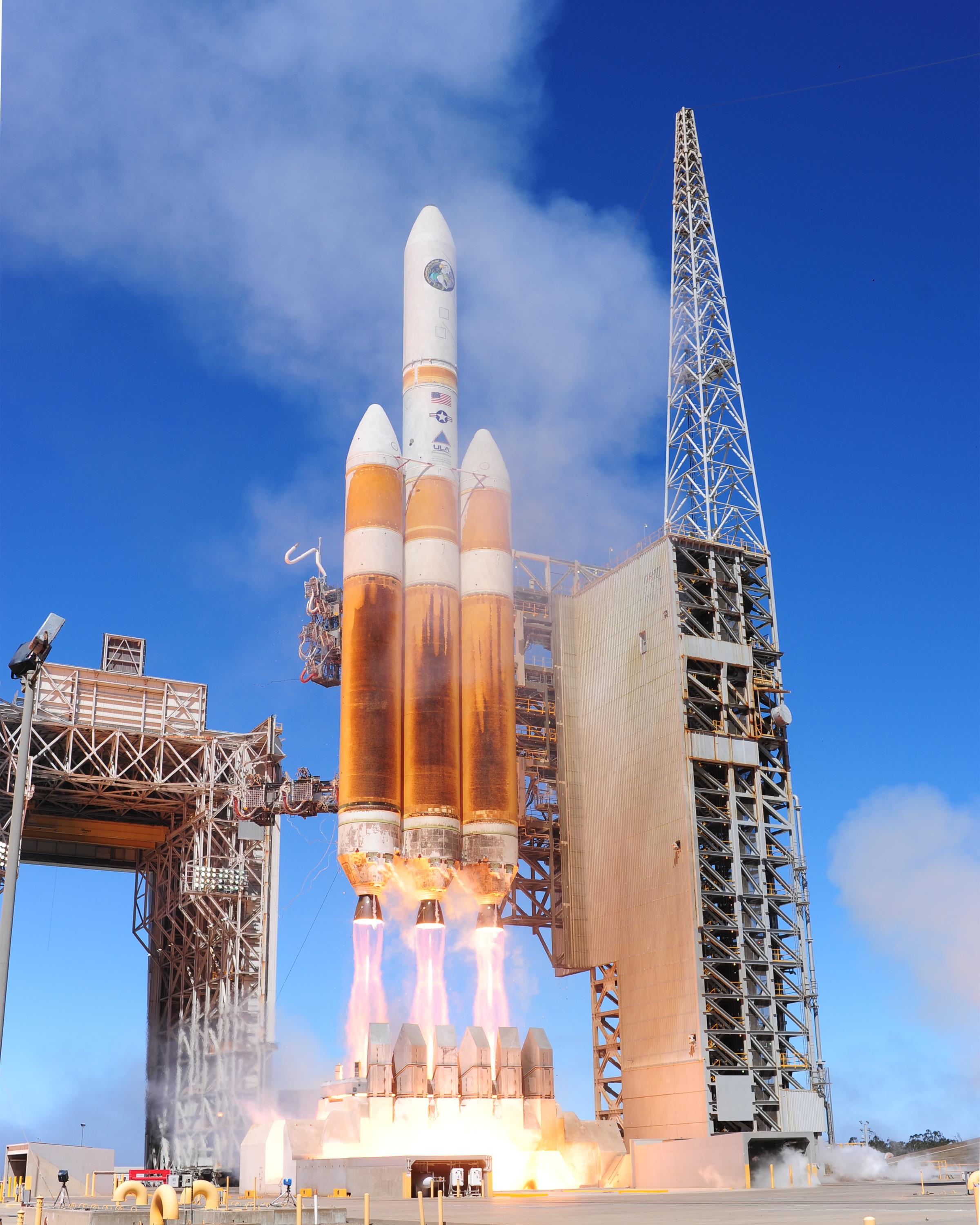
SpaceX Testing Merlin 1D Engine In Texas
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., commonly referred to as SpaceX, is an American space technology company headquartered at the Starbase development site in Starbase, Texas. Since its founding in 2002, the company has made numerous advancements in rocket propulsion, reusable launch vehicles, human spaceflight and satellite constellation technology. , SpaceX is the world's dominant space launch provider, its launch cadence eclipsing all others, including private competitors and national programs like the Chinese space program. SpaceX, NASA, and the United States Armed Forces work closely together by means of governmental contracts. SpaceX was founded by Elon Musk in 2002 with a vision of decreasing the costs of space launches, paving the way to a sustainable colony on Mars. In 2008, Falcon 1 successfully launched into orbit after three failed launch attempts. The company then pivoted towards the development of the larger Falcon 9 rocket and the Dragon 1 capsule to sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerolox
The highest specific impulse chemical rockets use liquid propellants (liquid-propellant rockets). They can consist of a single chemical (a monopropellant) or a mix of two chemicals, called bipropellants. Bipropellants can further be divided into two categories; hypergolic propellants, which ignite when the fuel and oxidizer make contact, and non-hypergolic propellants which require an ignition source. About 170 different propellants made of liquid fuel have been tested, excluding minor changes to a specific propellant such as propellant additives, corrosion inhibitors, or stabilizers. In the U.S. alone at least 25 different propellant combinations have been flown. Many factors go into choosing a propellant for a liquid-propellant rocket engine. The primary factors include ease of operation, cost, hazards/environment and performance. History Development in early 20th century Konstantin Tsiolkovsky proposed the use of liquid propellants in 1903, in his article ''Exploration of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NK-33
The NK-33 ( GRAU index: 14D15) and its vacuum-optimized variant, the NK-43, were rocket engines developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s by the Kuznetsov Design Bureau for the Soviet space program's ill-fated N1 Moon rocket. The NK-33 is among the most powerful LOX/RP-1 powered rocket engines ever built, noted for its high specific impulse and low structural mass. The NK-33 was an improved version of the earlier NK-15 engine, which powered the original N1 launch vehicle. Key upgrades included simplified pneumatic and hydraulic systems, advanced controls, enhanced turbopumps, an improved combustion chamber, fewer interfaces employing pyrotechnic devices, and modified interfaces to facilitate replacement of parts during refurbishment. Each N1F rocket would have utilized 30 NK-33 engines on its first stage and eight NK-43 engines on its second stage. Consequently, when the Soviet Union aborted its lunar landing effort in 1974, dozens already manufactured engines were left in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staged Combustion Cycle (rocket)
The staged combustion cycle (sometimes known as topping cycle, preburner cycle, or closed cycle) is a power cycle of a bipropellant rocket engine. In the staged combustion cycle, propellant flows through multiple combustion chambers, and is thus combusted in stages. The main advantage relative to other rocket engine power cycles is high fuel efficiency, measured through specific impulse, while its main disadvantage is engineering complexity. Typically, propellant flows through two kinds of combustion chambers; the first called and the second called . In the preburner, a small portion of propellant, usually fuel-rich, is partly combusted under non- stoichiometric conditions, increasing the volume of flow driving the turbopumps that feed the engine with propellant. The gas is then injected into the main combustion chamber and combusted completely with the other propellant to produce thrust. Tradeoffs The main advantage is fuel efficiency due to all of the propellant flowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it is difficult because it is a gas at standard temperature and pressure. In the Earth's atmosphere methane is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Methane is an organic compound, and among the simplest of organic compounds. Methane is also a hydrocarbon. Naturally occurring methane is found both below ground and under the seafloor and is formed by both geological and biological processes. The largest reservoir of methane is under the seafloor in the form of methane clathrates. When methane reaches the surface and the atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane. The Earth's atmospheric methane concentration h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Aeronautical Society
The Royal Aeronautical Society, also known as the RAeS, is a British multi-disciplinary professional institution dedicated to the global aerospace community. Founded in 1866, it is the oldest Aeronautics, aeronautical society in the world. Members, Fellows, and Companions of the society can use the post-nominal letters MRAeS, FRAeS, or CRAeS, respectively. Function The objectives of The Royal Aeronautical Society include: to support and maintain high professional standards in aerospace disciplines; to provide a unique source of specialist information and a local forum for the exchange of ideas; and to exert influence in the interests of aerospace in the public and industrial arenas, including universities. The Royal Aeronautical Society is a worldwide society with an international network of 67 branches. Many practitioners of aerospace disciplines use the Society's designatory Post-nominal letters, post-nominals such aFRAeS CRAeS, MRAeS, AMRAeS, and ARAeS (incorporating the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Propellant
Rocket propellant is used as reaction mass ejected from a rocket engine to produce thrust. The energy required can either come from the propellants themselves, as with a chemical rocket, or from an external source, as with ion engines. Overview Rockets create thrust by expelling mass rear-ward, at high velocity. The thrust produced can be calculated by multiplying the mass flow rate of the propellants by their exhaust velocity relative to the rocket (specific impulse). A rocket can be thought of as being accelerated by the pressure of the combusting gases against the combustion chamber and nozzle, not by "pushing" against the air behind or below it. Rocket engines perform best in outer space because of the lack of air pressure on the outside of the engine. In space it is also possible to fit a longer nozzle without suffering from flow separation. Most chemical propellants release energy through redox chemistry, more specifically combustion. As such, both an oxidizing agen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypergolic
A hypergolic propellant is a rocket propellant combination used in a rocket engine, whose components spontaneously ignite when they come into contact with each other. The two propellant components usually consist of a fuel and an oxidizer. The main advantages of hypergolic propellants are that they can be stored as liquids at room temperature and that engines which are powered by them are easy to ignite reliably and repeatedly. Common hypergolic propellants are extremely toxic or corrosive, making them difficult to handle. In contemporary usage, the terms "hypergol" and "hypergolic propellant" usually mean the most common such propellant combination: dinitrogen tetroxide plus hydrazine. History The fact that turpentine may spontaneously combust when mixed with nitric acid was discovered as early as the late 17th century by Frederick Slare, but it remained a scientific curiosity for centuries until it was proposed to use it for rocket-assisted take off during WWII. In 1935, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Control System
A reaction control system (RCS) is a spacecraft system that uses Thrusters (spacecraft), thrusters to provide Spacecraft attitude control, attitude control and translation (physics), translation. Alternatively, reaction wheels can be used for attitude control, rather than RCS. Use of diverted engine thrust to provide stable attitude control of a V/STOL, short-or-vertical takeoff and landing aircraft below conventional winged flight speeds, such as with the Hawker Siddeley Harrier#Controls and handling, Harrier "jump jet", may also be referred to as a reaction control system. Reaction control systems are capable of providing small amounts of thrust in any desired direction or combination of directions. An RCS is also capable of providing torque to allow control of rotation (aircraft principal axes, roll, pitch, and yaw). Reaction control systems often use combinations of large and small (vernier thruster, vernier) thrusters, to allow different levels of response. Uses Spacecr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |