|
Sp100 Nuclear Antigen
Sp100 nuclear antigen is an interferon stimulated antigen found in the cell nuclei of many human and higher animal cells. Autoantibodies directed against Sp100 are often found in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Histologically Sp100 'dots' regions of the cell nucleus. Viral infection and mitogens affect the expression of the Sp100 autoantigen. Cells grown in the presence of interferons (α, β, and γ) revealed an increase both in size and number of the Sp100 protein-containing nuclear dots and increase the protein concentration. This raises "the question whether cytokine-mediated increase of Sp100 protein expression plays a role in induction of anti-Sp100 autoantibodies." Sp100 and nuclear dots Two proteins, Sp100 and promyelocytic leukemia ( PML) factor are localized to punctate domains in the nucleus ( nuclear dots or nuclear bodies). These domains (few to 20) were found to form a donut shaped structure when cells were starved of amino acids. In particular, deprav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses. IFNs belong to the large class of proteins known as cytokines, molecules used for communication between cells to trigger the protective defenses of the immune system that help eradicate pathogens. Interferons are named for their ability to "interfere" with viral replication by protecting cells from virus infections. However, virus-encoded genetic elements have the ability to antagonize the IFN response contributing to viral pathogenesis and viral diseases. IFNs also have various other functions: they activate immune cells, such as natural killer cells and macrophages, and they increase host defenses by up-regulating antigen presentation by virtue of increasing the expression of major histocompatibility complex (M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-react and bind more than one antigen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It results from a slow, progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, causing bile and other toxins to build up in the liver, a condition called cholestasis. Further slow damage to the liver tissue can lead to scarring, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis. Common symptoms are tiredness, itching, and in more advanced cases, jaundice. In early cases, the only changes may be those seen in blood tests. PBC is a relatively rare disease, affecting up to one in 3,000–4,000 people. It is much more common in women, with a sex ratio of at least 9:1 female to male. The condition has been recognised since at least 1851, and was named "primary biliary cirrhosis" in 1949. Because cirrhosis is a feature only of advanced disease, a change of its name to "primary biliary cholangitis" was proposed by patient advocacy groups in 2014. Signs and symptoms Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitogens
A mitogen is a small bioactive protein or peptide that induces a cell to begin cell division, or enhances the rate of division (mitosis). Mitogenesis is the induction (triggering) of mitosis, typically via a mitogen. The mechanism of action of a mitogen is that it triggers signal transduction pathways involving mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), leading to mitosis. The cell cycle Mitogens act primarily by influencing a set of proteins which are involved in the restriction of progression through the cell cycle. The G1 checkpoint is controlled most directly by mitogens: further cell cycle progression does not need mitogens to continue. The point where mitogens are no longer needed to move the cell cycle forward is called the "restriction point" and depends on cyclins to be passed.Bohmer et al. "Cytoskeletal Integrity Is Required throughout the Mitogen Stimulation Phase of the Cell Cycle and Mediates the Anchorage-dependent Expression of Cyclin DI". January 1996, Molecular B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturation, growth, and res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-sp100 Antibodies
Anti-sp100 antibodies are found in association with primary biliary cirrhosis. The autoimmune target of anti-sp100 is the sp100 nuclear antigen which was identified by its association with primary biliary cirrhosis. 20-30% of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis have sp100 Abs. The sera of these patients exhibit a characteristic "nuclear dots" pattern in indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) on Hep-2 cells. Immunodominant regions of sp100 * Antigenic region 1 - positions 296-311 - Sequence (I K K E K P F S N S K V E C Q A) * Antigenic region 2 - positions 332-351 - Sequence (E G S T D V D E P L E V F I S A P R S E) (Bolded areas represent the core epitope.) References {{Autoantibodies Autoantibodies PBC autoantibodies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
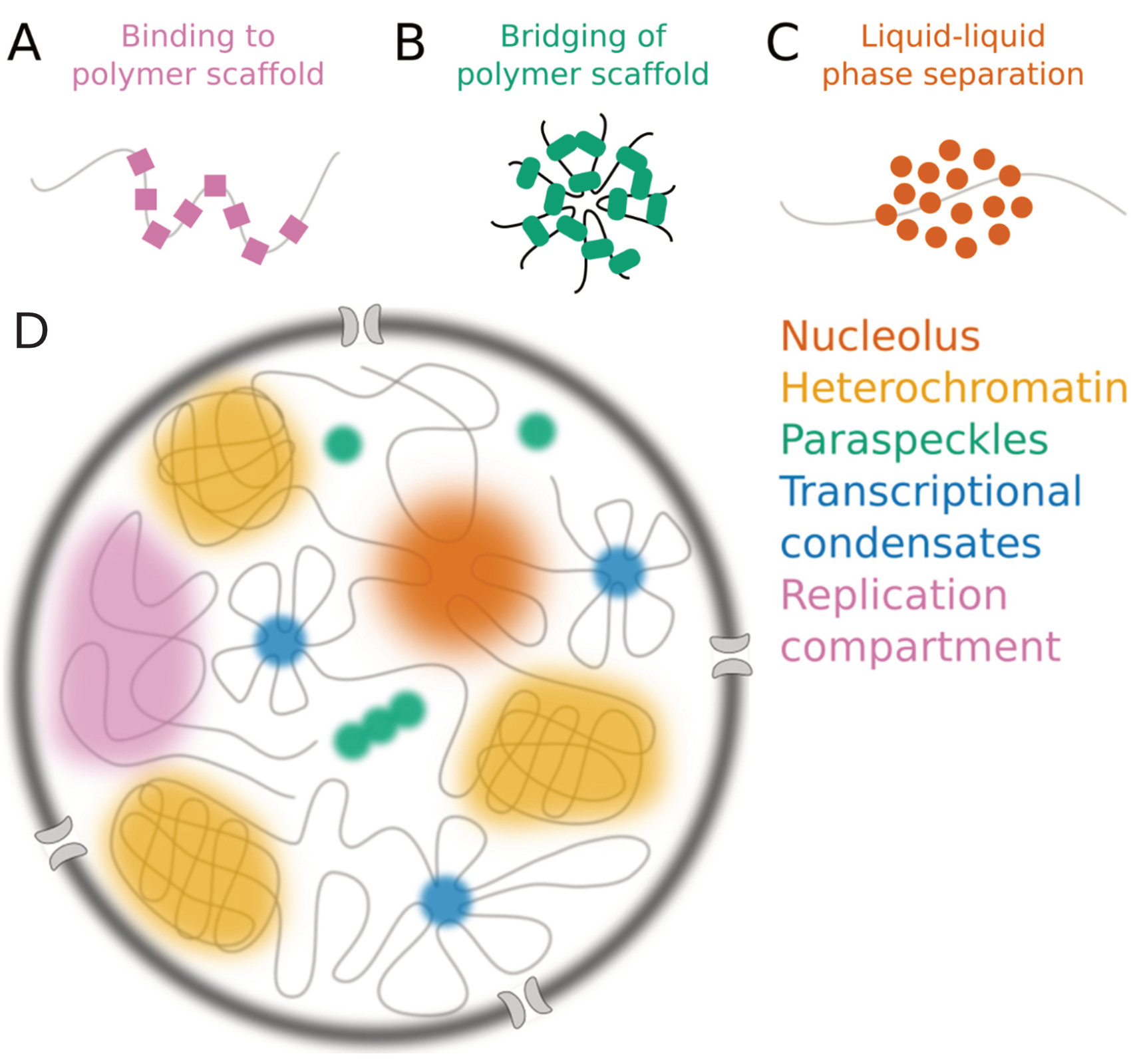
NUCLEAR DOTS
Nuclear bodies (also known as nuclear domains, or nuclear dots) are membraneless structures found in the cell nuclei of eukaryotic cells. Nuclear bodies include Cajal bodies, the nucleolus, and promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) nuclear bodies (also called PML oncogenic dots). Nuclear bodies also include ND10s. ND stands for nuclear domain, and 10 refers to the number of dots seen. Nuclear bodies were first seen as prominent interchromatin structures in the nuclei of malignant or hyperstimulated animal cells identified using anti-sp100 autoantibodies from primary biliary cirrhosis and subsequently the promyelocytic leukemia (PML) factor, but appear also to be elevated in many autoimmune and cancerous diseases. Nuclear dots are metabolically stable and resistant to nuclease digestion and salt extraction. A nuclear body subtype is a clastosome suggested to be a site of protein degradation. Structure Simple nuclear bodies (types I and II) and the shells of complex nuclear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein
Promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) (also known as MYL, RNF71, PP8675 or TRIM19) is the protein product of the PML gene. PML protein is a tumor suppressor protein required for the assembly of a number of nuclear structures, called PML-nuclear bodies, which form amongst the chromatin of the cell nucleus. These nuclear bodies are present in mammalian nuclei, at about 1 to 30 per cell nucleus. PML-NBs are known to have a number of regulatory cellular functions, including involvement in programmed cell death, genome stability, antiviral effects and controlling cell division. PML mutation or loss, and the subsequent dysregulation of these processes, has been implicated in a variety of cancers. History PML was poorly understood until described in the findings of Grignani ''et al'' in their 1996 study of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). It was found that the karyotype of 90% of APL patients included a reciprocal translocation, resulting in the fusion of the Retinoic A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Dots
Nuclear bodies (also known as nuclear domains, or nuclear dots) are membraneless structures found in the cell nuclei of eukaryotic cells. Nuclear bodies include Cajal bodies, the nucleolus, and promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) nuclear bodies (also called PML oncogenic dots). Nuclear bodies also include ND10s. ND stands for nuclear domain, and 10 refers to the number of dots seen. Nuclear bodies were first seen as prominent interchromatin structures in the nuclei of malignant or hyperstimulated animal cells identified using anti-sp100 autoantibodies from primary biliary cirrhosis and subsequently the promyelocytic leukemia (PML) factor, but appear also to be elevated in many autoimmune and cancerous diseases. Nuclear dots are metabolically stable and resistant to nuclease digestion and salt extraction. A nuclear body subtype is a clastosome suggested to be a site of protein degradation. Structure Simple nuclear bodies (types I and II) and the shells of complex nuclear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Ubiquitin-related Modifier 1
Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SUMO1'' gene. Function This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the SUMO (small ubiquitin-like modifier) protein family. It is a ubiquitin-like protein and functions in a manner similar to ubiquitin in that it is bound to target proteins as part of a post-translational modification system. However, unlike ubiquitin, which is primarily associated with targeting proteins for proteasomal degradation, SUMO1 is involved in a variety of cellular processes, such as nuclear transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, and protein stability. It is not active until the last four amino acids of the carboxy-terminus have been cleaved off. Several pseudogenes have been reported for this gene. Alternate transcriptional splice variants encoding different isoforms have been characterized. Most cleft genes have a sumoylation component. Analysis of chromosomal anomalies in patients has led to the iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Pore
A nuclear pore is a part of a large complex of proteins, known as a nuclear pore complex that spans the nuclear envelope, which is the double membrane surrounding the eukaryotic cell nucleus. There are approximately 1,000 nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) in the nuclear envelope of a vertebrate cell, but this number varies depending on cell type and the stage in the life cycle. The human nuclear pore complex (hNPC) is a 110 megadalton (MDa) structure. The proteins that make up the nuclear pore complex are known as nucleoporins; each NPC contains at least 456 individual protein molecules and is composed of 34 distinct nucleoporin proteins. About half of the nucleoporins typically contain solenoid protein domains—either an alpha solenoid or a beta-propeller fold, or in some cases both as separate structural domains. The other half show structural characteristics typical of "natively unfolded" or intrinsically disordered proteins, i.e. they are highly flexible proteins that lack ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoproteins
A phosphoprotein is a protein that is posttranslationally modified by the attachment of either a single phosphate group, or a complex molecule such as 5'-phospho-DNA, through a phosphate group. The target amino acid is most often serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues (mostly in eukaryotes), or aspartic acid or histidine residues (mostly in prokaryotes). Biological function The phosphorylation of proteins is a major regulatory mechanism in cells. Clinical significance Phosphoproteins have been proposed as biomarkers for breast cancer Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a re .... See also * Protein phosphorylation References Phosphoproteins {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |