|
Sources Of Ancient Tamil History
There are literary, archaeological, epigraphic and numismatic sources of ancient Tamil history. The foremost among these sources is the Sangam literature, generally dated to 5th century BCE to 3rd century CE. The poems in Sangam literature contain vivid descriptions of the different aspects of life and society in Tamilakam during this age; scholars agree that, for the most part, these are reliable accounts. Greek and Roman literature, around the dawn of the Christian era, give details of the maritime trade between Tamilakam and the Roman empire, including the names and locations of many ports on both coasts of the Tamil country. There are evidences as could be seen comparing standard forms of Sumerian literature and those recovered through present form of Tamil, for example the word for father in Sumerian transliteration is given as, "a-ia" that could easily be compared with Tamil word, "ayya". This also places ancient form of Tamil to early Sumerian period, say as ancient as 3500 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangam Literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam'';) historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ'') connotes the ancient Tamil literature and is the earliest known literature of South India. The Tamil tradition and legends link it to three literary gatherings around Madurai and Kapāṭapuram ( Pandyan capitals): the first over 4,440 years, the second over 3,700 years, and the third over 1,850 years before the start of the common era. Scholars consider this Tamil tradition-based chronology as ahistorical and mythical. Most scholars suggest the historical Sangam literature era spanned from c. 300 BCE to 300 CE, while others variously place this early classical Tamil literature period a bit later and more narrowly but all before 300 CE. According to Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar, the most acceptable range for the Sangam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ainkurnuru
Ainkurunuru ( meaning ''five hundred short poems'') is a classical Tamil poetic work and traditionally the third of the Eight Anthologies (''Ettuthokai'') in the Sangam literature. It is divided into five groups of 100 short stanzas of 3 to 6 lines, each hundred subdivided into 10s, or ''pattu''. The five groups are based on ''tinai'' (landscapes): riverine, sea coast, mountain, arid and pastoral. According to Martha Selby, the love poems in ''Ainkurunuru'' are generally dated from about the late-2nd-to-3rd-century-CE (Sangam period).Selby, Martha Ann. Tamil Love Poetry: The Five Hundred Short Poems of the Aiṅkuṟunūṟu, an Early Third-Century Anthology. Columbia University Press, 2011. . pp. 1-6 According to Takanobu Takahashi – a Tamil literature scholar, these poems were likely composed between 300 and 350 CE based on the linguistic evidence, while Kamil Zvelebil – another Tamil literature scholar – suggests the Ainkurunuru poems were composed by 210 CE, with some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
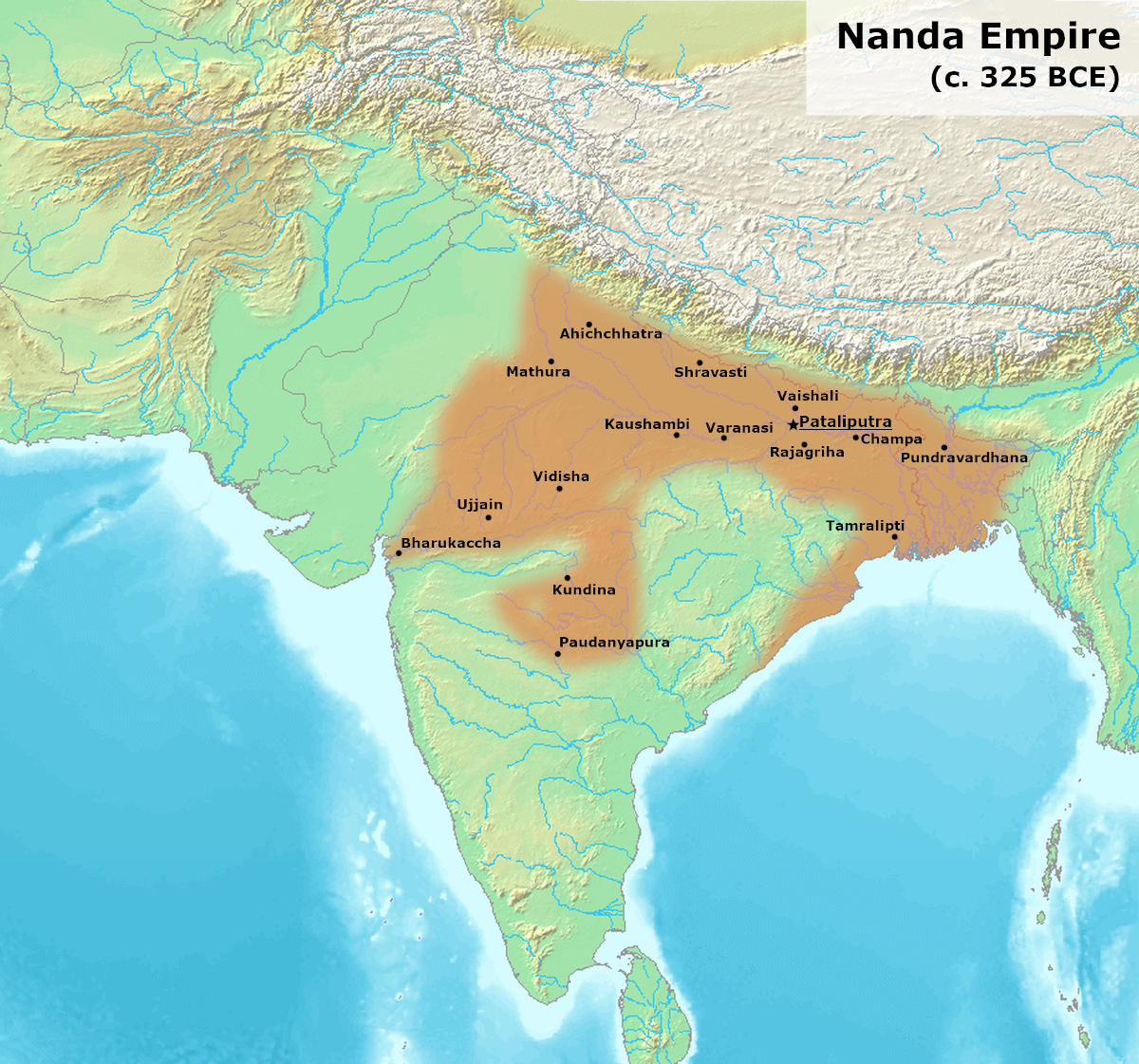
Arthashastra
The ''Arthashastra'' ( sa, अर्थशास्त्रम्, ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, political science, economic policy and military strategy. Kautilya, also identified as Vishnugupta and Chanakya, is traditionally credited as the author of the text.: "References to the work in other Sanskrit literature attribute it variously to , and . The same individual is meant in each case. The '' Pańcatantra'' explicitly identifies Chanakya with ." The latter was a scholar at Takshashila, the teacher and guardian of Emperor Chandragupta Maurya. Some scholars believe them to be the same person, while a few have questioned this identification.; : "while in his character as author of an ''arthaśāstra'' he is generally referred to by his ''gotra'' name, ;": "T. Burrow... has now shown that Cāṇakya is also a ''gotra'' name, which in conjunction with other evidence makes it clear that we are dealing with distinct persons, the minister Cāṇakya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kautilya
Chanakya (Sanskrit: चाणक्य; IAST: ', ; 375–283 BCE) was an ancient Indian polymath who was active as a teacher, author, strategist, philosopher, economist, jurist, and royal advisor. He is traditionally identified as Kauṭilya or Vishnugupta, who authored the ancient Indian political treatise, the ''Arthashastra'', a text dated to roughly between the fourth century BCE and the third century CE. As such, he is considered the pioneer of the field of political science and economics in India, and his work is thought of as an important precursor to classical economics.Waldauer, C., Zahka, W.J. and Pal, S. 1996Kauṭilya's Arthashastra: A neglected precursor to classical economics ''Indian Economic Review'', Vol. XXXI, No. 1, pp. 101–108. His works were lost near the end of the Gupta Empire in the sixth century CE and not rediscovered until the early 20th century. Around 321 BCE, Chanakya assisted the first Mauryan emperor Chandragupta in his rise to power and is wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anne E
Anne, alternatively spelled Ann, is a form of the Latin female given name Anna. This in turn is a representation of the Hebrew Hannah, which means 'favour' or 'grace'. Related names include Annie. Anne is sometimes used as a male name in the Netherlands, particularly in the Frisian speaking part (for example, author Anne de Vries). In this incarnation, it is related to Germanic arn-names and means 'eagle'.See entry on "Anne" in th''Behind the Name'' databaseand th"Anne"an"Ane"entries (in Dutch) in the Nederlandse Voornamenbank (Dutch First Names Database) of the Meertens Instituut (23 October 2018). It has also been used for males in France ( Anne de Montmorency) and Scotland (Lord Anne Hamilton). Anne is a common name and the following lists represent a small selection. For a comprehensive list, see instead: . As a feminine name Anne * Saint Anne, Mother of the Virgin Mary * Anne, Queen of Great Britain (1665–1714), Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland (1702–07) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriella Eichinger Ferro-Luzzi
Gabriella Eichinger Ferro-Luzzi is an Italian anthropologist and dravidologist who has done field studies in India, mainly in the Tamil Nadu state. Born in 1931 in Germany, she studied modern languages at the University of Mainz and did a Ph.D. at the University of Rome in 1968. Between 1985 to 1991, she worked briefly at the University of Venice, University of Bologna, and University of Rome. She taught Tamil language and literature at the University of Naples "L'Orientale" and also worked as a professor of Asian Studies at the university. Education Ferro-Luzzi did a Diploma in Modern Languages at the University of Mainz in Germany in 1954. In 1968, she completed her Ph.D. in geography at the University of Rome in Italy with a doctoral thesis in anthropology. Academic career and research Ferro-Luzzi is a dravidologist. Since 1971, she has traveled several times to India, mostly to Tamil Nadu, to execute field studies. Her research studies have been focused on the study of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naṟṟiṇai
''Naṟṟiṇai'' ( ta, நற்றிணை meaning ''excellent tinai''), is a classical Tamil poetic work and traditionally the first of the Eight Anthologies (''Ettuthokai'') in the Sangam literature. The collection – sometimes spelled as Natrinai or Narrinai – contains both ''akam'' (love) and ''puram'' (war, public life) category of poems. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' anthology contains 400 poems, mainly of 9 to 12 lines, but a few with 8 to 13 lines each. According to Takanobu Takahashi – a Tamil literature scholar, the ''Naṟṟiṇai'' poems were likely composed between 100–300 CE based on the linguistics, style and dating of the authors. While Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar , dates some poems to the 1st century BCE. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' manuscript colophon states that it was compiled under the patronage of the Pandyan king named ''Pannatu Tanta Pantiyan Maran Valuti'', but the compiler remained anonymous. The ''Naṟṟiṇai'' poems a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuṟuntokai
Kuṟuntokai ( ta, குறுந்தொகை, meaning ''the short-collection'') is a classical Tamil poetic work and traditionally the second of the Eight Anthologies (''Ettuthokai'') in the Sangam literature. The collection belongs to the ''akam'' (love) category, and each poem consists of 4 to 8 lines each (except poem 307 and 391 which have 9 lines). The Sangam literature structure suggests that the original compilation had 400 poems, but the surviving ''Kuruntokai'' manuscripts have 402 poems. According to Takanobu Takahashi – a Tamil literature scholar, these poems were likely composed between 100 CE and 300 CE based on the linguistics, style and dating of the authors. Kamil Zvelebil, a Tamil literature and history scholar, states that the majority of the poems in the ''Kuruntokai'' were likely composed between the 1st century BCE and the 2nd century CE. The ''Kuruntokai'' manuscript colophon states that it was compiled by Purikko (உரை), however nothing is known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eelattu Poothanthevanar
Eelattu Poothanthevanar () was one of the earliest known classical Ceylon (present day Sri Lanka) Tamil poets from the Sangam period. He hailed from the ancient international port of Manthai (''Manthottam/ Manthoddam'' in Tamil, Manthota in derived Sinhalese) in Ceylon, the ruins of which are in present-day Mannar District, Sri Lanka. His poems were included in the Tamil language anthologies of the Sangam literature compiled in Tamilakam before 250 CE Writing in the city of Madurai, he praises the valour of the contemporaneous King Pasum Poon Pandyan, who, as per the '' Narkudi Velalar Varalaru'', reigned from 275 to 240 BCE. Seven of his poetic verses feature in the '' Akananuṟu'', '' Natriṇai'' and '' Kurunthokai''. Other Sri Lankan Tamil poets whose contemporary work feature in the anthologies include Pūtan Ila Naganar and Marudan Ila Naganar. Contribution to the Sangam literature Eelattu Poothanthevanar has written two Sangam verses, including one each in Akananuru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eelam
Eelam ( ta, ஈழம், ''īḻam'', , also spelled Eezham, Ilam or Izham in English) is the native Tamil name for the South Asian island now known as Sri Lanka. The exact etymology and the original meaning of the word are not clearly known, and there are number of conflicting theories. The Retroflex approximant ''ḻ'' in ''īḻam'' is a characteristic phoneme for Dravidian languages, now only retained in the closely related languages Tamil and Malayalam. Conventionally it has been represented in the Latin script with the digraph ''zh''. History The earliest use of the word is found in a Tamil-Brahmi inscription as well as in the Sangam literature. The Tirupparankunram inscription found near Madurai in Tamil Nadu and dated on palaeographical grounds to the 1st century BCE, refers to a person as a householder from Eelam (''Eela-kudumpikan''). The inscription reads, The Sangam literature '' Paṭṭiṉappālai'', mentions ''Eelattu-unavu'' (food from Eelam). One of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaveripumpattinam
Puhar (also known as Poompuhar) is a town in the Mayiladuthurai district in the southern Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It was once a flourishing ancient port city known as Kaveri Poompattinam, which is described in Sangam literature like Silappadikaram, Manimekalai, Pattinapalai and Akananuru as the capital of the Early Chola kings in Tamilakam. Puhar is located near the mouth of the Kaveri river, on the sea coast. It is mentioned in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea. It has now been established by marine archaeological research (conducted by the National institute of marine archaeology, Goa) that much of the town was washed away by progressive erosion and floods. In the 1960s and 1970s, archaeological research was conducted under the leadership of the noted archaeologist K. V. Soundararajan. Submerged wharves and several meter lengths of pier walls excavated in recent times have corroborated the literary references to Poompuhar. It was rebuilt several times after that. Anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cholas
The Early Cholas were a Tamil kingdom of the pre and post Sangam period (600 BCE–300 CE). It was one of the three main kingdoms of South India. Their early capitals were Urayur or Tiruchirapalli and Kaveripattinam. Along with Pandyas and Cheras, Chola history goes back to the period when written records were scarce. Sources Ancient Tamil Nadu contained three monarchical states, headed by kings called ''Vendhar'' and several chieftaincies, headed by the chiefs called by the general denomination ''Vel'' or '' Velir''. Still lower at the local level there were clan chiefs called ''kizhar'' or ''mannar''. The Tamil area had an independent existence outside the control of these northern empires. The Tamil kings and chiefs were always in conflict with each other mostly over property. The royal courts were mostly places of social gathering rather than places of dispensation of authority; they were centres for distribution of resources. The names of the three dynasties, Cholas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |